Abstract
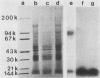
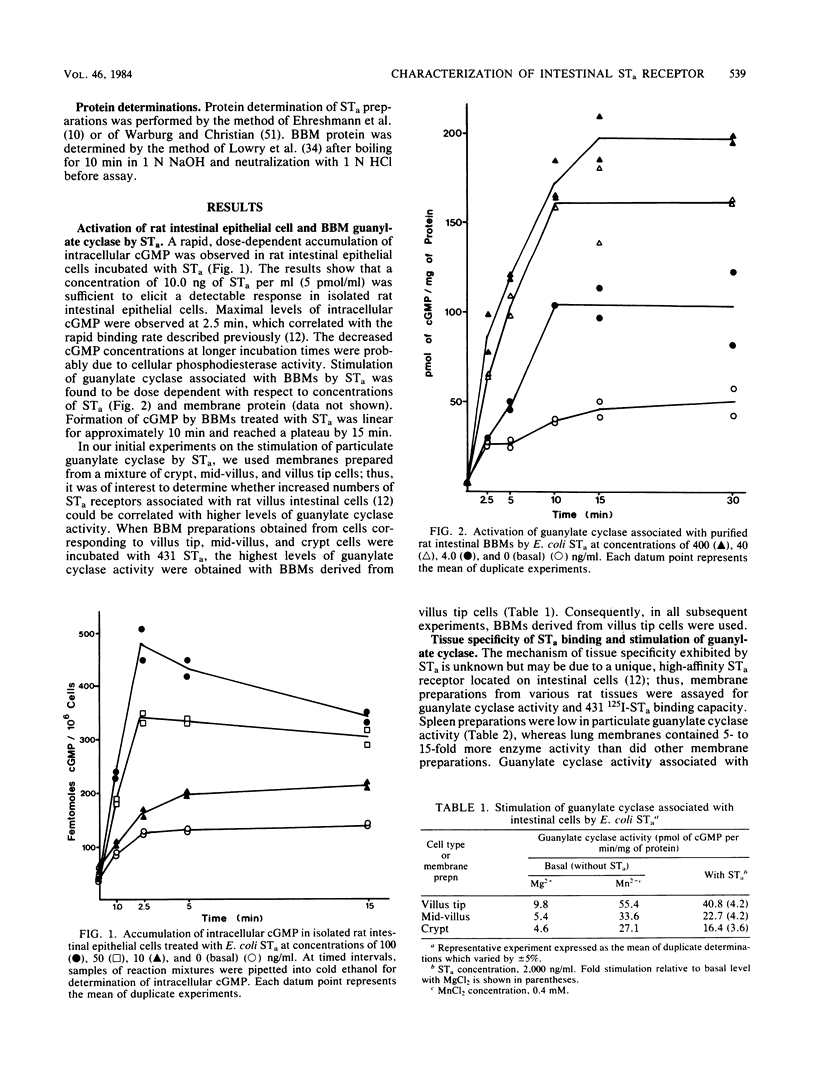
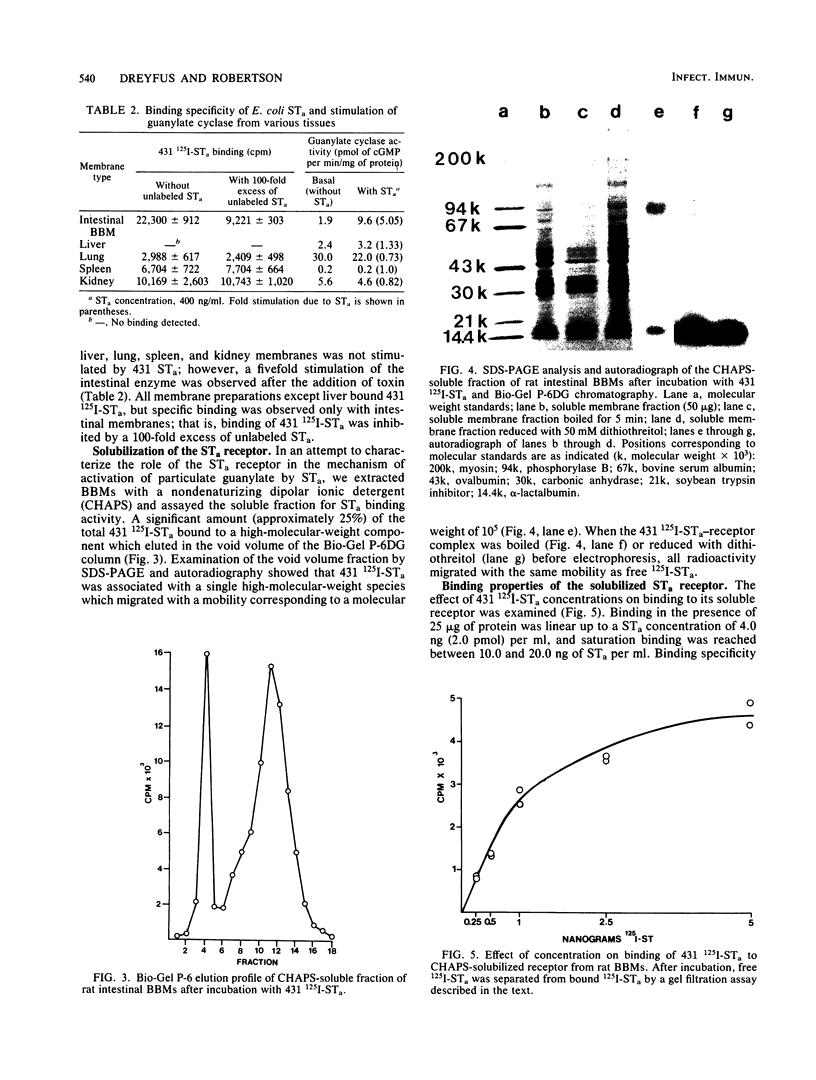
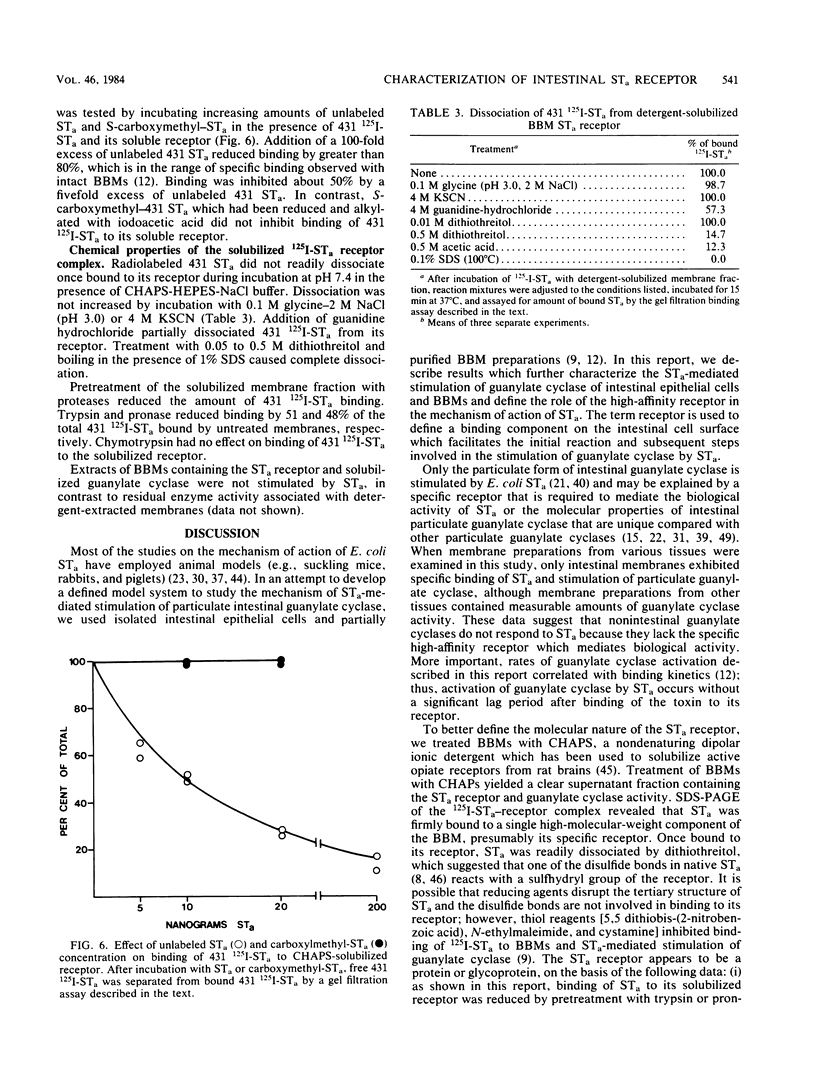
Binding of Escherichia coli strain 431 heat-stable enterotoxin (STa) and activation of intestinal particulate guanylate cyclase by E. coli STa were studied with rat intestinal epithelial cells and brush border membranes (BBMs). The rates of guanylate cyclase stimulation by 431 STa in cells and BBMs were rapid, with maximal levels of cyclic GMP observed within 5 min. Specific binding of 125I-labeled STa from E. coli 431 (431 125I-STa) and activation of guanylate cyclase by unlabeled 431 STa were observed with intestinal BBMs; however, neither was detected with membranes from nonintestinal tissues. The STa receptor was solubilized with 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate, a nondenaturing dipolar ionic detergent, in yields of approximately 50%. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of the detergent-solubilized receptor-431 125I-STa complex, followed by autoradiography, showed that 431 125I-STa bound to a single BBM component with a molecular weight of about 100,000. Binding of 431 STa to its solubilized receptor was saturable, specific, and essentially irreversible. Pretreatment of the soluble receptor with trypsin and pronase but not chymotrypsin decreased binding of 431 125I-STa. The 431 STa-receptor complex was dissociated by boiling in the presence of 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate, incubation with 0.5 M acetic acid, or reduction with dithiothreitol. In contrast to the residual particulate guanylate cyclase activity of detergent-treated membranes, solubilized guanylate cyclase was not stimulated by STa. Membrane structure appears to play an important role in the coordination of STa binding and stimulation of guanylate cyclase activity.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderete J. F., Robertson D. C. Purification and chemical characterization of the heat-stable enterotoxin produced by porcine strains of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):1021–1030. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.1021-1030.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooker G., Harper J. F., Terasaki W. L., Moylan R. D. Radioimmunoassay of cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESTFIELD A. M., MOORE S., STEIN W. H. The preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of reduced and S-carboxymethylated proteins. J Biol Chem. 1963 Feb;238:622–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Demonstration of shared and unique immunological determinants in enterotoxins from Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1978 Dec;22(3):709–713. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.3.709-713.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven P. A., DeRubertis F. R. Effects of thiol inhibitors on hepatic guanylate cylase activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 11;524(1):231–244. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90121-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonge H. R. The localization of guanylate cyclase in rat small intestinal epithelium. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 1;53(2):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Chemical properties of heat-stable enterotoxins produced by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli of different host origins. