Abstract
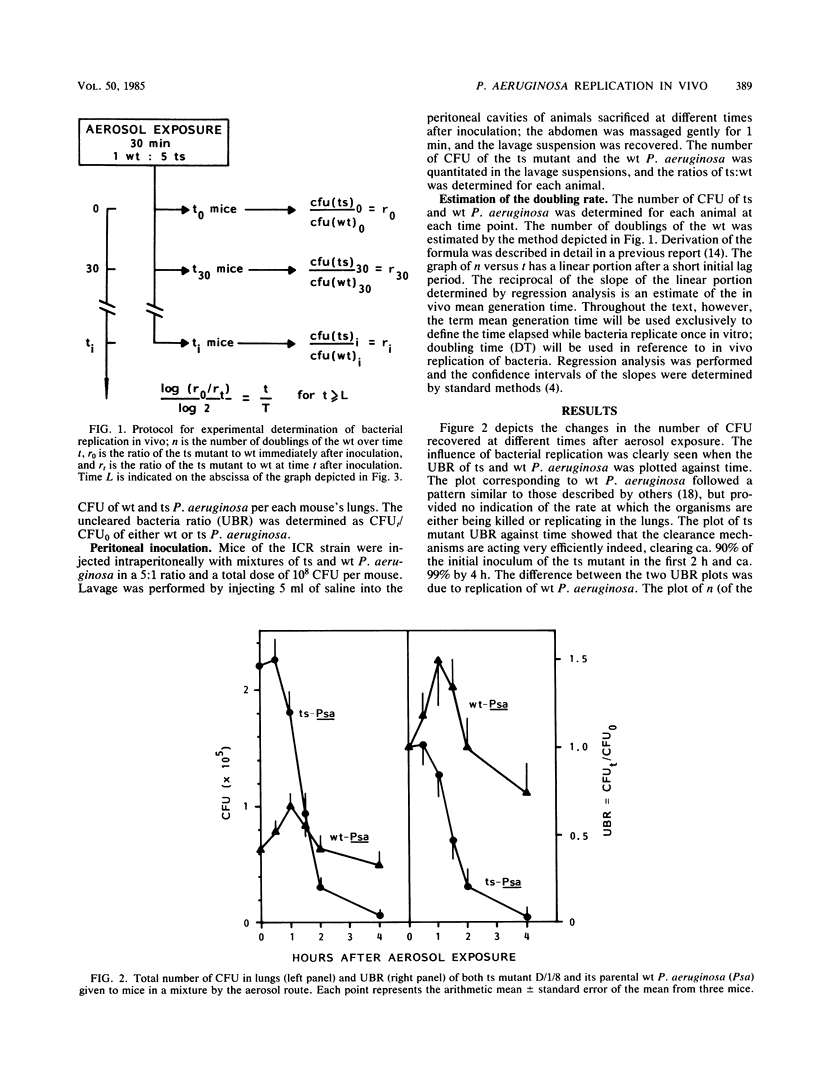
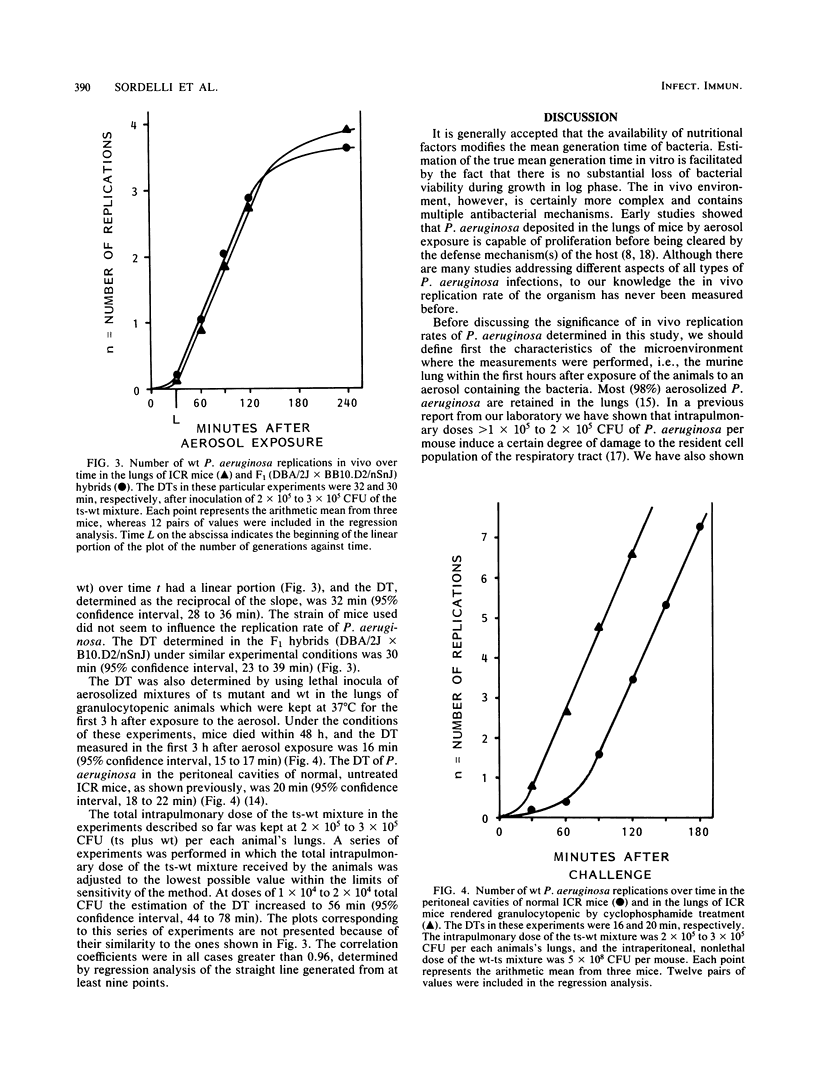
Using a method recently developed at our laboratory, we determined the initial rate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa replication in the lung under different experimental conditions. Mice were exposed to aerosols containing mixtures of a temperature-sensitive (ts) mutant of P. aeruginosa and its parental wild type (wt). The changes in the ratio of ts:wt were determined by quantitatively culturing homogenates of lungs from animals sacrificed over different time periods. The doubling time (DT) was calculated as the reciprocal of the slope of the linear portion of the curve generated by plotting n = (log [r0/rt])/log 2 against time where r is the ratio of ts:wt at a given time. The DTs measured in both outbred ICR mice and F1 hybrids (DBA/2J X B10.D2/nSnJ) were 32 and 30 min, respectively. These DTs were higher than that determined in the peritoneal cavities of ICR mice (20 min). The DT in the lungs of ICR mice rendered granulocytopenic by treatment with cyclophosphamide was 16 min. Experiments performed with inocula of different sizes showed that DTs tended to be higher in animals aerosolized with low doses of the ts-wt mixture.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cerquetti M. C., Sordelli D. O., Ortegon R. A., Bellanti J. A. Impaired lung defenses against Staphylococcus aureus in mice with hereditary deficiency of the fifth component of complement. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1071–1076. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1071-1076.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART P. D., REES R. J. Effect of macrocyclon in acute and chronic pulmonary tuberculous infection in mice as shown by viable and total bacterial counts. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Aug;41:414–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENDERSON D. W. An apparatus for the study of airborne infection. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Mar;50(1):53–68. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400019422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooke A. M., Oeschger M. P., Zeligs B. J., Bellanti J. A. Ideal target organism for quantitative bactericidal assays. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):406–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.406-411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. The in vivo division and death rates of Salmonella typhimurium in the spleens of naturally resistant and susceptible mice measured by the superinfecting phage technique of Meynell. Immunology. 