Abstract
Hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies (MABs) specific for Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin were produced by fusion of P3X63Ag8.653 myeloma cells with spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized with purified enterotoxin. Wells containing hybridomas secreting immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies against enterotoxin were specifically identified by an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and 10 ELISA-positive hybridomas were selected and cloned twice by limiting dilution. All 10 hybridomas produced MABs containing immunoglobulin G1 heavy chains and kappa (kappa) light chains. These hybridomas were then grown as ascitic tumors in mice, and MABs were purified from the ascites fluids with DEAE Affi-gel blue. The specificity of the MABs for enterotoxin was demonstrated by immunoblotting and ELISA. Competitive radioimmunoassay with 125I-MABs suggests that these MABs recognized at least four epitopes on the enterotoxin molecule. The enterotoxin-neutralizing ability of MABs from both hybridoma culture supernatants and ascites fluids was assessed by using a 3H-nucleotide-release Vero (African green monkey kidney) cell assay. Only 2 of the 10 hybridomas produced MABs which completely (greater than 90%) neutralized the biologic activity of enterotoxin. Preincubation of 125I-enterotoxin with MABs demonstrated that MAB neutralizing ability correlated with MAB-specific inhibition of specific binding of enterotoxin to intestinal brush border membranes.
Full text
PDF





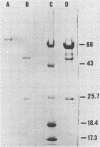
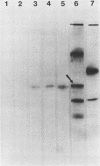
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruck C., Portetelle D., Glineur C., Bollen A. One-step purification of mouse monoclonal antibodies from ascitic fluid by DEAE Affi-Gel blue chromatography. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Sep 30;53(3):313–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy L. K., McDonel J. L., McClane B. A., Kurosky A. Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin: characterization of the amino-terminal region. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):386–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.386-388.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan C. L., Strong D. H., Sebald M. Sporulation and enterotoxin production by mutants of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):378–391. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.378-391.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieben W. R., Duncan C. L. Heterogeneity of enterotoxin-like protein extracted from spores fo Clostridium perfringens type A. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jul 1;55(2):455–463. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02182.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Whitaker J. R. Improved method for purification of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jun;39(6):1120–1122. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.6.1120-1122.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granum P. E., Whitaker J. R., Skjelkvåle R. Trypsin activation of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A: fragmentation and some physicochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 29;668(3):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90165-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Twiddy E. M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies that react with unique and cross-reacting determinants of cholera enterotoxin and its subunits. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.914-923.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenimer J. G., Habig W. H., Hardegree M. C. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of tetanus toxin structure and function. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):942–948. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.942-948.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., McDonel J. L. Characterization of membrane permeability alterations induced in Vero cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Aug 14;600(3):974–985. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90499-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., McDonel J. L. The effects of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin on morphology, viability, and macromolecular synthesis in Vero cells. J Cell Physiol. 1979 May;99(2):191–200. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A. Osmotic stabilizers differentially inhibit permeability alterations induced in Vero cells by Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Oct 17;777(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90501-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane B. A., Strouse R. J. Rapid detection of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Feb;19(2):112–115. doi: 10.1128/jcm.19.2.112-115.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L. Binding of Clostridium perfringens [125I]enterotoxin to rabbit intestinal cells. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4801–4807. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L. Clostridium perfringens toxins (type A, B, C, D, E). Pharmacol Ther. 1980;10(3):617–655. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(80)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L., Demers G. W. In vivo effects of enterotoxin from Clostridium perfringens type A in the rabbit colon: binding vs. biologic activity. J Infect Dis. 1982 Apr;145(4):490–494. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.4.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L., McClane B. A. Binding versus biological activity of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin in Vero cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Mar 30;87(2):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91823-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonel J. L., McClane B. A. Highly sensitive assay for Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin that uses inhibition of plating efficiency of Vero cells grown in culture. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 May;13(5):940–946. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.5.940-946.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shandera W. X., Tacket C. O., Blake P. A. Food poisoning due to Clostridium perfringens in the United States. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jan;147(1):167–170. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard A. J., Cussell D., Hughes M. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to tetanus toxin. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):710–714. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.710-714.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigrist H., Ronner P., Semenza G. A hydrophobic form of the small-intestinal sucrase-isomaltase complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 17;406(3):433–446. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skjelkvåle R., Uemura T. Experimental Diarrhoea in human volunteers following oral administration of Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. J Appl Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;43(2):281–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1977.tb00752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark R. L., Duncan C. L. Purification and biochemical properties of Clostridium perfringens type A enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1972 Nov;6(5):662–673. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.5.662-673.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stähli C., Staehelin T., Miggiano V., Schmidt J., Häring P. High frequencies of antigen-specific hybridomas: dependence on immunization parameters and prediction by spleen cell analysis. J Immunol Methods. 1980;32(3):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thelestam M., Möllby R. Sensitive assay for detection of toxin-induced damage to the cytoplasmic membrane of human diploid fibroblasts. Infect Immun. 1975 Aug;12(2):225–232. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.2.225-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Heyningen V., Brock D. J., Van Heyningen S. A simple method for ranking the affinities of monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Aug 26;62(2):147–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90000-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wnek A. P., McClane B. A. Identification of a 50,000 Mr protein from rabbit brush border membranes that binds Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 May 16;112(3):1099–1105. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91731-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]