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):539–548. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.539-548.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus L. A., Jaso-Friedmann L., Robertson D. C. Characterization of the mechanism of action of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):493–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.493-501.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann B., Imbault P., Weil J. H. Spectrophotometric determination of protein concentration in cell extracts containing tRNA's and rRNA's. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):454–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field M., Graf L. H., Jr, Laird W. J., Smith P. L. Heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: in vitro effects on guanylate cyclase activity, cyclic GMP concentration, and ion transport in small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Jaso-Friedman L., Robertson D. C. Binding of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin to rat intestinal cells and brush border membranes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):622–630. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.622-630.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz J. C., Robertson D. C. Immunological properties of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxins: development of a radioimmunoassay specific for heat-stable enterotoxins with suckling mouse activity. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):193–198. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.193-198.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B. How many distinct enzymes are responsible for the several cellular processes involving thiol:protein-disulphide interchange? FEBS Lett. 1979 Jan 15;97(2):201–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbers D. L., Radany E. W. Characteristics of the soluble and particulate forms of guanylate cyclase. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1981;14:241–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert H. F. Biological disulfides: the third messenger? Modulation of phosphofructokinase activity by thiol/disulfide exchange. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12086–12091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Clements J. D., Robertson D. C., Finkelstein R. A. Subunit number and arrangement in Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):677–682. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.677-682.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Richardson S. H. Adenosine diphosphate-ribosylation of adenylate cyclase catalyzed by heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: comparison with cholera toxin. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jan;141(1):64–70. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilligan P. H., Brown J. C., Robertson D. C. Immunological relationships between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):683–691. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.683-691.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg R. N., Dunn J. A., Guerrant R. L. Reduction of the secretory response to Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin by thiol and disulfide compounds. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):174–180. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.174-180.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant R. L., Hughes J. M., Chang B., Robertson D. C., Murad F. Activation of intestinal guanylate cyclase by heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli: studies of tissue specificity, potential receptors, and intermediates. J Infect Dis. 1980 Aug;142(2):220–228. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haguenauer-Tsapis R., Ben Salah A., Lacombe M. L., Hanoune J. Trypsin solubilization of rat liver membrane-bound guanylate cyclase results in a form kinetically distinct from the cytosolic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1651–1655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton D. L., Roe W. E., Nielsen N. O. Effect of heat stable and heat labile Escherichia coli enterotoxins, cholera toxin and theophylline on unidirectional sodium and chloride fluxes in the proximal and distal jejunum of weanling swine. Can J Comp Med. 1977 Jul;41(3):306–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Howell K., Dawson R. M., Bowyer D. E. Rabbit small intestinal brush border membrane preparation and lipid composition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 18;602(3):567–577. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. M., Murad F., Chang B., Guerrant R. L. Role of cyclic GMP in the action of heat-stable enterotoxin of Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Feb 23;271(5647):755–756. doi: 10.1038/271755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Kadowitz P. J., Baricos W. H. Evidence that regulation of hepatic guanylate cyclase activity involves interactions between catalytic site -SH groups and both substrate and activator. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 15;208(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura H., Murad F. Evidence for two different forms of guanylate cyclase in rat heart. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6910–6916. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Lee C. S., Engert R. F. Assay of Escherichia coli enterotoxins by in vivo perfusion in the rat jejunum. Infect Immun. 1976 Oct;14(4):1004–1010. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.4.1004-1010.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacombe M. L., Haguenauer-Tsapis R., Stengel D., Ben Salah A., Hanoune J. Solubilization by proteolysis of an activated form of rat liver membrane guanylate cyclase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 11;116(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80533-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehotay D. C., Levey G. S., Rogerson B., Ruiz E., Yourist J. E., Miller K. D. Activation of guanylate cyclase by alpha-toxins from krait and cobra venom. Toxicon. 1980;18(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Osborne J. C., Jr, Fishman P. H., Nakaya S., Robertson D. C. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Ganglioside specificity and ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12861–12865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee S. P., Mukherjee C. Role of sulfhydryl oxidation in adipocyte plasma membrane surface in the response of adenylate cyclase to isoproterenol and glucagon. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 5;677(3-4):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsome P. M., Burgess M. N., Mullan N. A. Effect of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin on cyclic GMP levels in mouse intestine. Infect Immun. 1978 Oct;22(1):290–291. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.1.290-291.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettit F. H., Humphreys J., Reed L. J. Regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase activity by protein thiol-disulfide exchange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3945–3948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radany E. W., Gerzer R., Garbers D. L. Purification and characterization of particulate guanylate cyclase from sea urchin spermatozoa. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8346–8351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao M. C., Guandalini S., Smith P. L., Field M. Mode of action of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin. Tissue and subcellular specificities and role of cyclic GMP. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 17;632(1):35–46. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90247-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saviolakis G. A., Harrison L. C., Roth J. The binding of 125I-insulin to specific receptors in IM-9 human lymphocytes. Detection of radioactivity covalently linked to receptors. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4924–4928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonds W. F., Koski G., Streaty R. A., Hjelmeland L. M., Klee W. A. Solubilization of active opiate receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4623–4627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staples S. J., Asher S. E., Giannella R. A. Purification and characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by a strain of E. coli pathogenic for man. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4716–4721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner A. L., Parker C. W., Kipnis D. M. Radioimmunoassay for cyclic nucleotides. I. Preparation of antibodies and iodinated cyclic nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1106–1113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschesche H., Macartney H. W. A new principle of regulation of enzymic activity. Activation and regulation of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte collagenase via disulfide-thiol exchange as catalysed by the glutathione cycle in a peroxidase-coupled reaction to glucose metabolism. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldman S. A., Lewicki J. A., Brandwein H. J., Murad F. Partial purification and characterization of particulate guanylate cyclase from rat liver after solubilization with trypsin. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1982;8(6):359–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling M. W., Mircheff A. K., Van Os C. H., Wright E. M. Subcellular distribution of nucleotide cyclases in rat intestinal epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1978 Nov;235(5):E539–E545. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.5.E539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonge H. R. Properties of guanylate cyclase and levels of cyclic GMP in rat small intestinal villous and crypt cells. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80980-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]