Abstract
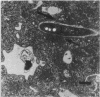
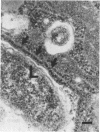
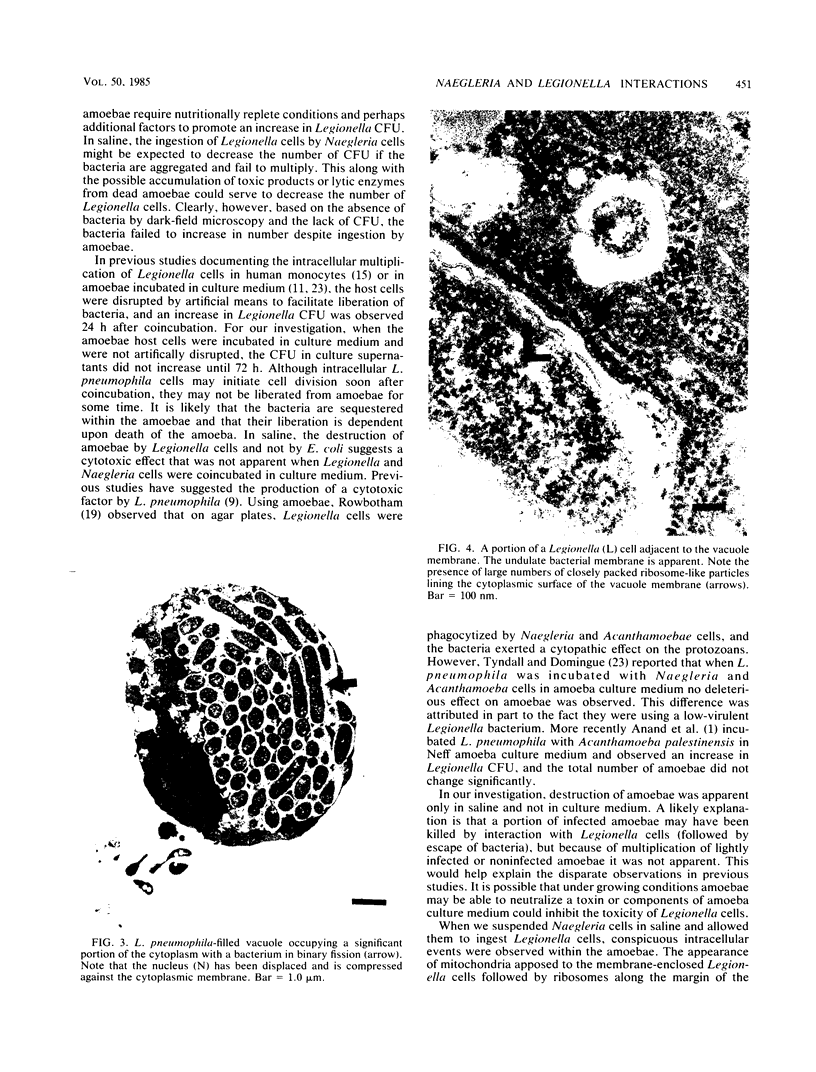
Using electron microscopy we documented some of the intracellular events that occur in Naegleria fowleri suspended in Page amoeba saline after ingestion of Legionella pneumophila. Photomicrographs showed intracellular vacuoles containing bacteria in the process of binary fission that was accompanied by alignment of mitochondria and ribosome-like structures along the vacuole membrane. Although these intracellular events are remarkably similar to that seen in Legionella replication within human monocytes, we could not demonstrate an increase in the number of bacteria by CFU or dark-field microscopy. However, when the Naegleria cells were allowed to ingest Legionella cells while suspended in amoeba culture medium, the number of bacteria increased, and this was contingent upon the presence of viable amoebae.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anand C. M., Skinner A. R., Malic A., Kurtz J. B. Interaction of L. pneumophilia and a free living amoeba (Acanthamoeba palestinensis). J Hyg (Lond) 1983 Oct;91(2):167–178. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400060174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler F. W., Hicklin M. D., Blackmon J. A. Demonstration of the agent of Legionnaires' disease in tissue. N Engl J Med. 1977 Dec 1;297(22):1218–1220. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197712012972206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jonckheere J. Use of an axenic medium for differentiation between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Naegleria fowleri isolates. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):751–757. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.751-757.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Smith S. J., Tison D. L., Pope D. H. Ecological distribution of Legionella pneumophila. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):9–16. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.9-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliermans C. B., Cherry W. B., Orrison L. H., Thacker L. Isolation of Legionella pneumophila from nonepidemic-related aquatic habitats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jun;37(6):1239–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.6.1239-1242.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser D. W. Legionnaires' disease: four summers' harvest. Am J Med. 1980 Jan;68(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90151-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L., Iglewski B. H., Miller R. D. Identification of a cytotoxin produced by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):271–274. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.271-274.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glavin F. L., Winn W. C., Jr, Craighead J. E. Ultrastructure of lung in Legionnaires' disease. Observations of three biopsies done during the Vermont epidemic. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Apr;90(4):555–559. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-90-4-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden E. P., Winkler H. H., Wood D. O., Leinbach E. D. Intracellular growth of Legionella pneumophila within Acanthamoeba castellanii Neff. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):18–24. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.18-24.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Formation of a novel phagosome by the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1319–1331. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. Phagocytosis of the Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) occurs by a novel mechanism: engulfment within a pseudopod coil. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90070-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A., Silverstein S. C. Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) multiples intracellularly in human monocytes. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):441–450. doi: 10.1172/JCI109874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz M. A. The Legionnaires' disease bacterium (Legionella pneumophila) inhibits phagosome-lysosome fusion in human monocytes. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):2108–2126. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page F. C. Taxonomic criteria for limax amoebae, with descriptions of 3 new species of Hartmannella and 3 of Vahlkampfia. J Protozool. 1967 Aug;14(3):499–521. doi: 10.1111/j.1550-7408.1967.tb02036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasculle A. W., Feeley J. C., Gibson R. J., Cordes L. G., Myerowitz R. L., Patton C. M., Gorman G. W., Carmack C. L., Ezzell J. W., Dowling J. N. Pittsburgh pneumonia agent: direct isolation from human lung tissue. J Infect Dis. 1980 Jun;141(6):727–732. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.6.727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowbotham T. J. Preliminary report on the pathogenicity of Legionella pneumophila for freshwater and soil amoebae. J Clin Pathol. 1980 Dec;33(12):1179–1183. doi: 10.1136/jcp.33.12.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. R., Tyndall R. L., Coutant C. C., Willaert E. Isolation of the etiological agent of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis from artifically heated waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Dec;34(6):701–705. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.6.701-705.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Pope D. H., Cherry W. B., Fliermans C. B. Growth of Legionella pneumophila in association with blue-green algae (cyanobacteria). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Feb;39(2):456–459. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.2.456-459.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tison D. L., Seidler R. J. Legionella incidence and density in potable drinking water supplies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):337–339. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.337-339.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyndall R. L., Domingue E. L. Cocultivation of Legionella pneumophila and free-living amoebae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):954–959. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.954-959.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jonckheere J., Voorde H. The distribution of Naegleria fowleri in man-made thermal waters. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jan;26(1):10–15. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]