Abstract
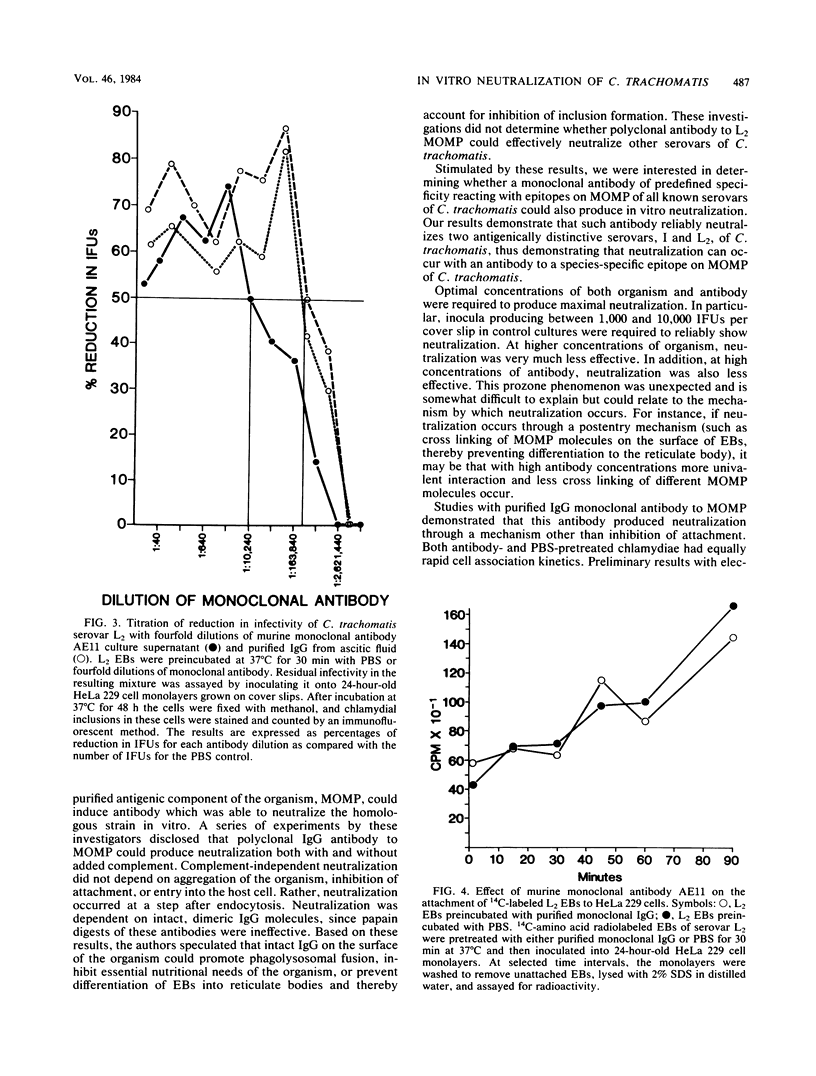
A murine monoclonal antibody, which binds to an epitope on the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis and with species specificity in the micro-immunofluorescent assay, effectively neutralized in vitro two antigenically distinct serovars of C. trachomatis. Optimal concentrations of both organism and antibody were required to produce maximal neutralization of the organism. Neutralization was less effective and more variable at lower dilutions of antibody than at higher dilutions, suggesting a prozone phenomenon. A radiolabeled attachment assay demonstrated that attachment of elementary bodies was unaffected by earlier treatment with antibody and that neutralization occurred at a step after attachment. The epitope to which this antibody is directed, on the major outer membrane protein of C. trachomatis, may have an important role in determining infectivity of the organism.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ainsworth S., Allan I., Pearce J. H. Differential neutralization of spontaneous and centrifuge-assisted chlamydial infectivity. J Gen Microbiol. 1979 Sep;114(1):61–67. doi: 10.1099/00221287-114-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLYTH W. A., REEVE P., GRAHAM D. M., TAVERNE J. The production of antisera that neutralize inclusion blennorrhoea virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Jun;43:340–343. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blyth W. A., Taverne J. Neutralization of TRIC organisms by antibody: enhancement by antisera prepared against immunoglobulins. J Hyg (Lond) 1974 Feb;72(1):129–134. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400023299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunham R. C., Kuo C. C., Cles L., Holmes K. K. Correlation of host immune response with quantitative recovery of Chlamydia trachomatis from the human endocervix. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1491–1494. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1491-1494.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kromhout J., Schachter J. Purification and partial characterization of the major outer membrane protein of Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1161–1176. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1161-1176.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Perry L. J. Neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis infectivity with antibodies to the major outer membrane protein. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):745–754. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.745-754.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURNESS G., GRAHAM D. M., REEVE P. The titration of trachoma and inclusion blennorrhoea viruses in cell cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Dec;23:613–619. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-3-613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V. Neutralization of Chlamydia trachomatis in cell culture. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):698–703. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.698-703.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L., Oertley R. E., Fraser E. C., MacDonald A. B., McComb D. E. Immunity to chlamydial infections of the eye. VI. Homologous neutralization of trachoma infectivity for the owl monkey conjuctivae by eye secretions from humans with trachoma. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):429–432. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REEVE P., GRAHAM D. M. A neutralization test for trachoma and inclusion blennorrhoea viruses grown in HeLa cell cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jan;27:177–180. doi: 10.1099/00221287-27-1-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. S., Tam M. R., Kuo C. C., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis: antibody specificities and antigen characterization. J Immunol. 1982 Mar;128(3):1083–1089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. P., Kuo C. C., Grayston J. T. Formalinized Chlamydia trachomatis organisms as antigen in the micro-immunofluorescence test. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):259–261. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.259-261.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Schachter J., Grubbs B., Sumaya C. V. The role of antibody in host defense against the agent of mouse pneumonitis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):200–205. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]