Abstract
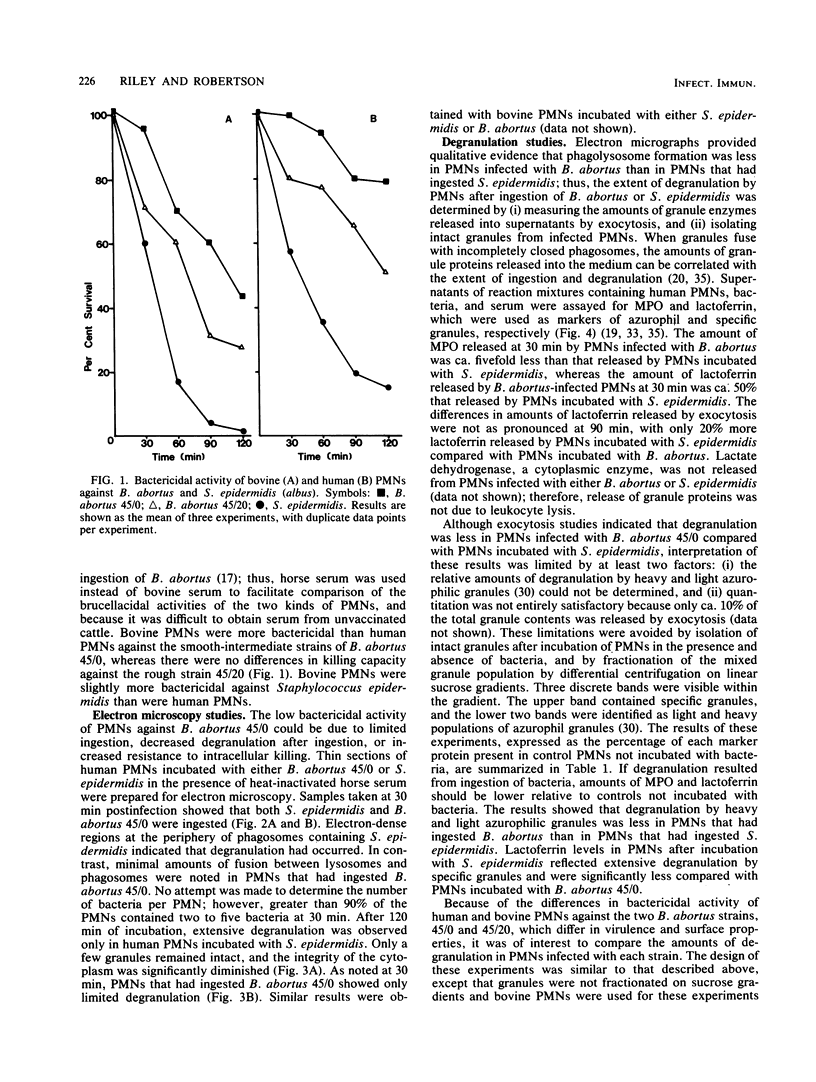
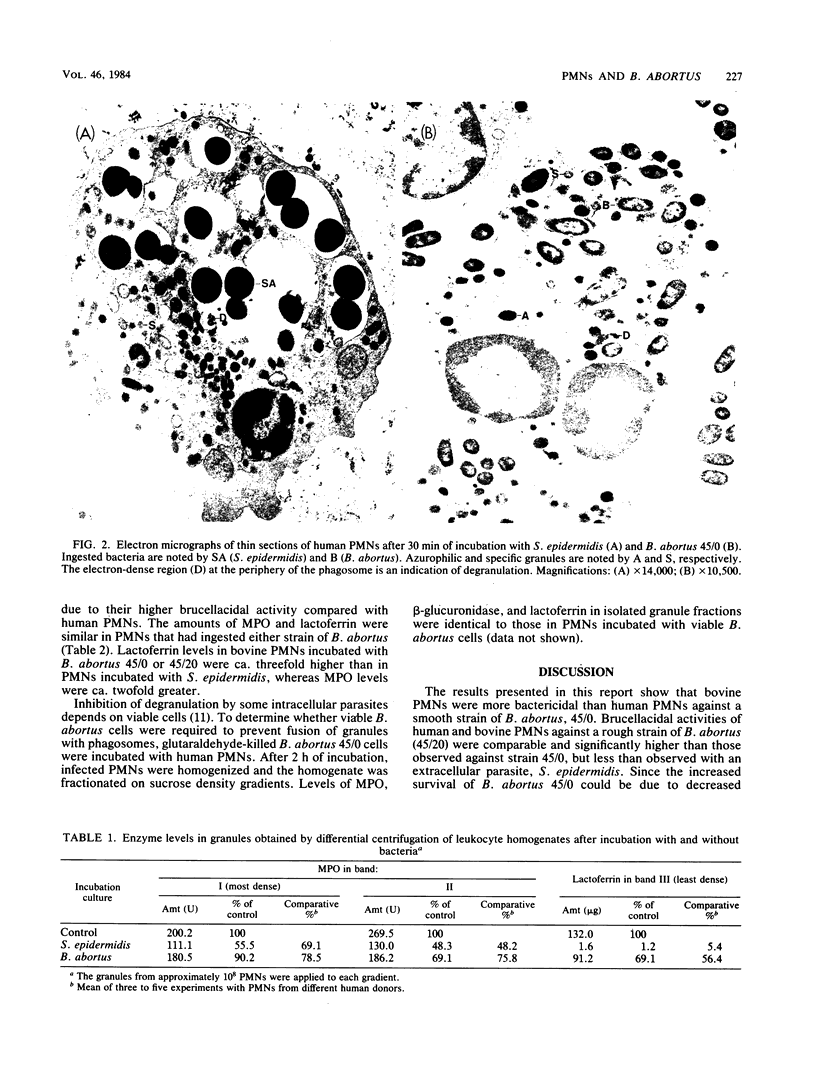
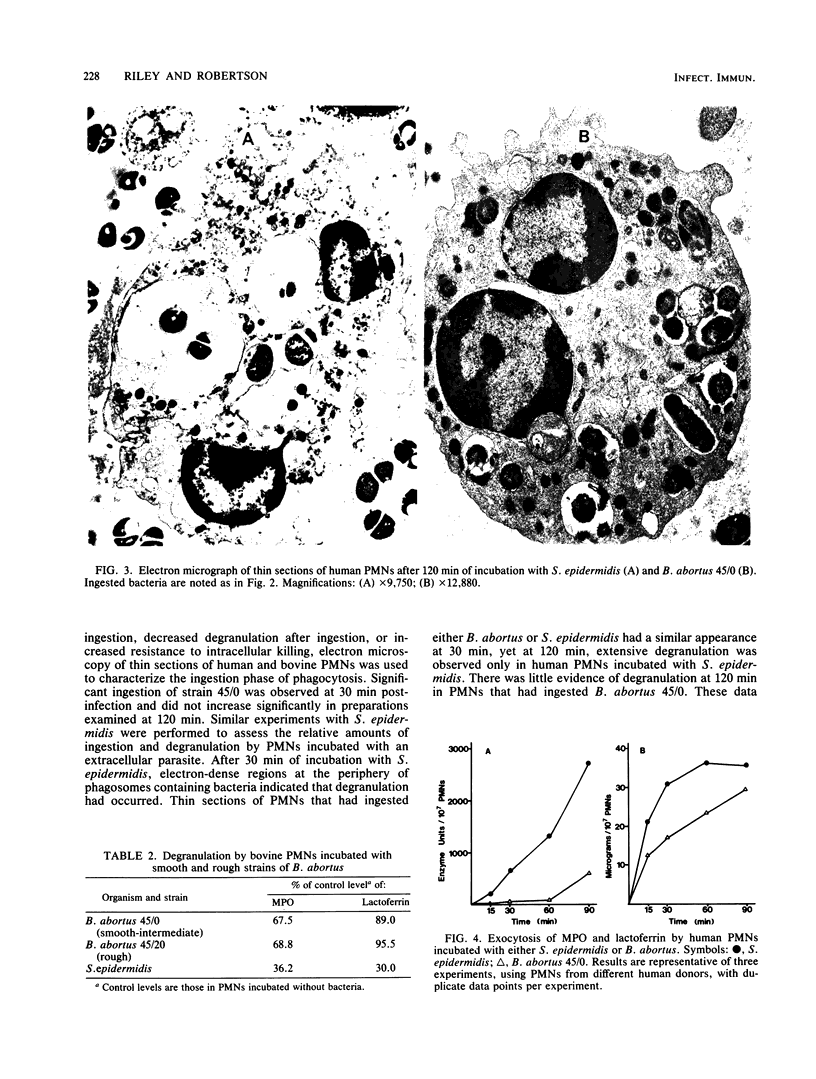
Bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) were found to be significantly more bactericidal than human PMNs against a smooth-intermediate strain of Brucella abortus (45/0), whereas there was no difference in bactericidal activity of the two kinds of PMNs against a rough strain of B. abortus (45/20). Electron microscopy of thin sections of PMNs revealed that both strains of B. abortus were readily ingested; however, the extent of degranulation was significantly less than in PMNs incubated with an extracellular parasite, Staphylococcus epidermidis. Amounts of myeloperoxidase and lactoferrin released through exocytosis by PMNs incubated with S. epidermidis were 4.7- and 1.2-fold greater, respectively, than those released from PMNs incubated with B. abortus 45/0. When azurophil and specific granules were isolated after incubation of PMNs with either B. abortus 45/0 or S. epidermidis, results showed that the extent of degranulation by both types of granules was greater in PMNs incubated with S. epidermidis than in those incubated with B. abortus 45/0. Amounts of degranulation by azurophil and specific granules were similar in PMNs incubated with either the smooth-intermediate strain 45/0 or the rough strain 45/20. Degranulation was not stimulated when glutaraldehyde-killed strain 45/0 was substituted for viable cells. These data suggest that B. abortus does not stimulate an effective level of degranulation after ingestion, as observed with extracellular parasites, and that the smooth intermediate strain 45/0 is more resistant to intraleukocytic killing system than the rough strain 45/20.
Full text
PDF



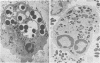
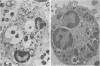
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUN W., POMALES-LEBRON A., STINEBRING W. R. Interactions between mononuclear phagocytes and Brucella abortus strains of different virulence. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Feb;97(2):393–397. doi: 10.3181/00379727-97-23752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babior B. M. Oxygen-dependent microbial killing by phagocytes (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 23;298(12):659–668. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803232981205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badwey J. A., Karnovsky M. L. Active oxygen species and the functions of phagocytic leukocytes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrol M. E., Jackett P. S., Aber V. R., Lowrie D. B. Phagolysosome formation, cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate and the fate of Salmonella typhimurium within mouse peritoneal macrophages. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):421–429. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson C. A., Sells D. M., Ristic M. A method for separation of bovine blood leukocytes for in vitro studies. Am J Vet Res. 1975 Aug;36(08):1091–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeChatelet L. R. Initiation of the respiratory burst in human polymorphonuclear neutrophils: a critical review. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1978 Jul;24(1):73–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN B. A., VANA L. R. Host-parasite relationships in brucellosis. I. Infection of normal guinea pig macrophages in tissue culture. J Infect Dis. 1958 May-Jun;102(3):258–267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/102.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., D'Arcy Hart P., Young M. R., Armstrong J. A. Prevention of phagosome-lysosome fusion in cultured macrophages by sulfatides of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2510–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. II. The absence of lysosomal fusion with phagocytic vacuoles containing living parasites. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebanoff S. J. Antimicrobial mechanisms in neutrophilic polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Semin Hematol. 1975 Apr;12(2):117–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossack R. E., Guerrant R. L., Densen P., Schadelin J., Mandell G. L. Diminished neutrophil oxidative metabolism after phagocytosis of virulent Salmonella typhi. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):674–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.674-678.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., Buller C. S., Robertson D. C. Chemical characterization and biological properties of lipopolysaccharides isolated from smooth and rough strains of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):811–818. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.811-818.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., Dreyfus L. A., Robertson D. C. Interaction of polymorphonuclear leukocytes with smooth and rough strains of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):737–742. