Abstract
An enhanced memory response, as shown by increased titers of specific immunoglobulin A (IgA), was seen in intestinal secretions from isolated Thiry-Vella loops in rabbits primed orally with live, locally invasive Shigella sp. X16 and challenged 60 days later with a single oral dose of the same antigen. Heat-killed shigella preparations, when used as either the priming or challenge antigen, did not elicit such a memory response in this system. In the present study, the role of antigen form and dosage in eliciting the enhanced local IgA response was investigated. A noninvasive strain, Shigella flexneri 2457-0, was capable of significantly enhancing the mucosal IgA memory response, whereas heat-killed Shigella sp. X16 was unable to augment the local IgA response, even when the priming dose was increased 100-fold. A proposed mucosal adjuvant, DEAE-dextran, given orally with live Shigella sp. X16, did not enhance the local IgA response. Viable, noninvasive shigellae were effective priming agents in enhancing the local IgA memory response. The poor mucosal response to heat-killed shigella preparations is thought to be related to an ineffective delivery of nonviable bacterial antigens into gut-associated lymphoid tissues. The ability of the live, noninvasive strain to elicit a vigorous local IgA memory response when given orally to rabbits was consistent with previous findings that live preparations elicit the best mucosal IgA response.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beh K. J. Antibody-containing cell response in lymph of sheep after intra-intestinal infusion of ovalbumin with and without DEAE-dextran. Immunology. 1979 May;37(1):279–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebersole J. L., Taubman M. A., Smith D. J. Cellular and humoral IgA responses after single and multiple local injections of antigen. Cell Immunol. 1983 Apr 15;77(2):372–384. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., LABREC E. H., KENT T. H., FALKOW S. ABORTIVE INTESTINAL INFECTION WITH AN ESCHERICHIA COLI-SHIGELLA FLEXNERI HYBRID STRAIN. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1374-1382.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Labrec E. H., Palmer A., Falkow S. Protection of Monkeys Against Experimental Shigellosis with Attenuated Vaccines. J Bacteriol. 1965 Jul;90(1):63–68. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.1.63-68.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., O'Brien P. C., Macsai M. S. Effect of chemotaxis on the interaction of cholera vibrios with intestinal mucosa. Am J Clin Nutr. 1979 Jan;32(1):128–132. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/32.1.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., Cebra J. J. Special features of the priming process for a secretory IgA response. B cell priming with cholera toxin. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):534–544. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry C., Faulk W. P., Kuhn L., Yoffey J. M., Fudenberg H. H. Peyer's patches: immunologic studies. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1200–1210. