Abstract
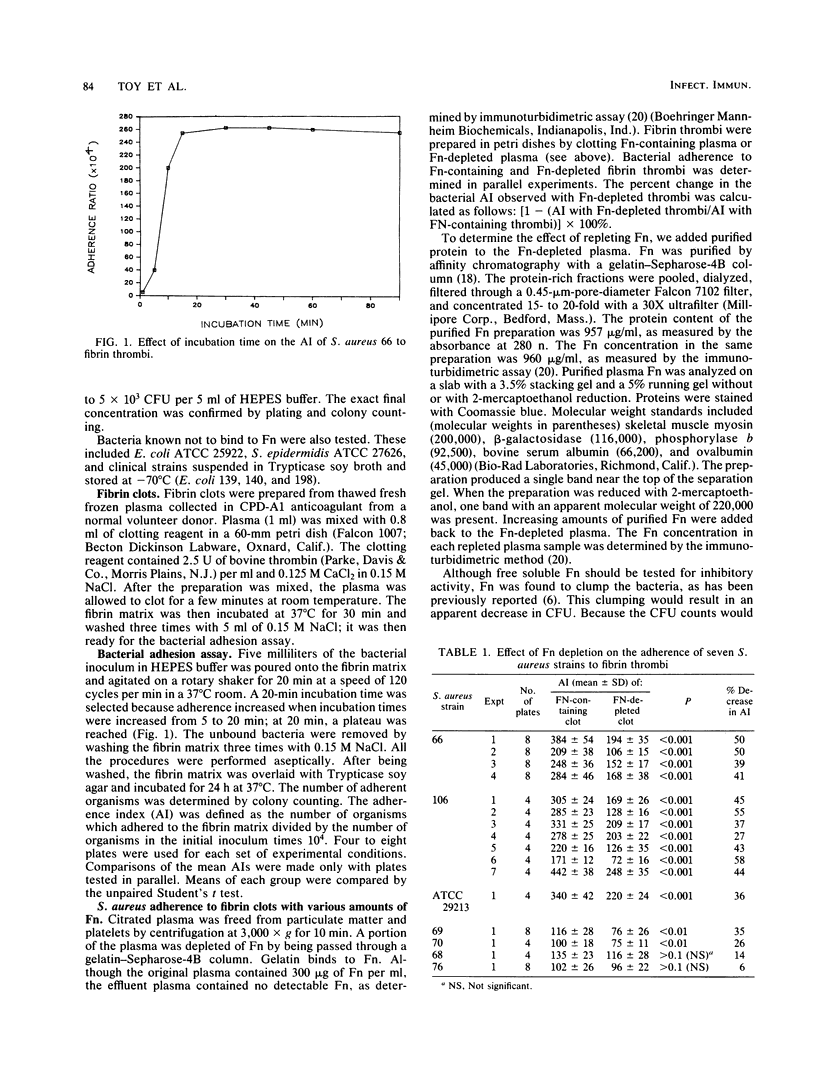
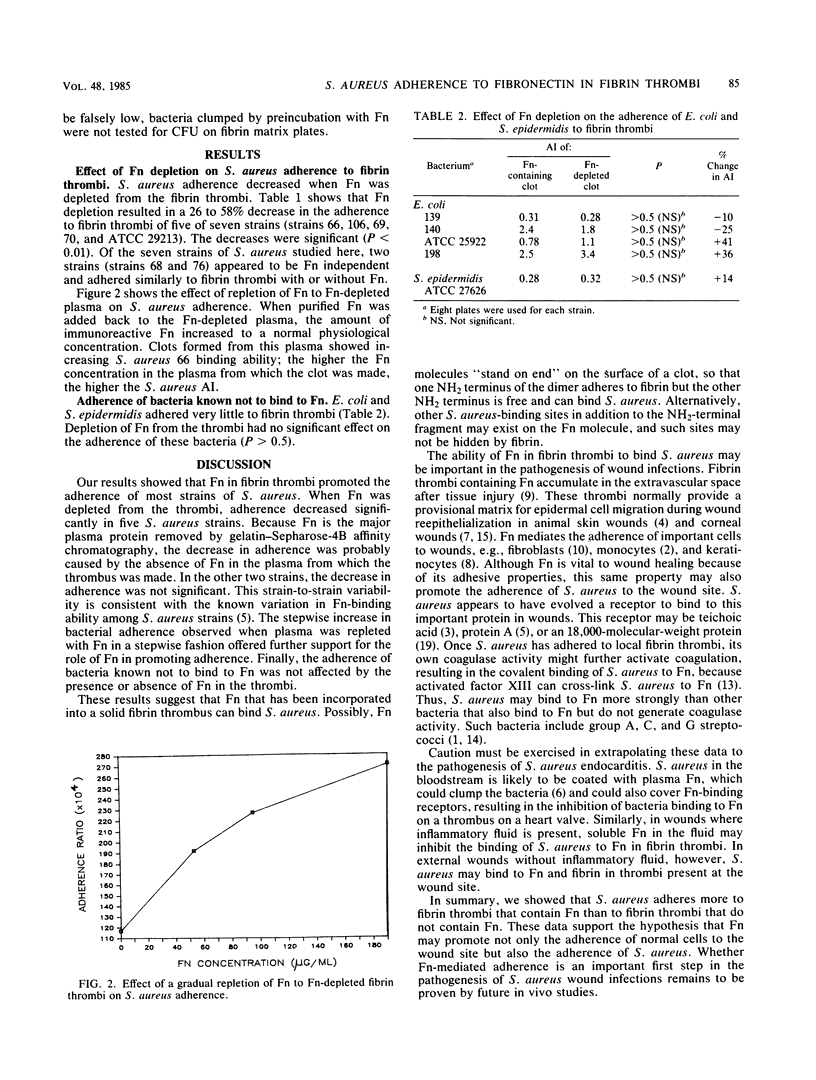
Staphylococcus aureus binds to purified fibronectin in solution and may bind to fibronectin present in wound tissue. When incorporated into a solid fibrin thrombus, however, plasma fibronectin may fail to bind S. aureus, because the S. aureus-binding sites on fibronectin may be occupied by fibrin. Both S. aureus and fibrin bind to the same 27-kilodalton amino-terminal fragment of fibronectin. To determine whether fibronectin incorporated into fibrin still promotes the adherence of S. aureus, we clotted citrated normal plasma and fibronectin-depleted plasma onto petri dishes. We then measured bacterial adherence to these in vitro fibrin thrombi. We found that the adherence of five of seven S. aureus strains decreased significantly (by 26 to 58%) when fibronectin had been depleted from the fibrin thrombi. Adding fibronectin back reversed this decrease in adherence. The reversal was dose dependent; the increase was in proportion to the amount of fibronectin added back to the plasma. Bacteria known not to bind to fibronectin (Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus epidermidis) adhered 100-fold less than S. aureus, and their adherence was unaffected by the absence of fibronectin in the fibrin thrombus. We conclude that fibronectin incorporated into solid fibrin thrombi does mediate the adherence of most S. aureus strains to fibrin thrombi. Fibronectin may be an important molecule that mediates the adherence of S. aureus to fibrin in wounds.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beachey E. H., Simpson W. A. The adherence of group A streptococci to oropharyngeal cells: the lipoteichoic acid adhesin and fibronectin receptor. Infection. 1982;10(2):107–111. doi: 10.1007/BF01816738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Amrani D., Mosesson M. W., Bianco C. Receptors for cold-insoluble globulin (plasma fibronectin) on human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1981 Jan 1;153(1):42–60. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.1.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibel D. J., Aly R., Shinefield H. R., Maibach H. I. The Staphylococcus aureus receptor for fibronectin. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jun;80(6):494–496. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12535001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Lanigan J. M., DellaPelle P., Manseau E., Dvorak H. F., Colvin R. B. Fibronectin and fibrin provide a provisional matrix for epidermal cell migration during wound reepithelialization. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Nov;79(5):264–269. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12500075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran J. E., Raynor R. H. Fibronectin binding to protein A-containing staphylococci. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):683–689. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.683-689.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espersen F., Clemmensen I. Clumping of Staphylococcus aureus by human fibronectin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1981 Oct;89(5):317–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1981.tb00195_89b.