Abstract
The binding of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin to rabbit and human erythrocytes was studied by hemolytic assays and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis immunoblotting. Hemolytic assays showed that toxin binding to 10% cell suspensions at neutral pH was very ineffective in the concentration range 3 X 10(-8) to 3 X 10(-7) M (1 to 10 micrograms/ml), and less than 5% of added toxin became cell bound. However, binding was augmented as toxin levels were raised, abruptly increasing to 50 to 60% at 2 X 10(-6) to 3 X 10(-6) M (60 to 100 micrograms/ml). When rabbit erythrocytes were lysed with 1 to 5 micrograms of toxin per ml, both monomeric and hexameric forms of the toxin could be detected on the membranes by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis immunoblotting. In contrast, human erythrocytes treated with 1 to 6 micrograms of toxin per ml did not lyse, and membrane-bound toxin was not detectable. When toxin concentrations were raised to 30 to 100 micrograms/ml, human erythrocytes also lysed and toxin hexamers became membrane bound in comparable amounts as on rabbit cell membranes. Lowering the pH led to a marked increase in susceptibility of human, but not rabbit erythrocytes towards alpha-toxin. When human cells were lysed at pH 5.0 with 5 micrograms of toxin per ml, membrane-bound hexameric toxin became detectable. The demonstrated correlation between the presence of hexameric, cell-bound toxin and hemolytic activity supports the channel concept of toxin-mediated cytolysis. The results also show that toxin binding does not exhibit overall characteristics of a simple receptor-ligand interaction.
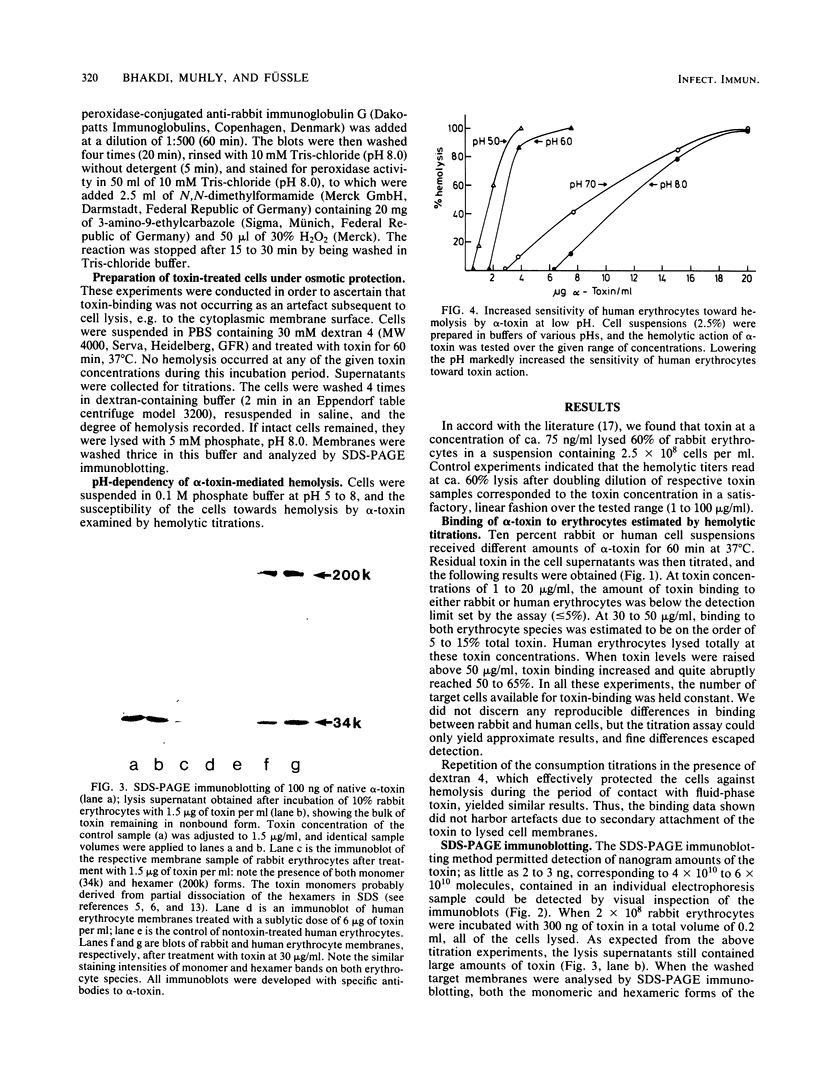
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arbuthnott J. P., Freer J. H., Bernheimer A. W. Physical states of staphylococcal alpha-toxin. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1170–1177. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1170-1177.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Freer J. H., Billcliffe B. Lipid-induced polymerization of staphylococcal -toxin. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):309–319. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W. Cytolytic toxins of bacterial origin. The nature and properties of cytolytic proteins are discussed with emphasis on staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Science. 1968 Feb 23;159(3817):847–851. doi: 10.1126/science.159.3817.847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Füssle R., Tranum-Jensen J. Staphylococcal alpha-toxin: oligomerization of hydrophilic monomers to form amphiphilic hexamers induced through contact with deoxycholate detergent micelles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5475–5479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Membrane damage by complement. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):343–372. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J., Utermann G., Füssle R. Binding and partial inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin by human plasma low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5899–5904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckelew A. R., Jr, Colacicco G. Lipid monolayers. Interactions with staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 9;233(1):7–16. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90352-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Harshman S. Iodination of a tyrosyl residue in staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2342–2348. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassidy P., Harshman S. Studies on the binding of staphylococcal 125I-labeled alpha-toxin to rabbit erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 1;15(11):2348–2355. doi: 10.1021/bi00656a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Bernheimer A. W. Interaction of staphylococcal alpha-toxin with artificial and natural membranes. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1153–1168. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1153-1168.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freer J. H., Arbuthnott J. P., Billcliffe B. Effects of staphylococcal -toxin on the structure of erythrocyte membranes: a biochemical and freeze-etching study. J Gen Microbiol. 1973 Apr;75(2):321–332. doi: 10.1099/00221287-75-2-321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN H., BARROW P., GOLDBERG B. Effect of antibody and complement on permeability control in ascites tumor cells and erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1959 Nov 1;110:699–713. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.5.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
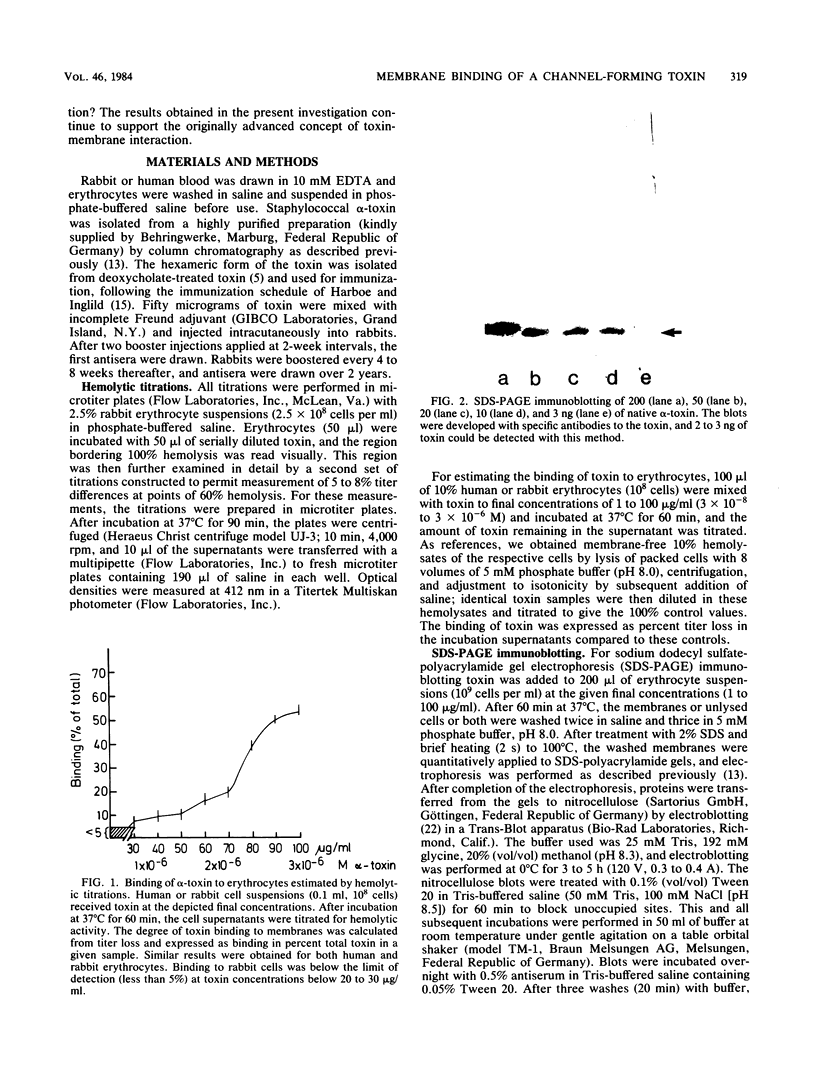
- Harboe N., Ingild A. Immunization, isolation of immunoglobulins, estimation of antibody titre. Scand J Immunol Suppl. 1973;1:161–164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1973.tb03798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato I., Naiki M. Ganglioside and rabbit erythrocyte membrane receptor for staphylococcal alpha-toxin. Infect Immun. 1976 Jan;13(1):289–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.1.289-291.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEARS D. A., WEED R. I., SWISHER S. N. DIFFERENCES IN THE MECHANISM OF IN VITRO IMMUNE HEMOLYSIS RELATED TO ANTIBODY SPECIFICITY. J Clin Invest. 1964 May;43:975–985. doi: 10.1172/JCI104983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Sensitive assay for detection of toxin-induced damage to the cytoplasmic membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):225–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.225-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R., Wadström T. Effects of staphylococcal alpha-, beta-, delta-, and gamma-hemolysins on human diploid fibroblasts and HeLa cells: evaluation of a new quantitative as say for measuring cell damage. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):938–946. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.938-946.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