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff B., André C., Fontanges R., Jourdan G. Secondary immune response to oral and nasal rough mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1982 Jul-Aug;133D(1):61–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Collins H. H., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Intestinal immunoglobulin A responses in rabbits to a Salmonella typhi strain harboring a Shigella sonnei plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):387–389. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.387-389.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
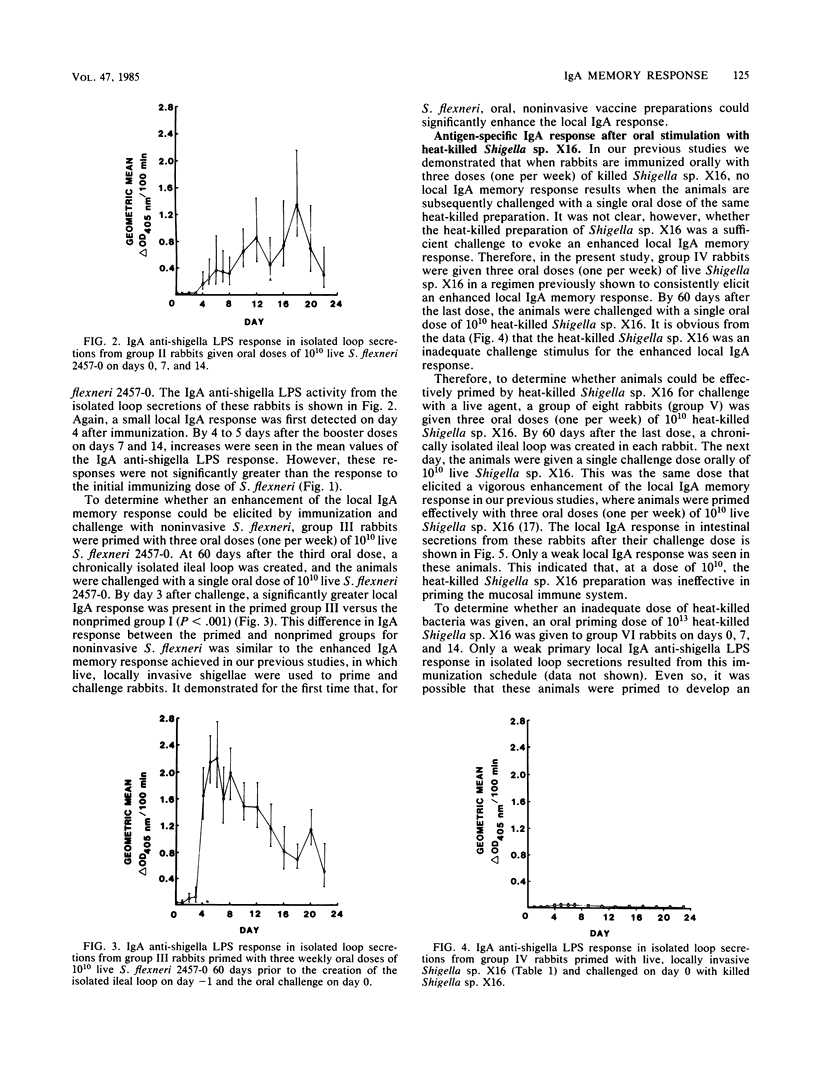
- Keren D. F., Collins H. H., Gemski P., Holt P. S., Formal S. B. Role of antigen form in development of mucosal immunoglobin A response to Shigella flexneri Antigens. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1193–1202. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1193-1202.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Elliott H. L., Brown G. D., Yardley J. H. Atrophy of villi with hypertrophy and hyperplasia of Paneth cells in isolated (thiry-Vella) ileal loops in rabbits. Light-microscopic studies. Gastroenterology. 1975 Jan;68(1):83–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin A antibodies to Shigella flexneri antigens. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):441–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.441-448.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
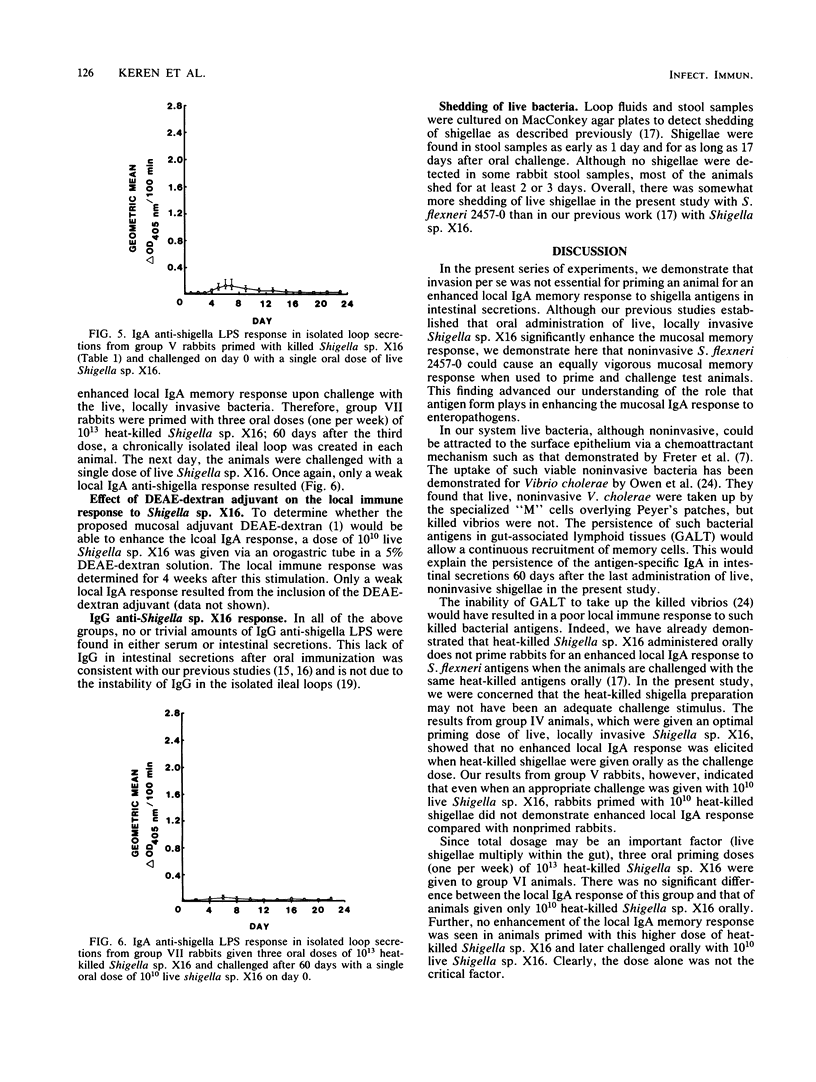
- Keren D. F., Holt P. S., Collins H. H., Gemski P., Formal S. B. The role of Peyer's patches in the local immune response of rabbit ileum to live bacteria. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1892–1896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Holt P. S., Collins H. H., Gemski P., Formal S. B. Variables affecting local immune response in ileal loops: role of immunization schedule, bacterial flora, and postsurgical inflammation. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):950–956. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.950-956.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Kern S. E., Bauer D. H., Scott P. J., Porter P. Direct demonstration in intestinal secretions of an IgA memory response to orally administered Shigella flexneri antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Jan;128(1):475–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Scott P. J., Bauer D. Variables affecting the local immune response in Thiry-Vella loops. II. Stability of antigen-specific IgG and secretory IgA in acute and chronic Thiry-Vella loops. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2620–2624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keren D. F., Scott P. J., McDonald R. A., Wiatrak M. Effect of parenteral immunization on the local immunoglobulin A response of the intestine to Shigella flexneri antigens. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):202–207. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.202-207.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Engert R. F. Influence of route of administration on immediate and extended protection in rats immunized with Escherichia coli heart-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.81-86.