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa L. S., Foster C. S., Harrist T. J., Lanigan J. M., Colvin R. B. Fibronectin in healing rabbit corneal wounds. Lab Invest. 1981 Aug;45(2):120–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilchrest B. A., Nemore R. E., Maciag T. Growth of human keratinocytes on fibronectin -coated plates. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1980 Nov;4(11):1009–1016. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(80)90173-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Billingham R. E., Burgess L. Distribution of fibronectin during wound healing in vivo. J Invest Dermatol. 1981 Mar;76(3):181–189. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12525694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinnell F., Feld M., Minter D. Fibroblast adhesion to fibrinogen and fibrin substrata: requirement for cold-insoluble globulin (plasma fibronectin). Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90526-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawiger J., Hammond D. K., Timmons S., Budzynski A. Z. Interaction of human fibrinogen with staphylococci: presence of a binding region on normal and abnormal fibrinogen variants and fibrinogen derivatives. Blood. 1978 May;51(5):799–812. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P. Fibronectin binds to Staphylococcus aureus. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):718–720. doi: 10.1038/276718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F., Proctor R. A. Binding and factor XIIIa-mediated cross-linking of a 27-kilodalton fragment of fibronectin to Staphylococcus aureus. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):927–929. doi: 10.1126/science.7403857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B., Kuusela P. Binding of human fibronectin to group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):29–34. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.29-34.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishida T., Nakagawa S., Nishibayashi C., Tanaka H., Manabe R. Fibronectin enhancement of corneal epithelial wound healing of rabbits in vivo. Arch Ophthalmol. 1984 Mar;102(3):455–456. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1984.01040030369040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J., Kim Y., Schmeling D., Quie P. G. Influence of encapsulation on staphylococcal opsonization and phagocytosis by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):943–949. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.943-949.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M., Engvall E. Fibronectin: purification, immunochemical properties, and biological activities. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):803–831. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén C., Rubin K., Speziale P., Hök M., Lindberg M., Wadström T. Fibronectin receptors from Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3396–3401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba T. M., Albert W. H., Blumenstock F. A., Evanega G., Staehler F., Cho E. Evaluation of a rapid immunoturbidimetric assay for opsonic fibronectin in surgical and trauma patients. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 Oct;98(4):482–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


