Abstract
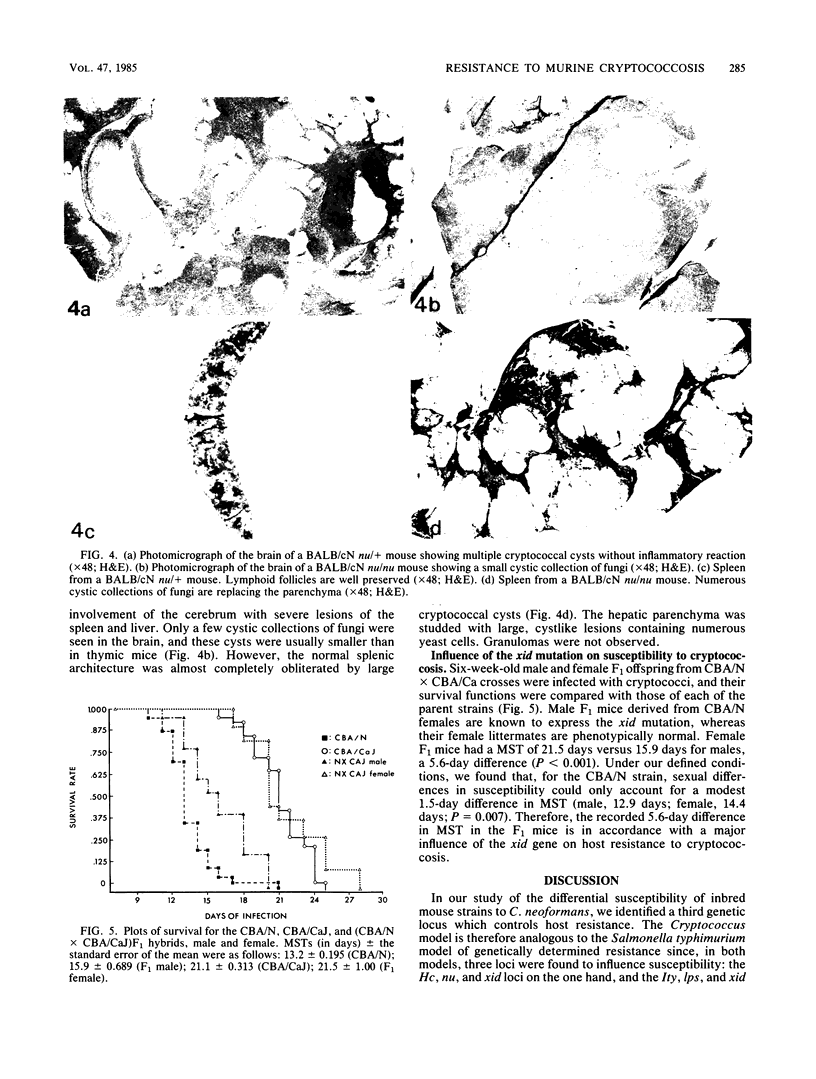
In a survey of 301 normocomplementemic inbred mice (belonging to nine different strains: BALB/cN nu/nu and nu/+, CBA/N, C57BL/KsJ, C57BR/cdJ, CBA/CaJ, BRVR, DW/+, and C57BL/6J) for natural resistance to Cryptococcus neoformans, cumulative survival values were found to range from 12 to 22 days. When the average organ weights of infected animals were compared with reference values obtained in uninfected mice of the same age and genetic lineage, the following changes were documented. In the CBA/N strain, the mean spleen and brain weights increased 313 and 13.5%, respectively, whereas the mean liver weight remained unchanged. In the CBA/Ca strain, cerebral cryptococcosis was the dominant clinical feature, and a 54% increase in mean brain weight was recorded at the time of death. The averaged liver weight was drastically lower, whereas spleen weight values evinced a biphasic pattern of transient splenomegaly followed by involution. At the median time of death, CBA/N mice had significantly more cryptococci in the liver and spleen than corresponding CBA/Ca mice. In the (CBA/N X CBA/Ca)F1 mice, susceptibility to C. neoformans segregated according to the sex-linked inheritance of the X-linked immunodeficiency (xid) gene. It is concluded that (i) susceptibility to cryptococcosis is under multigenic control, (ii) the xid locus on the X chromosome influences susceptibility to cryptococcosis, and (iii) xid mice behave differently than CBA/Ca mice in their organ response during the course of the infection.
