Abstract
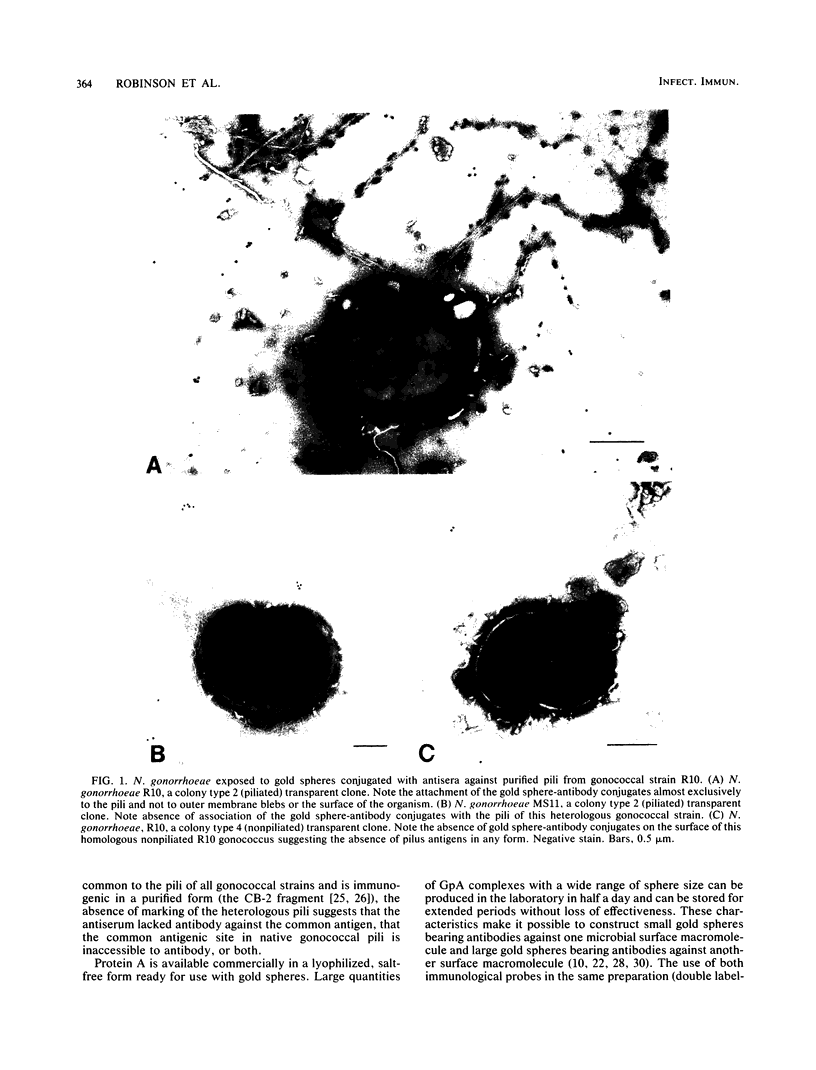
In an effort to determine the ultrastructural location of specific macromolecules on the surface of intact microorganisms and in experimentally infected tissues, a new method of rapidly conjugating antibodies to gold spheres via a staphylococcal protein A intermediary has been developed. This new technique provides the excellent density of marking and versatility of sphere size provided by existing gold methods, but decreases preparation time, decreases the chance of bacterial contamination of antibody reagents, and increases specificity of marking. Staphylococcal protein A-coated gold spheres were conjugated with antibodies from rabbits immunized with purified gonococcal pili. The resulting gold-antibody conjugates allowed demonstration of antibody binding to pilus structures of the same gonococcal strain whose pili were used to raise the antibody and demonstration of the lack of antibody recognition of pilus structures on two other gonococcal strains. The failure of gold spheres to attach to isogenic nonpiliated clones of the homologous gonococcus indicated the absence of pilus antigens on the surface of these organisms. The use of a double label--small gold spheres conjugated to anti-pilus antibody and larger gold spheres conjugated to anti-protein I antibody--allowed the simultaneous localization of two gonococcal antigens.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batten T. F., Hopkins C. R. Use of protein A-coated colloidal gold particles for immunoelectronmicroscopic localization of ACTH on ultrathin sections. Histochemistry. 1979 Apr 12;60(3):317–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00500659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beesley J. E., Orpin A., Adlam C. A comparison of immunoferritin, immuno-enzyme and gold-labelled protein A methods for the localization of capsular antigen on frozen thin sections of the bacterium, Pasteurella haemolytica. Histochem J. 1982 Sep;14(5):803–810. doi: 10.1007/BF01033629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendayan M. Use of the protein A-gold technique for the morphological study of vascular permeability. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Nov;28(11):1251–1254. doi: 10.1177/28.11.7430615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendayan M., Zollinger M. Ultrastructural localization of antigenic sites on osmium-fixed tissues applying the protein A-gold technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jan;31(1):101–109. doi: 10.1177/31.1.6187796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal membrane proteins: speculation on their role in pathogenesis. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:298–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ey P. L., Prowse S. J., Jenkin C. R. Isolation of pure IgG1, IgG2a and IgG2b immunoglobulins from mouse serum using protein A-sepharose. Immunochemistry. 1978 Jul;15(7):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90070-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Taylor G. M. An immunocolloid method for the electron microscope. Immunochemistry. 1971 Nov;8(11):1081–1083. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Slot J. W., van der Ley P. A., Scheffer R. C. Use of colloidal gold particles in double-labeling immunoelectron microscopy of ultrathin frozen tissue sections. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):653–665. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Hodges G. M., Livingston D. C. A review of the colloidal gold marker system. Scan Electron Microsc. 