Abstract
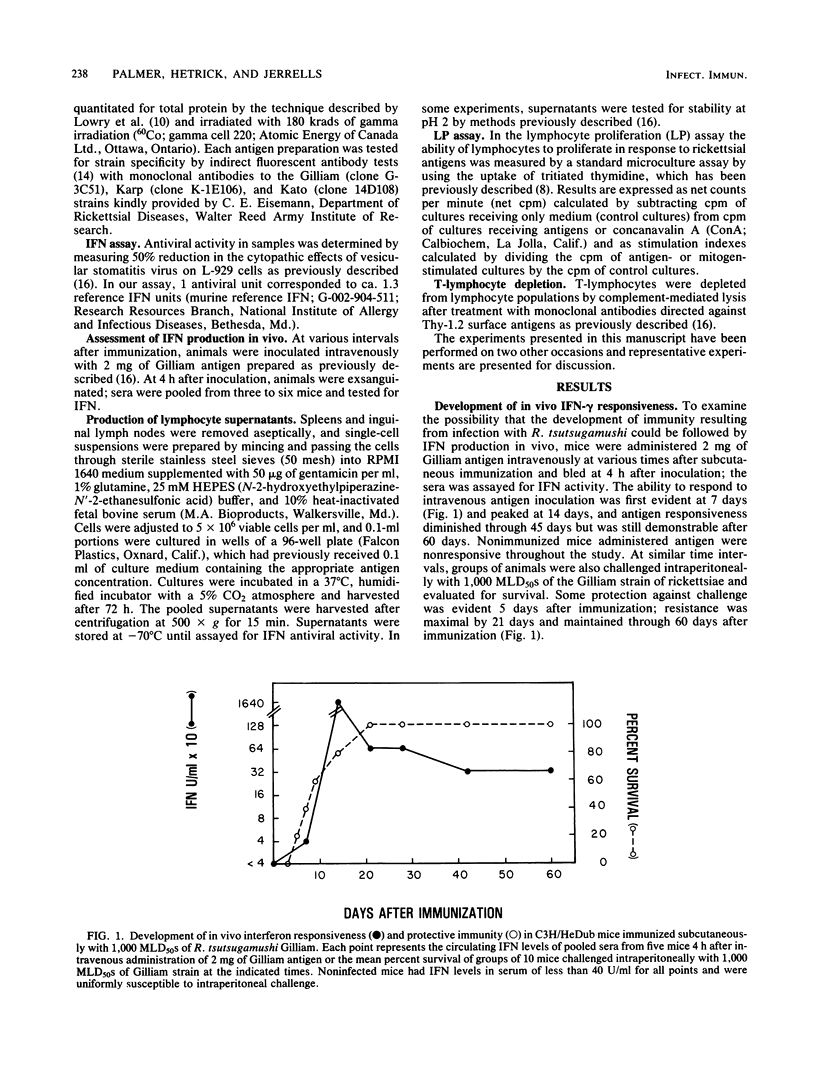
The ability of antigen-responsive, thymus-derived lymphocytes to produce immune (gamma) interferon was investigated during the development and expression of cellular immunity to Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. C3H/HeDub mice infected subcutaneously with the Gilliam strain developed the ability to produce serum interferon in response to intravenously inoculated antigen which correlated with the development of resistance to intraperitoneal rechallenge. Antigen-responsive lymphocytes, measured by interferon production and proliferation, were first apparent in draining lymph node cells, but spleen cell responses were detectable relatively soon after the appearance of reactive lymph node cells. The peak spleen cell response was of a greater magnitude and was found to be relatively long-lived. Reactivity to heterologous strains of R. tsutsugamushi also developed after immunization and paralleled the homologous responses, although reactivity was greatest to homologous antigens. Responses to heterologous strains differed in magnitude and time of appearances; however, immune mice resisted challenge with all strains of R. tsutsugamushi tested.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byrne G. I., Krueger D. A. Lymphokine-mediated inhibition of Chlamydia replication in mouse fibroblasts is neutralized by anti-gamma interferon immunoglobulin. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1152–1158. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1152-1158.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark C., Wheelock M. In vivo cyclophosphamide-mediated augmentation and aqueous HGG-induced suppression of murine delayed hypersensitivity to HGG are reflected by in vitro HGG-stimulated proliferation of lymph node cells from equivalent mice. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jul 1;52(2):404–413. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90361-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisemann C. S., Osterman J. V. Proteins of typhus and spotted fever group rickettsiae. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):155–162. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.155-162.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewing E. P., Jr, Takeuchi A., Shirai A., Osterman J. V. Experimental infection of mouse peritoneal mesothelium with scrub typhus rickettsiae: an ultrastructural study. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1068–1075. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1068-1075.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R. Association of an inflammatory I region-associated antigen-positive macrophage influx and genetic resistance of inbred mice to Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):549–557. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.549-557.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Osterman J. V. Development of specific and cross-reactive lymphocyte proliferative responses during chronic immunizing infections with Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):147–156. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.147-156.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: delayed-type hypersensitivity responses of inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):117–123. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.117-123.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jerrells T. R., Palmer B. A., Osterman J. V. Gamma-irradiated scrub typhus immunogens: development of cell-mediated immunity after vaccination of inbred mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jan;39(1):262–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.1.262-269.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Koster F. T., Mackaness G. B. The mediator of cellular immunity. I. The life-span and circulation dynamics of the immunologically committed lymphocyte. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):389–399. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nacy C. A., Meltzer M. S. Macrophages in resistance to rickettsial infection: macrophage activation in vitro for killing of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2544–2549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks S. C., Jr, Hetrick F. M., Osterman J. V. A plaque reduction assay for studying antigenic relationships among strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980 Sep;29(5):998–1006. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks S. C., Jr, Osterman J. V., Hetrick F. M. Plaque assay and cloning of scrub typhus rickettsiae in irradiated L-929 cells. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jul;6(1):76–80. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.1.76-80.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace J. L., Russell S. W., Schreiber R. D., Altman A., Katz D. H. Macrophage activation: priming activity from a T-cell hybridoma is attributable to interferon-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3782–3786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer B. A., Hetrick F. M., Jerrells T. J. Production of gamma interferon in mice immune to Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):59–65. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.59-65.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirai A., Catanzaro P. J., Phillips S. M., Osterman J. V. Host defenses in experimental scrub typhus: role of cellular immunity in heterologous protection. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.39-46.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Johnson H. M., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia antigen expression by a lymphokine with immune interferon activity. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Cloned mouse interferon-gamma inhibits the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured mouse fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2159–2164. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Comparison of the properties of antirickettsial activity and interferon in mouse lymphokines. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.27-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turco J., Winkler H. H. Inhibition of the growth of Rickettsia prowazekii in cultured fibroblasts by lymphokines. J Exp Med. 1983 Mar 1;157(3):974–986. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.3.974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisseman C. L., Jr, Waddell A. Interferonlike factors from antigen- and mitogen-stimulated human leukocytes with antirickettsial and cytolytic actions on Rickettsia prowazekii. Infected human endothelial cells, fibroblasts, and macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Jun 1;157(6):1780–1793. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.6.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


