Abstract
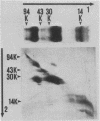
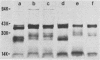
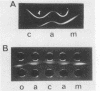
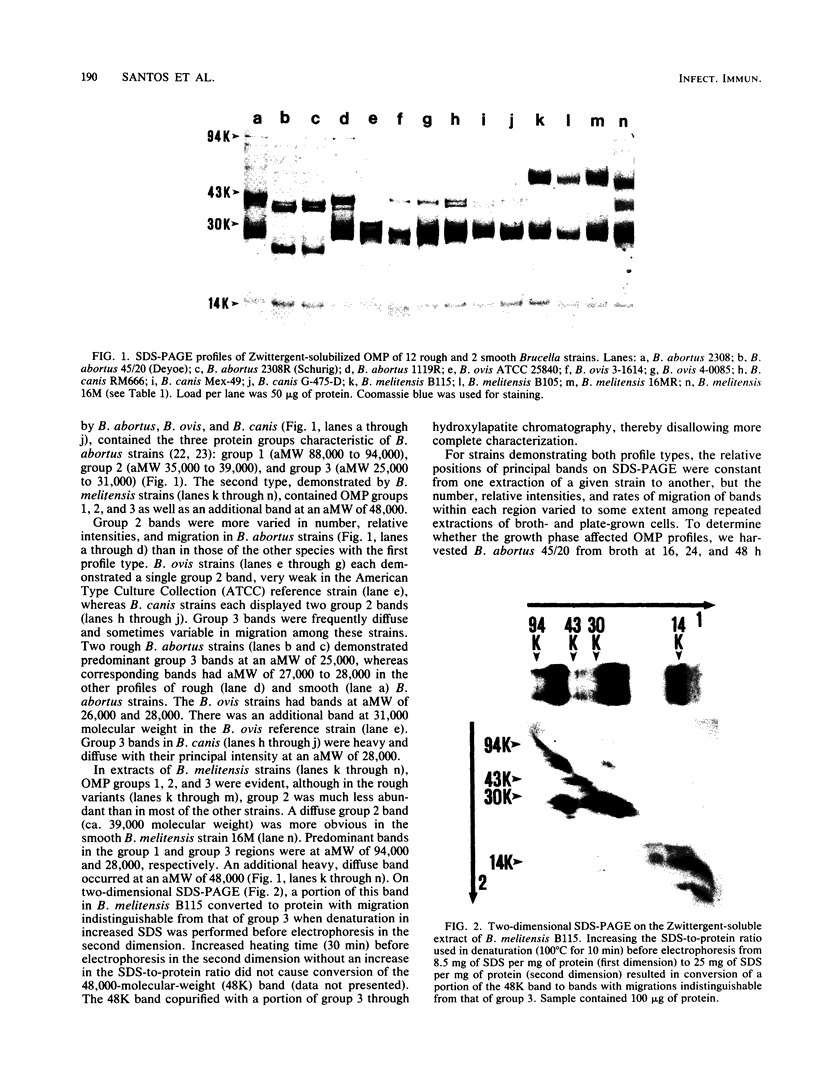
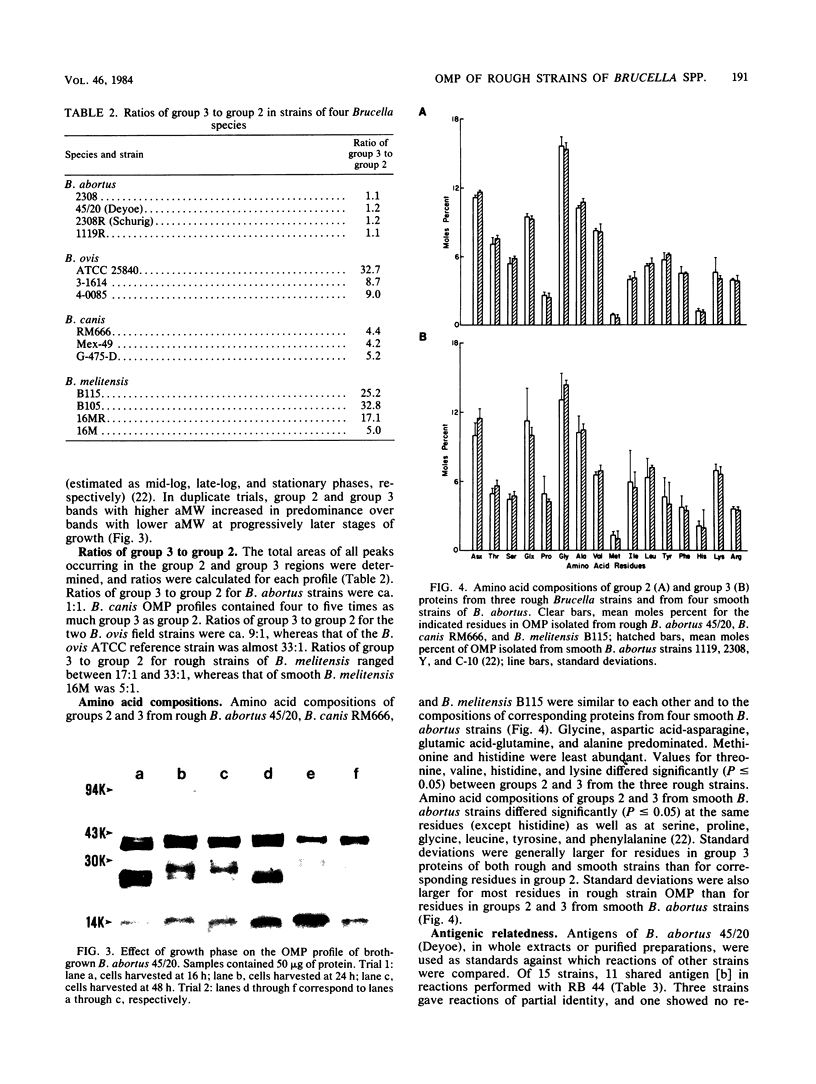
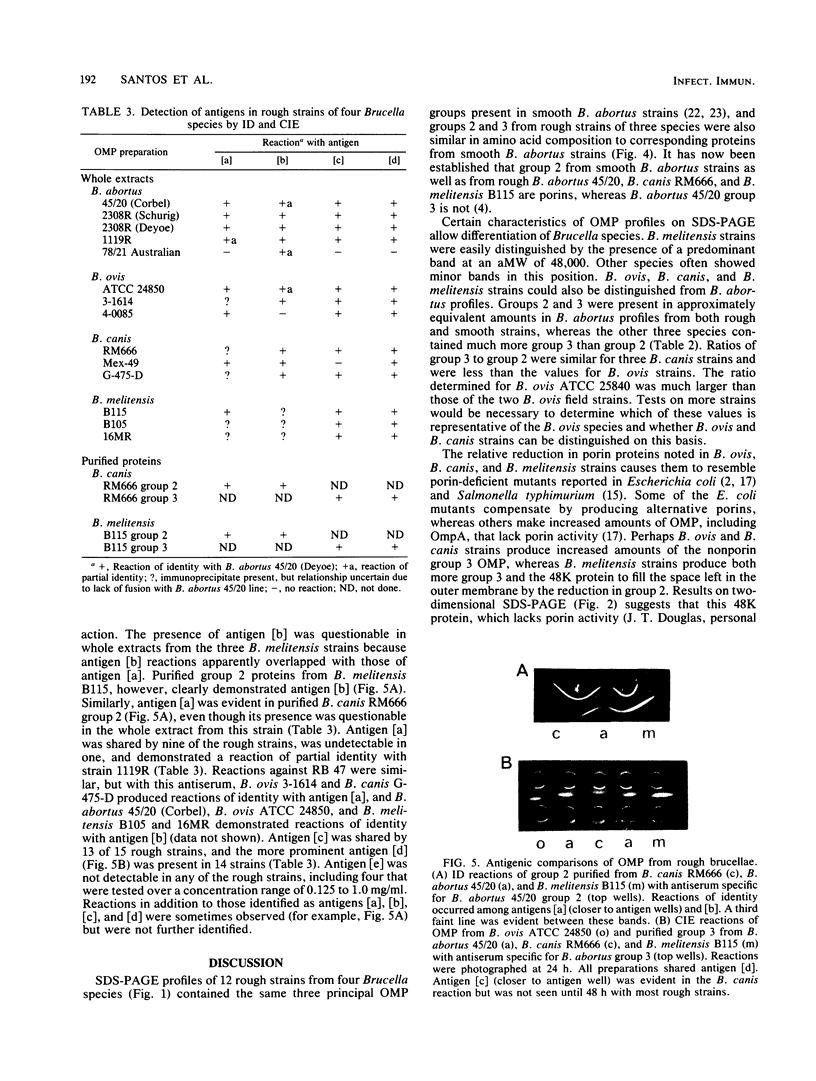
Outer membrane proteins from 15 rough strains of Brucella abortus, B. ovis, B. canis, and B. melitensis were extracted with a dipolar detergent, and outer membrane proteins from selected strains were purified by anion exchange chromatography and gel filtration (Verstreate et al., Infect. Immun. 35:979-989, 1982). Outer membrane proteins produced two types of profiles on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. One type, demonstrated by B. abortus, B. ovis, and B. canis strains, contained the three predominant protein groups present in smooth B. abortus strains (Verstreate et al., Infect. Immun. 35:979-989, 1982): groups 1, 2 (porin [Douglas et al., Infect. Immun. 44:16-21]), and 3. B. melitensis strains demonstrated the second profile type, in which there was an additional band between groups 1 and 2. The relative proportion of porin was considerably lower in B. ovis, B. canis, and B. melitensis than in B. abortus. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles could be used to distinguish B. abortus and B. melitensis from each other and from B. canis and B. ovis. The amino acid compositions of groups 2 and 3 from rough strains of B. abortus, B. canis, and B. melitensis were similar to those of corresponding proteins from smooth B. abortus strains. Zwittergent-soluble fractions from most rough strains contained antigen [b], which cross-reacted with group 2 from smooth B. abortus strains, and antigens [c] and [d], which cross-reacted with group 3 from smooth B. abortus strains. Antigen [a], shared by groups 2 and 3 (D. R. Verstreate and A. J. Winter, Infect. Immun. 