1980;(Pt 2):133–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. L., Hodges G. M., Trejdosiewicz L. K., Livingston D. C. Colloidal gold probes--a further evaluation. Scan Electron Microsc. 1979;(3):619–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M. Colloidal gold : a cytochemical marker for light and fluorescent microscopy and for transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Scan Electron Microsc. 1981;(Pt 2):9–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horisberger M., Rosset J. Colloidal gold, a useful marker for transmission and scanning electron microscopy. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Apr;25(4):295–305. doi: 10.1177/25.4.323352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. C., Lee J. C., Bucana C. Scanning immunoelectron microscopy for the identification and mapping of two or more antigens on cell surfaces. Scan Electron Microsc. 1979;(3):629–636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J. Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and related immunoglobulin receptors produced by streptococci and pneumonococci. Adv Immunol. 1982;32:157–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannweiler K., Hohenberg H., Bohn W., Rutter G. Protein-A gold particles as markers in replica immunocytochemistry: high resolution electron microscope investigations of plasma membrane surfaces. J Microsc. 1982 May;126(Pt 2):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1982.tb00363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee Z. A., Gross J., Dourmashkin R. R., Taylor-Robinson D. Nonpilar surface appendages of colony type 1 and colony type 4 gonococci. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):266–270. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.266-270.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Orci L. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Dec;26(12):1074–1081. doi: 10.1177/26.12.366014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. The preparation of protein A-gold complexes with 3 nm and 15nm gold particles and their use in labelling multiple antigens on ultra-thin sections. Histochem J. 1982 Sep;14(5):791–801. doi: 10.1007/BF01033628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Fernandez R., Tai J. Y., Rothbard J., Gotschlich E. C. Gonococcal pili. Primary structure and receptor binding domain. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1351–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoolnik G. K., Tai J. Y., Gotschlich E. C. A pilus peptide vaccine for the prevention of gonorrhea. Prog Allergy. 1983;33:314–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenep J. L., Munson R. S., Jr, Granoff D. M. Human antibody responses to lipopolysaccharide after meningitis due to Haemophilus influenzae type b. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):181–190. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. Sizing of protein A-colloidal gold probes for immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):533–536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam M. R., Buchanan T. M., Sandström E. G., Holmes K. K., Knapp J. S., Siadak A. W., Nowinski R. C. Serological classification of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):1042–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.1042-1053.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapia F. J., Varndell I. M., Probert L., De Mey J., Polak J. M. Double immunogold staining method for the simultaneous ultrastructural localization of regulatory peptides. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Jul;31(7):977–981. doi: 10.1177/31.7.6189888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]