Abstract
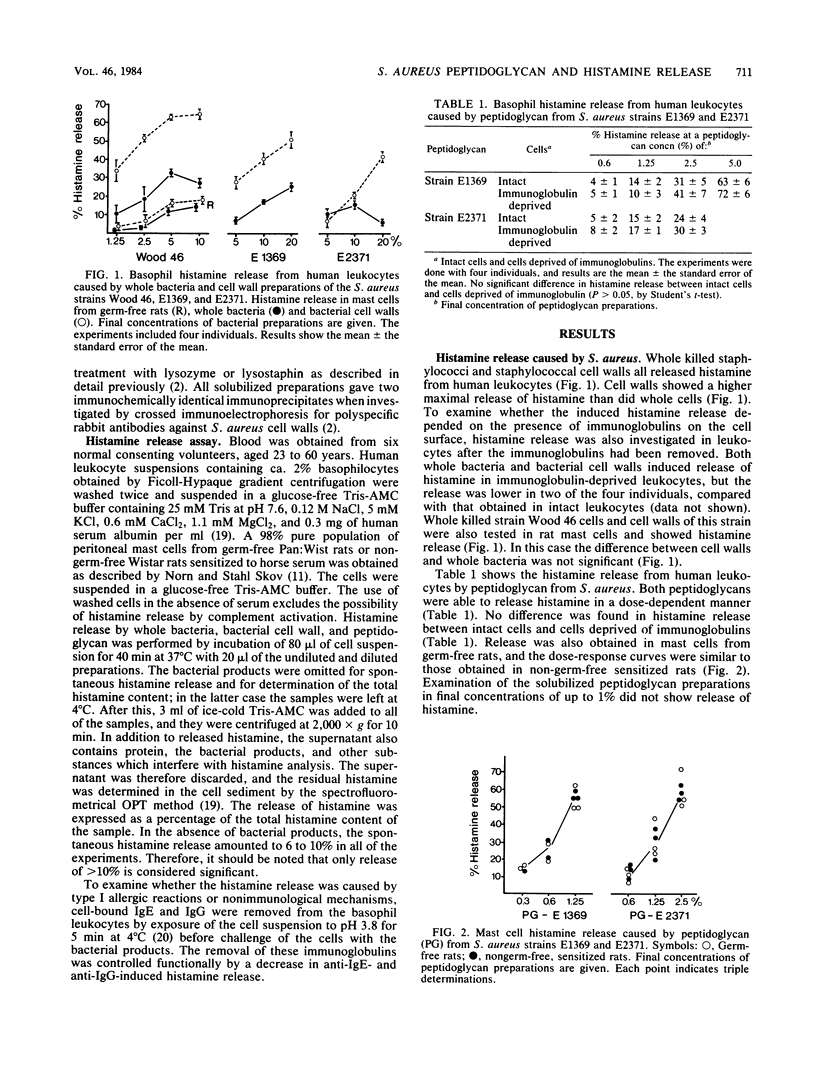
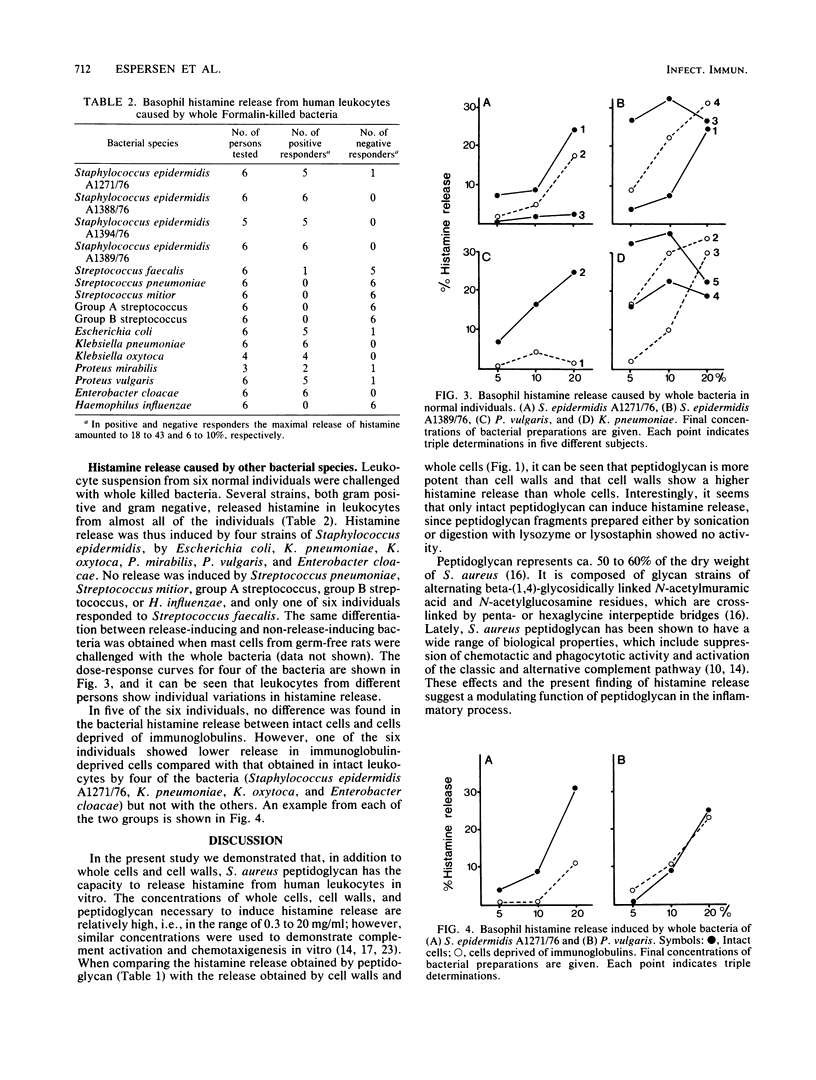
Whole killed cells, cell walls, and peptidoglycans of Staphylococcus aureus were found to release histamine from human leukocytes and isolated rat mast cells in vitro. The histamine-releasing capability increased in the order of whole bacteria, cell walls, and peptidoglycans. Peptidoglycan was found to release histamine by a nonimmunological mechanism, as demonstrated by release in cells deprived of surface immunoglobulins, whereas whole bacteria and cell walls seemed to operate both by immunological and nonimmunological mechanisms. Histamine release was not a specific property of S. aureus; a wide range of whole bacterial species had this activity. We suggest that peptidoglycan may be a common factor responsible for histamine release by different bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensson B., Espersen F., Hedström S. A., Kronvall G. Methodological aspects of Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan serology: comparisons between solid-phase radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 May;19(5):680–686. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.5.680-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensson B., Espersen F., Hedström S. A., Kronvall G. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of immunoglobulin G antibodies to Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan in patients with staphylococcal infections. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Dec;91(6):401–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I. Isolation of a fibronectin-binding protein from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):526–531. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.526-531.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Hertz J. B., Høiby N. Cross-reactions between Staphylococcus epidermidis and 23 other bacterial species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Aug;89(4):253–260. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00185_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henrichsen J., Blom J. Examination of fimbriation of some gram-negative rods with and without twitching and gliding motility. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1975 Jun;83(3):161–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen C., Norn S., Stahl Skov P., Espersen F., Koch C., Permin H. Bacterial histamine release by immunological and non-immunological lectin-mediated reactions. Allergy. 1984 Jul;39(5):371–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1984.tb01955.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen C., Stahl Skov P., Norn S., Espersen F., Bøg-Hansen T. C., Lihme A. Complexity of lectin-mediated reactions in bacteria-induced histamine release. Allergy. 1984 Aug;39(6):451–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1984.tb01967.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Andersen P., Boëtius Hertz J., Høiby N., Kappelgaard E., Møller N. E., Norn S., Pedersen M., Petersen P. S., Stahl Skov P. Studies on hypersensitivity to bacterial antigens in intrinsic asthma. Allergy. 1982 Apr;37(3):191–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1982.tb01896.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. R., White A. The in vitro release of leukocyte histamine by staphylococcal antigens. