Abstract
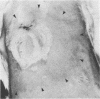
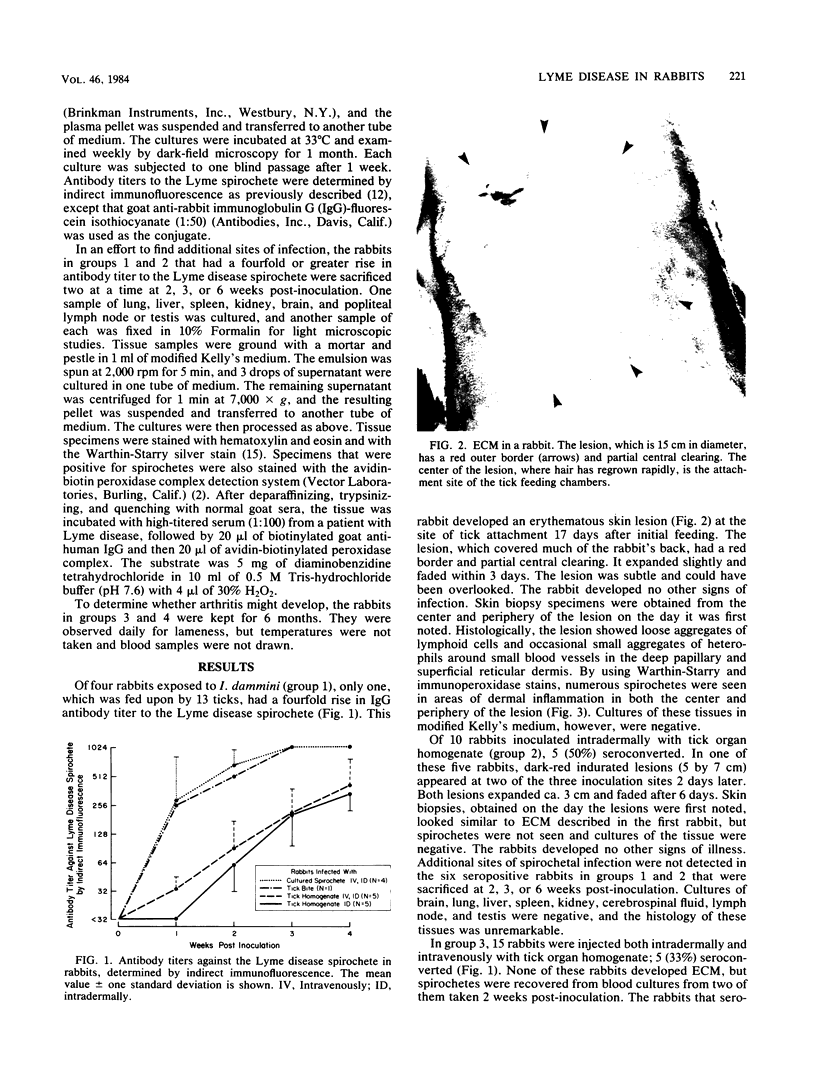
In attempts to produce experimental Lyme disease, 33 rabbits were inoculated with Lyme spirochetes by tick feeding or from tick organ homogenates or cultures. Two rabbits developed erythema chronicum migrans at the site of inoculation, in one instance 2 days after injection of a tick organ homogenate and in the other instance, 17 days after feeding of infected Ixodes dammini ticks. Spirochetes were seen in skin biopsy specimens of the second lesion with Warthin-Starry and immunoperoxidase stains. Spirochetes were also recovered from blood cultures of two additional rabbits 2 weeks post-inoculation. These findings are characteristic of early Lyme disease in humans and give additional support for the spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker-Zander S., Sell S. A histopathologic and immunologic study of the course of syphilis in the experimentally infected rabbit. Demonstration of long-lasting cellular immunity. Am J Pathol. 1980 Nov;101(2):387–414. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayer E. A., Wilchek M. The use of the avidin-biotin complex as a tool in molecular biology. Methods Biochem Anal. 1980;26:1–45. doi: 10.1002/9780470110461.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benach J. L., Bosler E. M., Hanrahan J. P., Coleman J. L., Habicht G. S., Bast T. F., Cameron D. J., Ziegler J. L., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W. Spirochetes isolated from the blood of two patients with Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):740–742. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W., Clemmensen O. J., Ackerman A. B. Lyme disease is a spirochetosis. A review of the disease and evidence for its cause. Am J Dermatopathol. 1983 Apr;5(2):111–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe-Beamer T. L., Fox R. R. Venereal spirochetosis of rabbits: description and diagnosis. Lab Anim Sci. 1981 Aug;31(4):366–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. Cultivation of Borrelia hermsi. Science. 1971 Jul 30;173(3995):443–444. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3995.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krinsky W. L., Brown S. J., Askenase P. W. Ixodes dammini: induced skin lesions in guinea pigs and rabbits compared to erythema chronicum migrans in patients with lyme arthritis. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Jun;53(3):381–395. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90081-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Craft J. E., Hutchinson G. J., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Spieler P. N., Stenn K. S., Malawista S. E. The early clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):76–82. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Broderick T. F., Malawista S. E. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis: epidemiologic evidence for a tick vector. Am J Epidemiol. 1978 Oct;108(4):312–321. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E. Cases of Lyme disease in the United States: locations correlated with distribution of Ixodes dammini. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):730–733. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]