Abstract
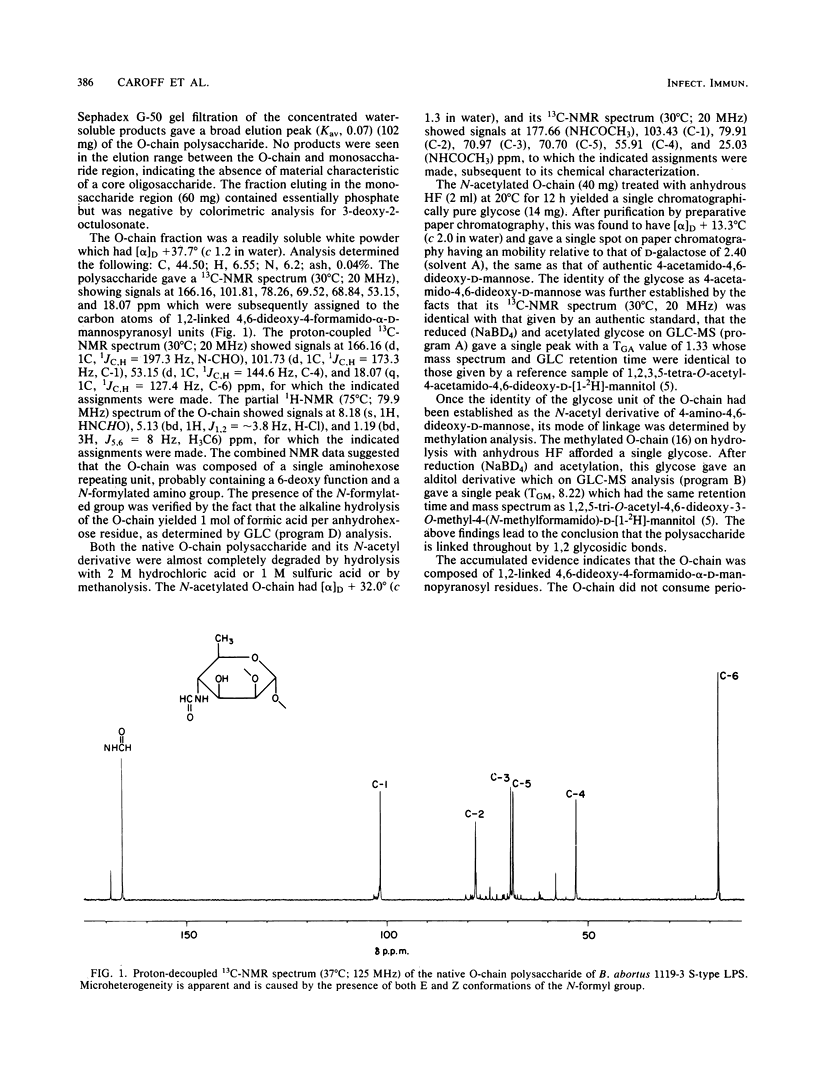
Antigenic phenol-phase soluble lipopolysaccharide isolated from Brucella abortus 1119-3 by hot phenol-water extraction was shown by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, controlled hydrolysis, periodate oxidation, methylation, and 1H and 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies to be an S-type lipopolysaccharide which could be cleaved to yield a lipid A and an O-chain polysaccharide identified as an unbranched linear homopolymer of 1,2-linked 4,6-dideoxy-4-formamido-alpha-D-mannopyranosyl residues. The serological reactivity of bovine antiserum to B. abortus 1119-3 with the lipopolysaccharides of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9 and Vibrio cholerae species has now been related to the occurrence of 1,2-linked N-acylated 4-amino-4,6-dideoxy-alpha-D-mannopyranosyl units in the O-chain polysaccharides of their lipopolysaccharides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMINOFF D. Methods for the quantitative estimation of N-acetylneuraminic acid and their application to hydrolysates of sialomucoids. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:384–392. doi: 10.1042/bj0810384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B. Structure of the O-chain of the phenol-phase soluble cellular lipopolysaccharide of Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O:9. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 15;139(1):195–200. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07994.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Leong D., Wilson J. B. Surface antigens of smooth brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):893–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.893-901.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Levieux D. Rôle respiectif en sérologie de la brucellose bovine des antigènes et des immunoglobulines G 1 et G 2 dans les tests d'agglutination, de Coombs et au Rose Bengale ainsi que dans le phénomène de zone. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1972 Mar 6;274(10):1593–1596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatt R., Berman E. R. A rapid procedure for the estimation of amino sugars on a micro scale. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):167–171. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAKOMORI S. A RAPID PERMETHYLATION OF GLYCOLIPID, AND POLYSACCHARIDE CATALYZED BY METHYLSULFINYL CARBANION IN DIMETHYL SULFOXIDE. J Biochem. 1964 Feb;55:205–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janda J., Work E. A colorimetric estimation of lipopolysaccharides. FEBS Lett. 1971 Sep 1;16(4):343–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(71)80386-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenne L., Lindberg B., Unger P., Holme T., Holmgren J. Structural studies of the Vibrio cholerae O-antigen. Carbohydr Res. 1979 Jan;68(1):C14–C16. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)84073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb V. L., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bovine immunoglobulin subclass-specific response to Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):240–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.240-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg A. A., Haeggman S., Karlson K., Carlsson H. E., Mair N. S. Enzyme immunoassay of the antibody response to Brucella and Yersinia enterocolitica 09 infections in humans. J Hyg (Lond) 1982 Apr;88(2):295–307. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400070157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee J. T. An enzyme-labelled immunosorbent assay for Brucella abortus antibodies. J Med Microbiol. 1980 Feb;13(1):167–172. doi: 10.1099/00222615-13-1-167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Berman D. T., Boettcher L. A. Biological activities of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):362–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.362-370.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Pitt M. W., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Purification and characterization of smooth and rough lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.361-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., Daoust V. Analysis of 2-amino-2,6-dideoxyhexoses by partition chromatography. Can J Biochem. 1973 Sep;51(9):1335–1339. doi: 10.1139/o73-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond J. W. The structure of the O-antigenic side chain of the lipopolysaccharide of Vibrio cholerae 569B (Inaba). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 May 1;584(2):346–352. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90280-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]