Abstract
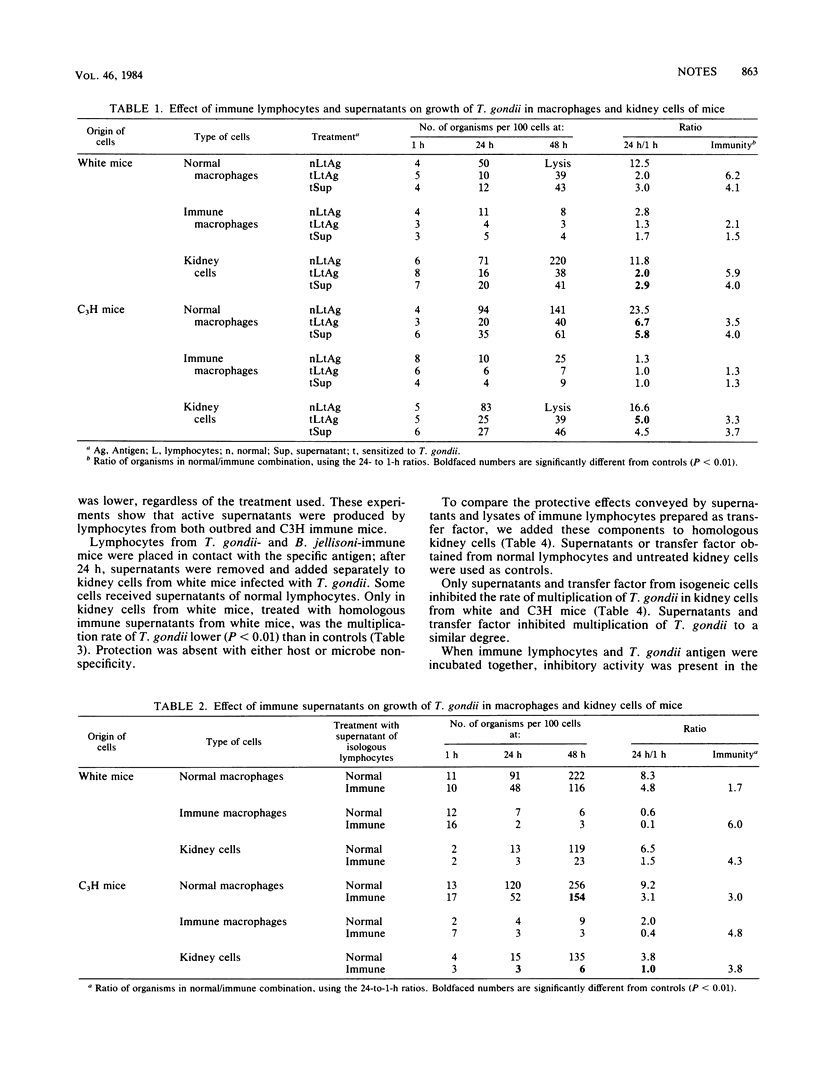
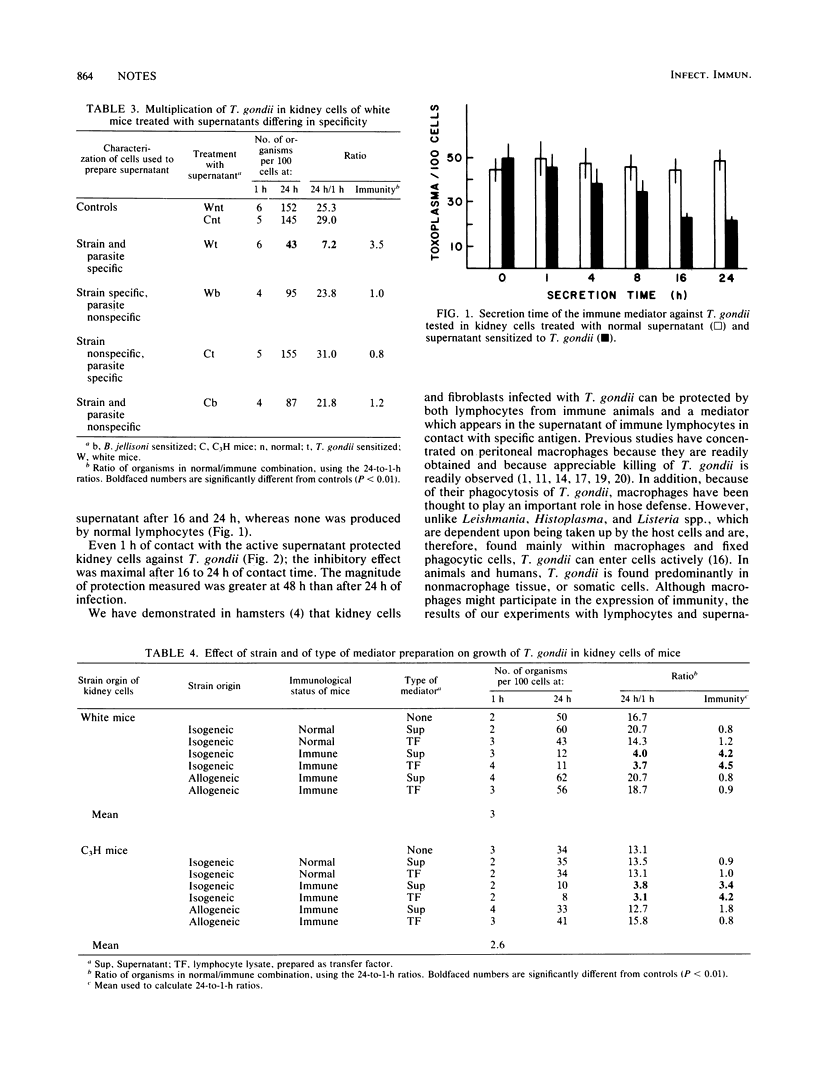
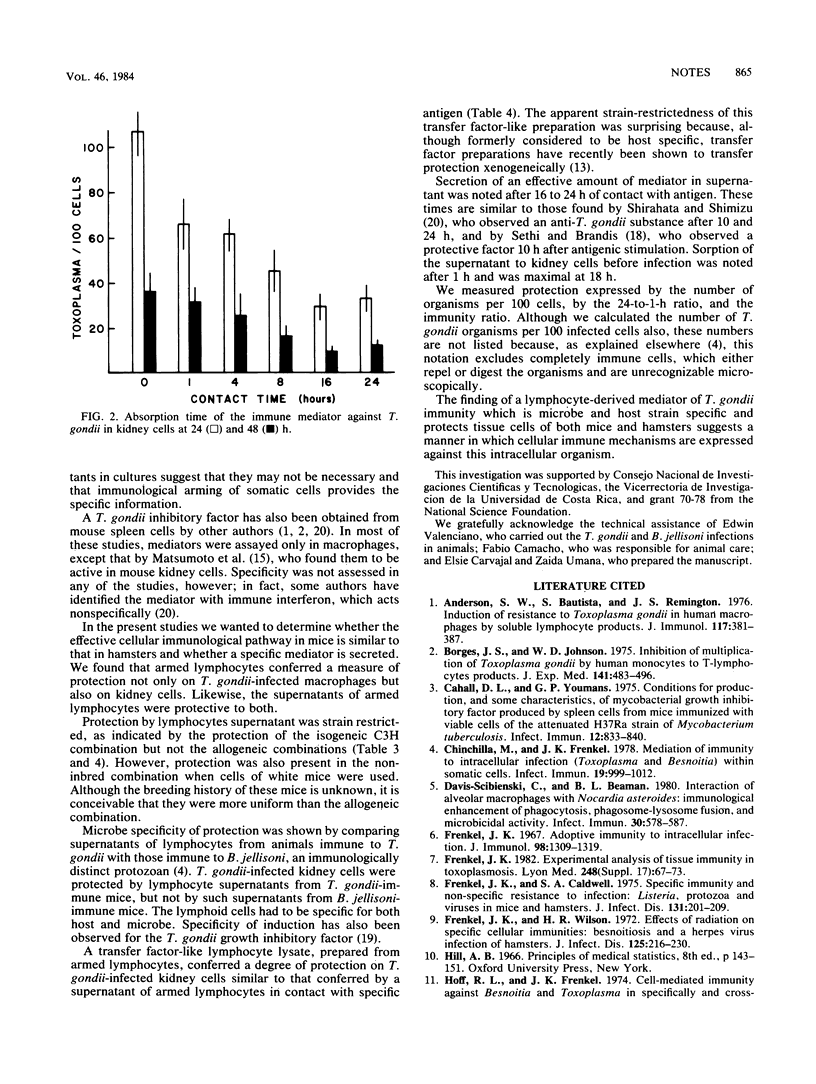
Lymphocytes from mice immunized against Toxoplasma gondii protected T. gondii-infected macrophage and kidney cell cultures. After contact with antigens, supernatants of such immune lymphocytes, also contained a factor protective for T. gondii-infected macrophages and kidney cells. Supernatants were protective only when the lymphocytes and kidneys cells were isogeneic. Protection was specific in that supernatants from only T. gondii-immune, but not Besnoitia jellisoni-immune, lymphocytes provided protection against toxoplasmosis. Sixteen to 24 h were required for an appreciable amount of protective factor to be secreted; a similar absorption time was necessary for kidney cells to be protected. Peritoneal lymphocyte lysates, prepared as transfer factor, contained protective substances with a potency similar to that of lymphocyte supernatants, which were also strain restricted in their effect.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. E., Bautista S., Remington J. S. Induction of resistance to Toxoplasma gondii in human macrophages by soluble lymphocyte products. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges J. S., Johnson W. D., Jr Inhibition of multiplication of Toxoplasma gondii by human monocytes exposed to T-lymphocyte products. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):483–496. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahall D. L., Youmans G. P. Conditions for production, and some characteristics, of mycobacterial growth inhibitory factor produced by spleen cells from mice immunized with viable cells of the attenuated H37Ra strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):833–840. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.833-840.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinchilla M., Frenkel J. K. Mediation of immunity to intracellular infection (Toxoplasma and Besnoitia) within somatic cells. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):999–1012. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.999-1012.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis-Scibienski C., Beaman B. L. Interaction of alveolar macrophages with Nocardia asteroides: immunological enhancement of phagocytosis, phagosome-lysosome fusion, and microbicidal activity. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):578–587. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.578-587.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K. Adoptive immunity to intracellular infection. J Immunol. 1967 Jun;98(6):1309–1319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Caldwell S. A. Specific immunity and nonspecific resistance to infection: listeria, protozoa, and viruses in mice and hamsters,. J Infect Dis. 1975 Mar;131(3):201–209. doi: 10.1093/infdis/131.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel J. K., Wilson H. R. Effects of radiation on specific cellular immunities: besnoitiosis and a herpesvirus infection of hamsters. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):216–230. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff R. L., Frenkel J. K. Cell-mediated immunity against Besnoitia and toxoplasma in specifically and cross-immunized hamsters and in cultures. J Exp Med. 1974 Mar 1;139(3):560–580. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.3.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Masur H., Len L., Fu T. L. Lymphocyte-macrophage interaction during control of intracellular parasitism. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Nov;26(6 Pt 2):187–193. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klesius P. H., Qualls D. F., Elston A. L., Fudenberg H. H. Effects of bovine transfer factor (TFd) in mouse coccidiosis (Eimeria ferrisi). Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1978 Jun;10(2):214–221. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(78)90029-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindberg R. E., Frenkel J. K. Cellular immunity to toxoplasma and besnoitia in hamsters: specificity and the effects of cortisol. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):855–862. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.855-862.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Nagasawa H., Sakurai H., Sasaki S., Suzuki N. Mouse spleen cell-derived toxoplasma growth inhibitory factor: its effect on toxoplasma multiplication in the mouse kidney cells. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1981 Sep;250(3):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. A., O'Connor G. R. Penetration of mouse peritoneal macrophages by the protozoon Toxoplasma gondii. New evidence for active invasion and phagocytosis. Lab Invest. 1981 Apr;44(4):324–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang T., Blanden R. V. The cell-mediated immune response to ectromelia virus infection. Secondary response in vitro: specificity, nature of effector and responder cells and requirements for induction of antigenic changes in stimulator cells. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1976 Jun;54(3):253–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethi K. K., Brandis H. Characteristics of soluble T-cell derived factors(s) which can induce non-immune murine macrophages to exert anti-Toxoplasma activity. Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1978 Jun;154(3):226–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K. Production and properties of immune interferon from spleen cell cultures of Toxoplasma-infected mice. Microbiol Immunol. 1980;24(11):1109–1120. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1980.tb02915.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K. Some physicochemical characteristics of an immune lymphocyte product which inhibits the multiplication of toxoplasma within mouse macrophages. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23(1):17–30. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1979.tb00436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirahata T., Shimizu K., Suzuki N. Effects of immune lymphocyte products and serum antibody on the multiplication of Toxoplasma in murine peritoneal macrophages. Z Parasitenkd. 1976 Mar 31;49(1):11–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00445014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch T. M., Triglia R., Spitler L. E., Fudenberg H. H. Preliminary studies on human "transfer factor" activity in guinea pigs. Systemic transfer of cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity to PPD and SKSD. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1976 May;5(3):407–415. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(76)90050-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


