Abstract
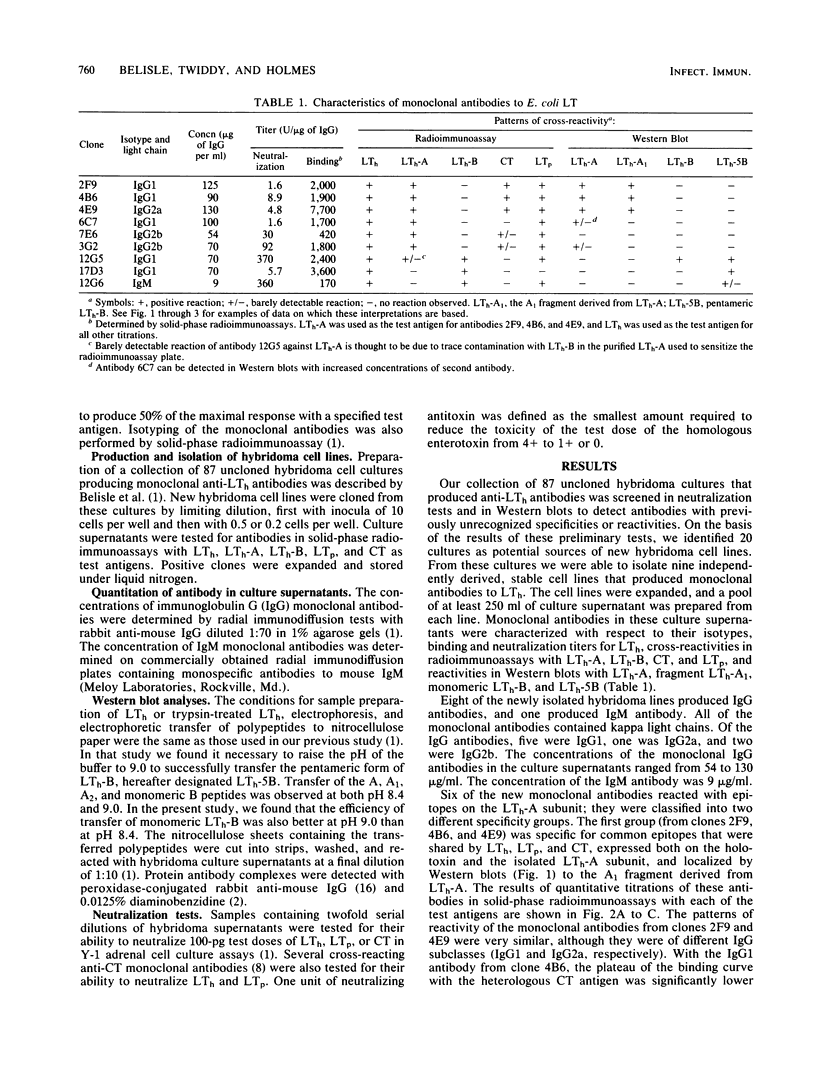
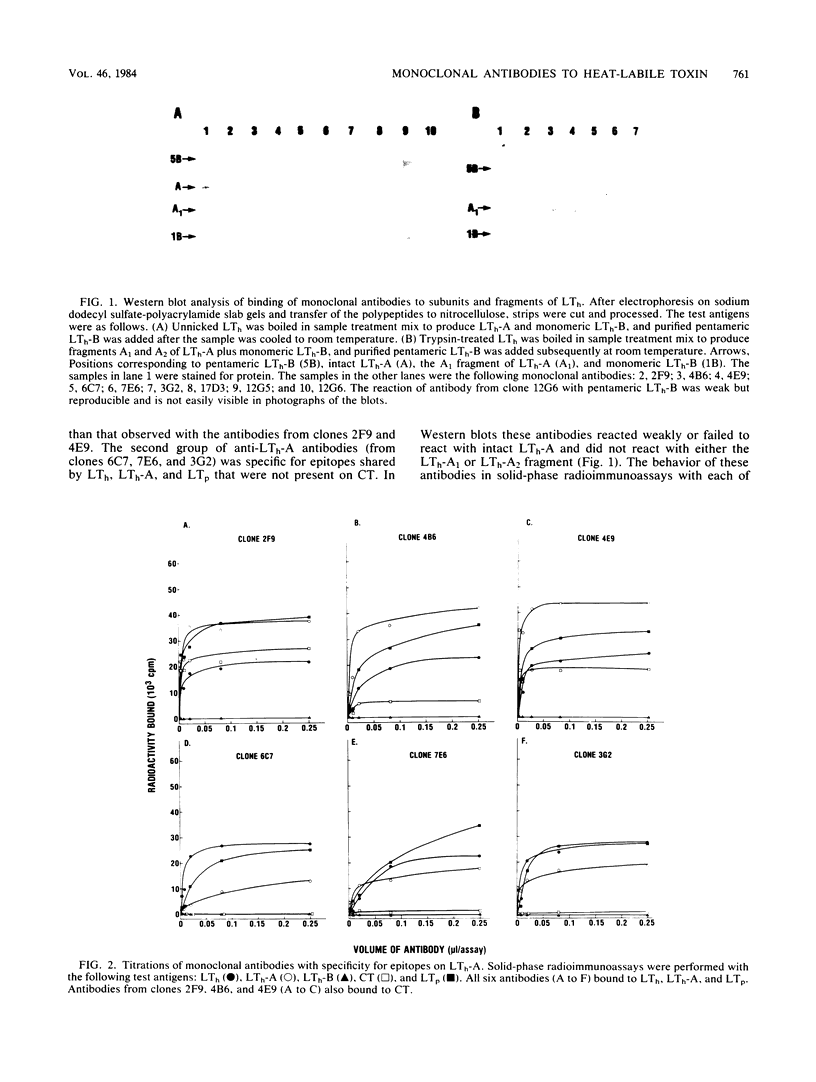
Nine selected hybridoma cell lines that produced monoclonal antibodies against the heat-labile enterotoxin encoded by a plasmid from an Escherichia coli strain of human origin (LTh) were characterized. Hybridomas that produced anti-LTh antibodies with previously unrecognized specificities or reactivities were selected for cloning. Each monoclonal antibody was tested for isotype and for binding to LTh holotoxin, the A and B subunits derived from LTh (LTh-A and LTh-B), holotoxin encoded by a plasmid from an E. coli strain of porcine origin (LTp), and cholera enterotoxin (CT). Binding was also tested in Western blots with the following antigens: pentameric LTh-B, monomeric LTh-B, LTh-A, and the A1 and A2 fragments produced from LTh-A by treatment with trypsin. These monoclonal anti-LTh antibodies and selected anti-LTh and anti-CT monoclonal antibodies described previously were tested for neutralization of LTh, LTp, and CT. Five of the nine new monoclonal antibodies gave detectable cross-reactions with LTp and CT. Four reacted with determinants of LTh that were not present on CT; one of these four did not react with LTp and was specific for a unique epitope of LTh. Three antibodies were specific for LTh-B. All three reacted with pentameric LTh-B, but only one reacted in Western blots with monomeric LTh-B. Six antibodies were specific for LTh-A. Three reacted in Western blots with LTh-A and its A1 fragment; the other three did not react in Western blots. All nine of the new monoclonal antibodies neutralized LTh but not CT; the eight that cross-reacted with LTp in binding assays also neutralized LTp. Of four neutralizing anti-CT monoclonal antibodies that bound to LTh, none had significant neutralizing activity against LTh.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belisle B. W., Twiddy E. M., Holmes R. K. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to heat-labile enterotoxin encoded by a plasmid from a clinical isolate of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):1027–1032. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.1027-1032.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohn W. A fixation method for improved antibody penetration in electron microscopical immunoperoxidase studies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Apr;26(4):293–297. doi: 10.1177/26.4.77869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Finkelstein R. A. Isolation and characterization of homogeneous heat-labile enterotoxins with high specific activity from Escherichia coli cultures. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):760–769. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.760-769.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. D., Flint D. C., Klipstein F. A. Immunological and physicochemical characterization of heat-labile enterotoxins isolated from two strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):806–809. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.806-809.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geary S. J., Marchlewicz B. A., Finkelstein R. A. Comparison of heat-labile enterotoxins from porcine and human strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1982 Apr;36(1):215–220. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.1.215-220.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyles C. L. Relationships among heat-labile enterotoxins of Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae. J Infect Dis. 1974 Mar;129(3):277–283. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.3.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Twiddy E. M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies that react with unique and cross-reacting determinants of cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.914-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Tsuji T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Immunological nonidentity of heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Nov;34(2):337–340. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.2.337-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm L., Holmgren J., Wikström M., Karlsson U., Andersson K., Lycke N. Monoclonal antibodies to cholera toxin with special reference to cross-reactions with Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 May;40(2):570–576. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.2.570-576.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb M., Nichols J. C., Whoriskey S. K., Murphy J. R. Isolation of hybridoma cell lines and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):267–272. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.267-272.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Honda T., Sima H., Tsuji T., Miwatani T. Analysis of antigenic determinants in cholera enterotoxin and heat-labile enterotoxins from human and porcine enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):50–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.50-53.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