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.737-742.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer D. L., Robertson D. C. Surface macromolecules and virulence in intracellular parasitism: comparison of cell envelope components of smooth and rough strains of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):819–828. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.819-828.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffell M. S., Spitznagel J. K. Association of lactoferrin with lysozyme in granules of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):761–765. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.761-765.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffell M. S., Spitznagel J. K. Intracellular and extracellular degranulation of human polymorphonuclear azurophil and specific granules induced by immune complexes. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1241–1249. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1241-1249.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie D. B., Aber V. R., Jackett P. S. Phagosome-lysosome fusion and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in macrophages infected with Mycobacterium microti, Mycobacterium bovis BCG or Mycobacterium lepraemurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Feb;110(2):431–441. doi: 10.1099/00221287-110-2-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrie D. B., Jackett P. S., Ratcliffe N. A. Mycobacterium microti may protect itself from intracellular destruction by releasing cyclic AMP into phagosomes. Nature. 1975 Apr 17;254(5501):600–602. doi: 10.1038/254600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACRAE R. M., SMITH H. THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF THE VIRULENCE OF BRUCELLA ABORTUS. VI. STUDIES ON IMMUNITY AND INTRACELLULAR GROWTH. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Dec;45:595–603. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. R., Freeman B. A. Osmotically sensitive Brucella in infected normal and immune macrophages. Infect Immun. 1970 Feb;1(2):146–150. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.2.146-150.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. A. The interaction of "Brucella abortus" 544 and neutrophil polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Ann Sclavo. 