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koster F. T., Pierce N. F. Parenteral immunization causes antigen-specific cell-mediated suppression of an intestinal IgA response. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):115–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair P. N., Schroeder H. E. Local immune response to repeated topical antigen application in the simian labial mucosa. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):399–409. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.399-409.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaway C. A., Parrott D. M. Regional blood flow and the localisation of lymphoblasts in the small intestine of the mouse: effect of an elemental diet. Gut. 1981 May;22(5):376–382. doi: 10.1136/gut.22.5.376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr Cellular dissemination of priming for a mucosal immune response to cholera toxin in rats. J Immunol. 1981 Dec;127(6):2461–2464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F., Cray W. C., Jr, Sacci J. B., Jr, Craig J. P., Germanier R., Fürer E. Procholeragenoid: a safe and effective antigen for oral immunization against experimental cholera. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1112–1118. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1112-1118.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce N. F. The role of antigen form and function in the primary and secondary intestinal immune responses to cholera toxin and toxoid in rats. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):195–206. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman L. K., Graeff A. S., Yarchoan R., Strober W. Simultaneous induction of antigen-specific IgA helper T cells and IgG suppressor T cells in the murine Peyer's patch after protein feeding. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2079–2083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberg R. M., Kraft S. C., Michalek S. M. Systemic immunity after local antigenic stimulation of the lymphoid tissue of the gastrointestinal tract. J Immunol. 1973 Dec;111(6):1906–1913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman R. H., Grunspan R., Ganguly R. Oral immunization of mice with killed Salmonella typhimurium vaccine. Infect Immun. 1972 Jul;6(1):58–61. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.1.58-61.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. F., Murphy B. R., Kervina M., Lawrence E. M., Phelan M. A., Karzon D. T. Secretory immunological response after intranasal inactivated influenza A virus vaccinations: evidence for immunoglobulin A memory. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1092–1095. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1092-1095.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley J. H., Keren D. F., Hamilton S. R., Brown G. D. Local (immunoglobulin A) immune response by the intestine to cholera toxin and its partial suppression with combined systemic and intra-intestinal immunization. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):589–597. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.589-597.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


