Abstract
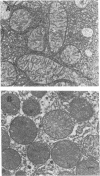
The administration of sublethal doses of Escherichia coli O111:B4 endotoxin to starved rats results in significant increases in plasma ammonia, free fatty acids, and serum lactate compared with starved controls. These metabolic alterations are associated with Reye syndrome-like histological findings of hepatic microvesicular fatty accumulation and hepatic ultrastructural evidence of mitochondrial pleomorphism with matrix disruption. This sublethal endotoxin model may help elucidate the relationship between the hepatic mitochondrial injury, characteristic metabolic impairment, and encephalopathy seen in patients with Reye syndrome.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adeleye G. A., Al-Jibouri L. M., Furman B. L., Parratt J. R. Exdotoxin-induced metabolic changes in the conscious, unrestrained rat: hypoglycemia and elevated blood lactate concentrations without hyperinsulinemia. Circ Shock. 1981;8(5):543–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUDE A. I., CAREY F. J., ZALESKY M. Studies with radioactive endotoxin. II. Correlation of physiologic effects with distribution of radioactivity in rabbits injected with radioactive sodium chromate. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):858–866. doi: 10.1172/JCI103141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley S. G. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of action of bacterial endotoxins. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:67–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M., Rutherford R. B., Smith F. O. Experimental ammonia encephalopathy in the primate. Arch Neurol. 1972 Feb;26(2):130–136. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1972.00490080048004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooperstock M. S., Tucker R. P., Baublis J. V. Possible pathogenic role of endotoxin in Reye's syndrome. Lancet. 1975 Jun 7;1(7919):1272–1274. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92553-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker J. F. Reye's syndrome. Semin Liver Dis. 1982 Nov;2(4):340–352. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong G. R., Glick T. H. Encephalopathy of Reye's syndrome: a review of pathogenetic hypotheses. Pediatrics. 1982 Jan;69(1):53–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J. P. Role of the RES in the pathogenesis of endotoxic hypoglycemia. Circ Shock. 1982;9(3):269–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish R. E., Spitzer J. A. Continuous infusion of endotoxin from an osmotic pump in the conscious, unrestrained rat: a unique model of chronic endotoxemia. Circ Shock. 1984;12(2):135–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRSCH R. L., MCKAY D. G., TRAVERS R. I., SKRALY R. K. HYPERLIPIDEMIA, FATTY LIVER, AND BROMSULFOPHTHALEIN RETENTION IN RABBITS INJECTED INTRAVENOUSLY WITH BACTERIAL ENDOTOXINS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Oct;5:563–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrich-Smith L., Erecinska M., Silver I. A. Early cellular responses in vitro to endotoxin administration. Circ Shock. 1981;8(5):585–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirn A., Gut J. P., Gendrault J. L. Interaction of viruses with sinusoidal cells. Prog Liver Dis. 1982;7:377–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. S., Spitzer J. J. In vitro effects of E. coli endotoxin on fatty acid and lactate oxidation in canine myocardium. Circ Shock. 1977;4(2):181–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mela L. Direct and indirect effects of endotoxin on mitochondrial function. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;62:15–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalek S. M., Moore R. N., McGhee J. R., Rosenstreich D. L., Mergenhagen S. E. The primary role of lymphoreticular cells in the mediation of host responses to bacterial endotoxim. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):55–63. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C. Bacterial endotoxins and pathogenesis. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Sep-Oct;5 (Suppl 4):S733–S747. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.supplement_4.s733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Ulevitch R. J. The effects of bacterial endotoxins on host mediation systems. A review. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):526–618. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson A. E., Drummond D. C., Adams A. C., Bradley S. G. Enhanced toxicity for mice of combinations of bacterial lipopolysaccharide and vincristine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1976 May;9(5):840–847. doi: 10.1128/aac.9.5.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOVAK M. COLORIMETRIC ULTRAMICRO METHOD FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FREE FATTY ACIDS. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:431–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar B. L., Schoolwerth A. C. An improved microfluorometric enzymatic assay for the determination of ammonia. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jun;95(2):507–511. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90763-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partin J. S., McAdams A. J., Partin J. C., Schubert W. K., McLaurin R. L. Brain ultrastructure in Reye's disease. II. Acute injury and recovery processes in three children. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1978 Nov-Dec;37(6):796–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Victor M., Adams R. D., Cole M. The acquired (non-Wilsonian) type of chronic hepatocerebral degeneration. Medicine (Baltimore) 1965 Sep;44(5):345–396. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196509000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino M. Effect of Shigella flexneri endotoxin on ureagenesis and liver ultrastructure in rabbits. Exp Mol Pathol. 1980 Jun;32(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(80)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]