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):437–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Verbrugh H. A., Verhoef J. Suppression of phagocytosis and chemotaxis by cell wall components of Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):84–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norn S., Skov P. S. Anaphylactic hyposensitization of rat mast cells in vitro by antigen. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Nov;18(3):431–437. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norn S., Skov P. S., Jensen C., Koch C., Permin H., Bøg-Hansen T. C., Løwenstein H., Høiby N. Intrinsic asthma and bacterial histamine release via lectin effect. Agents Actions. 1983 Apr;13(2-3):210–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01967333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norn S., Stahl Skov P., Kock C., Andersen P., Pedersen M., Tønnesen P., Pedersen P. S., Møller N. E., Hertz J., Høiby N. Intrinsic asthma and bacterial histamine release. Agents Actions. 1982 Apr;12(1-2):101–102. doi: 10.1007/BF01965116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Douglas S. D., Quie P. G., Verhoef J. The key role of peptidoglycan in the opsonization of Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Invest. 1978 Mar;61(3):597–609. doi: 10.1172/JCI108971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiøtz P. O., Høiby N., Hertz J. B. Cross-reactions between Staphylococcus aureus and fifteen other bacterial species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1979 Dec;87(6):329–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1979.tb02447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer K. H., Kandler O. Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):407–477. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.407-477.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeling D. J., Peterson P. K., Hammerschmidt D. E., Kim Y., Verhoef J., Wilkinson B. J., Quie P. G. Chemotaxigenesis by cell surface components of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):57–63. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.57-63.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skov P. S., Norn S. A simplified method for measuring basophil histamine release and blocking antibodies in hay fever patients. Basophil histamine content and cell preservation. Acta Allergol. 1977 Jun;32(3):170–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1977.tb01347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skov P. S., Permin H., Malling H. J. Quantitative and qualitative estimations of IgE bound to basophil leukocytes from hay fever patients. Scand J Immunol. 1977;6(10):1021–1028. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1977.tb00338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbrugh H. A., Peters R., Rozenberg-Arska M., Peterson P. K., Verhoef J. Antibodies to cell wall peptidoglycan of Staphylococcus aureus in patients with serious staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1981 Jul;144(1):1–9. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat L. J., Wilkinson B. J., Kohler R. B., White A. C. Antibody response to peptidoglycan during staphylococcal infections. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):16–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Peterson P. K. Factors affecting complement activation by Staphylococcus aureus cell walls, their components, and mutants altered in teichoic acid. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):216–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.216-224.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