46:182-187, 1984), was detected in most rough strains. None of these antigens were related to either rough or smooth lipopolysaccharide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bavoil P., Nikaido H., von Meyenburg K. Pleiotropic transport mutants of Escherichia coli lack porin, a major outer membrane protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Dec 14;158(1):23–33. doi: 10.1007/BF00455116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Garatea P., Jones L. M., Moriyon I. Radial immunodiffusion test with a Brucella polysaccharide antigen for differentiating infected from vaccinated cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.37-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. T., Rosenberg E. Y., Nikaido H., Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Porins of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Apr;44(1):16–21. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.1.16-21.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Bézard G. Isolation of three Brucella abortus cell-wall antigens protective in murine experimental brucellosis. Ann Rech Vet. 1980;11(4):367–373. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubray G., Charriaut C. Evidence of three major polypeptide species and two major polysaccharide species in the Brucella outer membrane. Ann Rech Vet. 1983;14(3):311–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Rietschel E. T., Lüderitz O., Westphal O., Kim Y. B., Watson D. W. Biological activities of lipid A complexed with bovine-serum albumin. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 4;31(2):230–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Schlecht S. Molecular composition of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and the importance of protein-lipopolysaccharide interactions. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Sep;127(2):81–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00428010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of rough Brucella lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):779–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.779-782.