1977 Jan-Feb;19(1):143–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querinjean P., Masson P. L., Heremans J. F. Molecular weight, single-chain structure and amino acid composition of human lactoferrin. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jun 11;20(3):420–425. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01408.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G. Perturbation of the normal mechanisms of intraleukocytic killing of bacteria. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):189–193. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Cooney M. H., Spitznagel J. K. Susceptibility of lipopolysaccharide mutants to the bactericidal action of human neutrophil lysosomal fractions. Infect Immun. 1977 Apr;16(1):145–151. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.1.145-151.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rest R. F., Spitznagel J. K. Subcellular distribution of superoxide dismutases in human neutrophils. Influence of myeloperoxidase on the measurement of superoxide dismutase activity. Biochem J. 1977 Aug 15;166(2):145–153. doi: 10.1042/bj1660145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. K., Robertson D. C. Brucellacidal activity of human and bovine polymorphonuclear leukocyte granule extracts against smooth and rough strains of Brucella abortus. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):231–236. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.231-236.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH H., FITZGEORGE R. B. THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF THE VIRULENCE OF BRUCELLA ABORTUS. V. THE BASIS OF INTRACELLULAR SURVIVAL AND GROWTH IN BOVINE PHAGOCYTES. Br J Exp Pathol. 1964 Apr;45:174–186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitznagel J. K., Dalldorf F. G., Leffell M. S., Folds J. D., Welsh I. R., Cooney M. H., Martin L. E. Character of azurophil and specific granules purified from human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1974 Jun;30(6):774–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Malawista S. E. The mobilization and extracellular release of granular enzymes from human leukocytes during phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):788–797. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyrick P. B., Brownridge E. A. Growth of Chlamydia psittaci in macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1054–1060. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1054-1060.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]