1980 Dec;41(4):973–979. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. E., Southern P. M., Pierce A. K., Fallis B. D., Sanford J. P. Pulmonary clearance of gram-negative bacilli. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 May;69(5):833–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G., SUBBAIAH T. V. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. I. Kinetics of infection by Salmonella typhi-murium in normal and streptomycin-treated mice studied with abortive transductants. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:197–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maw J., Meynell G. G. The true division and death rates of Salmonella typhimurium in the mouse spleen determined with superinfecting phage P22. Br J Exp Pathol. 1968 Dec;49(6):597–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer P., Walzl H. Studies of lung infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in mice treated with cyclophosphamide. Infection. 1983 Mar-Apr;11(2):87–96. doi: 10.1007/BF01641073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris Hooke A., Sordelli D. O., Cerquetti M. C., Vogt A. J. Quantitative determination of bacterial replication in vivo. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):424–427. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.424-427.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordelli D. O., Cerquetti M. C., Hooke A. M., Bellanti J. A. Enhancement of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung clearance after local immunization with a temperature-sensitive mutant. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1275–1279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1275-1279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordelli D. O., Cerquetti M. C., Morris Hooke A., Bellanti J. A. Effect of chemotactins released by Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa on the murine respiratory tract. Infect Immun. 1985 Aug;49(2):265–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.2.265-269.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordelli D. O., Zeligs B. J., Cerquetti M. C., Morris Hooke A., Bellanti J. A. Inflammatory responses to Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in the murine lung. Eur J Respir Dis. 1985 Jan;66(1):31–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. M., Jr, Mays B. B., Pierce A. K., Sanford J. P. Pulmonary clearance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Oct;76(4):548–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


