Abstract
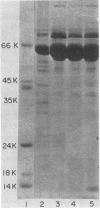
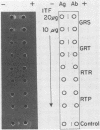
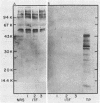
Mucoid fluid accumulating within syphilitic lesions has been considered to be of Treponema pallidum origin. To test this assumption, we examined testicular exudative fluids from T. pallidum-infected rabbits for the presence of T. pallidum antigens by various sensitive immunochemical methods, including Western blot analysis. Antigenic analysis of these fluids revealed host components but not treponemal antigens. Prolonged immunization of rabbits, guinea pigs, and a goat with this material in complete Freund adjuvant elicited low titers (fluorescent-treponemal-antibody test titer, less than or equal to 10) of antitreponemal antibodies in the rabbits and guinea pigs but not in the goat. The data suggest that these mucoid fluids are of host origin. The presence of mucopolysaccharides in these fluids may be related to the infective process. The possible mechanism by which mucopolysaccharides protect T. pallidum from immune mechanisms and its potential relationship to the pathogenesis of the disease are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Baseman J. B. Surface-associated host proteins on virulent Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):1048–1056. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.1048-1056.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson A. J. Interactions between glycosaminoglycans and proteins, with particular reference to a new technique for isolating serum glycoproteins. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):719–727. doi: 10.1042/bj1020719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BENSLEY S. H. Histological studies of the reactions of cells and intercellular substances of loose connective tissue to the spreading factor of testicular extracts. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1950 May 31;52(7):983–988. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1950.tb53993.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOLLET A. J., BONNER W. M., Jr, NANCE J. L. THE PRESENCE OF HYALURONIDASE IN VARIOUS MAMMALIAN TISSUES. J Biol Chem. 1963 Nov;238:3522–3527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baseman J. B., Nichols J. C., Rumpp J. W., Hayes N. S. Purification of Treponema pallidum from Infected Rabbit Tissue: Resolution into Two Treponemal Populations. Infect Immun. 1974 Nov;10(5):1062–1067. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.5.1062-1067.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bok S. W. The fundamental role of hyaluronidase in tissue. Med Hypotheses. 1979 Nov;5(11):1183–1200. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(79)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIANSEN S. Protective layer covering pathogenic treponemata. Lancet. 1963 Feb 23;1(7278):423–425. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)92309-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Salegui M., Plonska H., Pigman W. A comparison of serum and testicular hyaluronidase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Sep;121(3):548–554. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90037-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Cleveland P., Johnson R. C., Miller J. N., Sykes J. A. Scanning electron microscopy of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) attached to cultured mammalian cells. J Bacteriol. 1977 Jun;130(3):1333–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.3.1333-1344.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C. Mucopolysaccharidase of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):261–268. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.261-268.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Ritzi D. M. Relationship of Treponema pallidum to acidic mucopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):252–260. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.252-260.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C. Surface mucopolysaccharides of Treponema pallidum. Infect Immun. 1979 Apr;24(1):244–251. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.1.244-251.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Johnson R. C., Wolff E. T. Mucopolysaccharide material resulting from the interaction of Treponema pallidum (Nichols strain) with cultured mammalian cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):575–584. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.575-584.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald T. J., Repesh L. A., Oakes S. G. Morphological destruction of cultured cells by the attachment of Treponema pallidum. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Feb;58(1):1–11. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester J. V., Balazs E. A. Inhibition of phagocytosis by high molecular weight hyaluronate. Immunology. 1980 Jul;40(3):435–446. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HANSON A. W., CANNEFAX G. R. RECOVERY OF TREPONEMA AND BORRELIA AFTER LYOPHILIZATION. J Bacteriol. 1964 Sep;88:811–811. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.3.811-811.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan L. C. Rabbit globulin and antiglobulin factors associated with Treponema pallidum growth in rabbits. Br J Vener Dis. 1974 Dec;50(6):421–427. doi: 10.1136/sti.50.6.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUCHTERLONY O. Diffusion-in-gel methods for immunological analysis. Prog Allergy. 1958;5:1–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICE F. A. Chondroitin sulfate and hyaluronic acid in syphilomas of cortisone-treated rabbits. Science. 1956 Aug 10;124(3215):275–275. doi: 10.1126/science.124.3215.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart J., Reiser J., Stark G. R. Transfer of proteins from gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection with antisera: a method for studying antibody specificity and antigen structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter W. Non-immunogenicity of purified hyaluronic acid preparations tested by passive cutaneous anaphylaxis. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1974;47(2):211–217. doi: 10.1159/000231214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT V., DAMMIN G. J. Hyaluronidase and experimental syphilis. III. Metachromasia in syphilitic orchitis and its relationship to hyaluronic acid. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1950 Nov;34(6):501–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT V., DAMMIN G. J. Morphologic and histochemical sequences in syphilitic and in tuberculous orchitis in the rabbit. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 May;38(3):189–202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER T. B., HOLLANDER D. H. Cortisone in experimental syphilis; a preliminary note. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1950 Nov;87(5):505–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER T. B., HOLLANDER D. H. Studies on the mechanism of action of cortisone in experimental syphilis. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1954 Sep;38(5):371–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Oss C. J., Gillman C. F. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. II. Contact angles and phagocytosis of encapsulated bacteria before and after opsonization by specific antiserum and complement. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1972 Nov;12(5):497–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS R. G. The effects of continuous local injection of hyaluronidase on skin and subcutaneous tissue in rats. Anat Rec. 1955 Jul;122(3):349–361. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091220307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher V., Wicher K. Studies of rabbit testes infected with Treponema pallidum. II Local synthesis of antibodies. Br J Vener Dis. 1983 Dec;59(6):359–363. doi: 10.1136/sti.59.6.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeigler J. A., Jones A. M., Jones R. H., Kubica K. M. Demonstration of extracellular material at the surface of pathogenic T. pallidum cells. Br J Vener Dis. 1976 Feb;52(1):1–8. doi: 10.1136/sti.52.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]