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Pitt M. W., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Purification and characterization of smooth and rough lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.361-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyon I., Berman D. T. Effects of nonionic, ionic, and dipolar ionic detergents and EDTA on the Brucella cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):822–828. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.822-828.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H. Permeability of the outer membrane of bacteria. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1979 May;18(5):337–350. doi: 10.1002/anie.197903373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Song S. A., Shaltiel L., Nurminen M. Outer membrane of Salmonella XIV. Reduced transmembrane diffusion rates in porin-deficient mutants. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 May 23;76(2):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90728-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Wu H. C. Proteins of the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:369–422. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbusch J. P. Characterization of the major envelope protein from Escherichia coli. Regular arrangement on the peptidoglycan and unusual dodecyl sulfate binding. J Biol Chem. 1974 Dec 25;249(24):8019–8029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstreate D. R., Winter A. J. Comparison of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles and antigenic relatedness among outer membrane proteins of 49 Brucella abortus strains. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):182–187. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.182-187.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J., Verstreate D. R., Hall C. E., Jacobson R. H., Castleman W. L., Meredith M. P., McLaughlin C. A. Immune response to porin in cattle immunized with whole cell, outer membrane, and outer membrane protein antigens of Brucella abortus combined with trehalose dimycolate and muramyl dipeptide adjuvants. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1159–1167. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1159-1167.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]