Full text
PDF
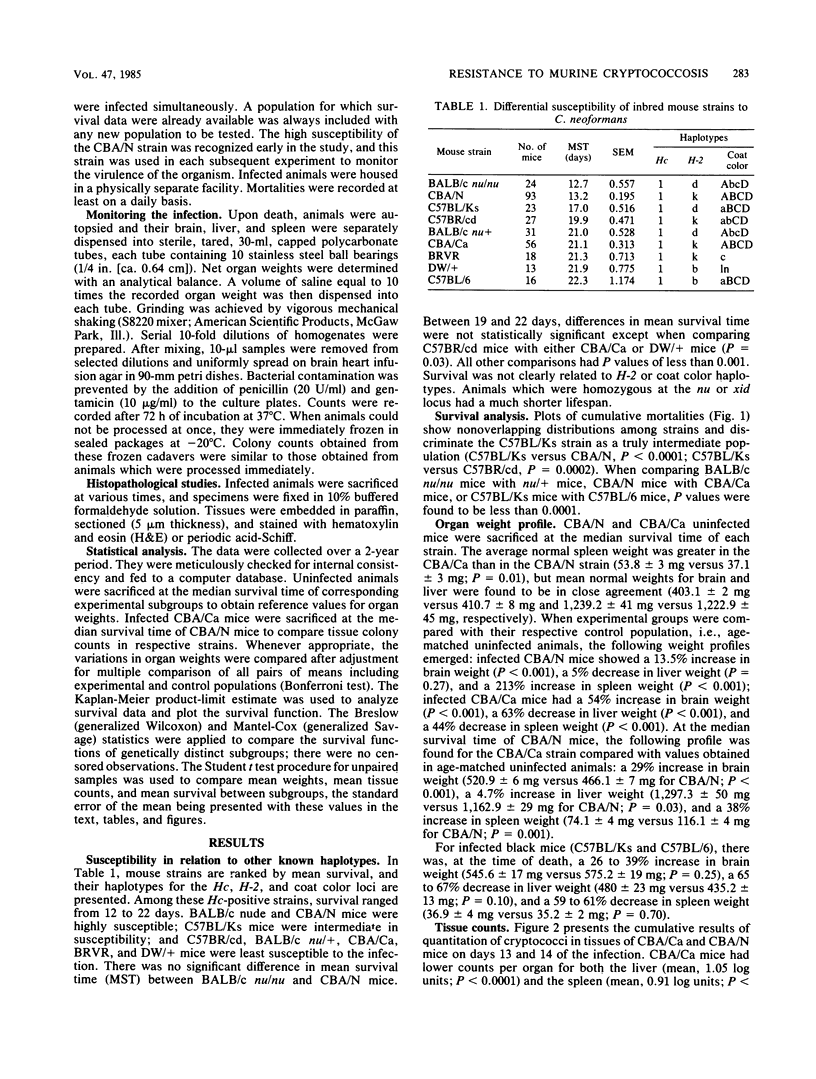
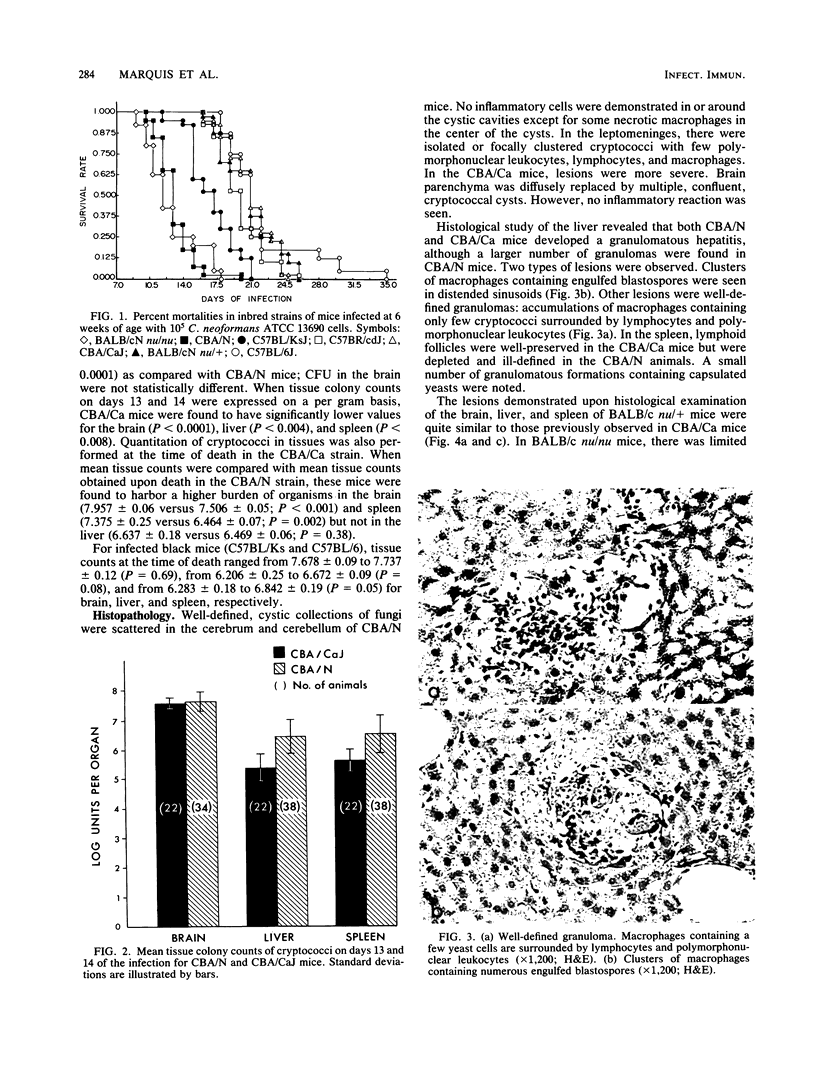


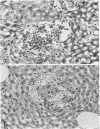
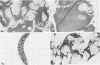
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auger P., Marquis G., Dallaire L. Viability assessment by dye exclusion. A fluorescent method for fungal cells. Arch Dermatol. 1979 Oct;115(10):1195–1196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauley L. K., Murphy J. W. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) and phenotypically normal mice to Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):644–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.644-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Drutz D. J. Host defense in cryptococcosis. II. Cryptococcosis in the nude mouse. Cell Immunol. 1978 Oct;40(2):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90334-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser S. A., Lyon F. L., Domer J. E., Williams J. E. Immunization of mice by intracutaneous inoculation with viable virulent Cryptococcus neoformans: immunological and histopathological parameters. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):685–696. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.685-696.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura K., Miyaji M. Histopathological studies on experimental cryptococcosis in nude mice. Mycopathologia. 1979 Sep 28;68(3):145–153. doi: 10.1007/BF00578522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Scher I., Metcalf E. S. Genetically conferred defect in anti-Salmonella antibody formation renders CBA/N mice innately susceptible to Salmonella typhimurium infection. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1368–1372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Wicker L. S., Urba W. J. Genetic control of susceptibility to Cryptococcus neoformans in mice. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):494–499. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.494-499.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I. CBA/N immune defective mice; evidence for the failure of a B cell subpopulation to be expressed. Immunol Rev. 1982;64:117–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00421.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimpff S. C., Bennett J. E. Abnormalities in cell-mediated immunity in patients with Cryptococcus neoformans infection. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1975 Jun;55(6):430–441. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(75)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skamene E., Gros P., Forget A., Kongshavn P. A., St Charles C., Taylor B. A. Genetic regulation of resistance to intracellular pathogens. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):506–509. doi: 10.1038/297506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]