Abstract
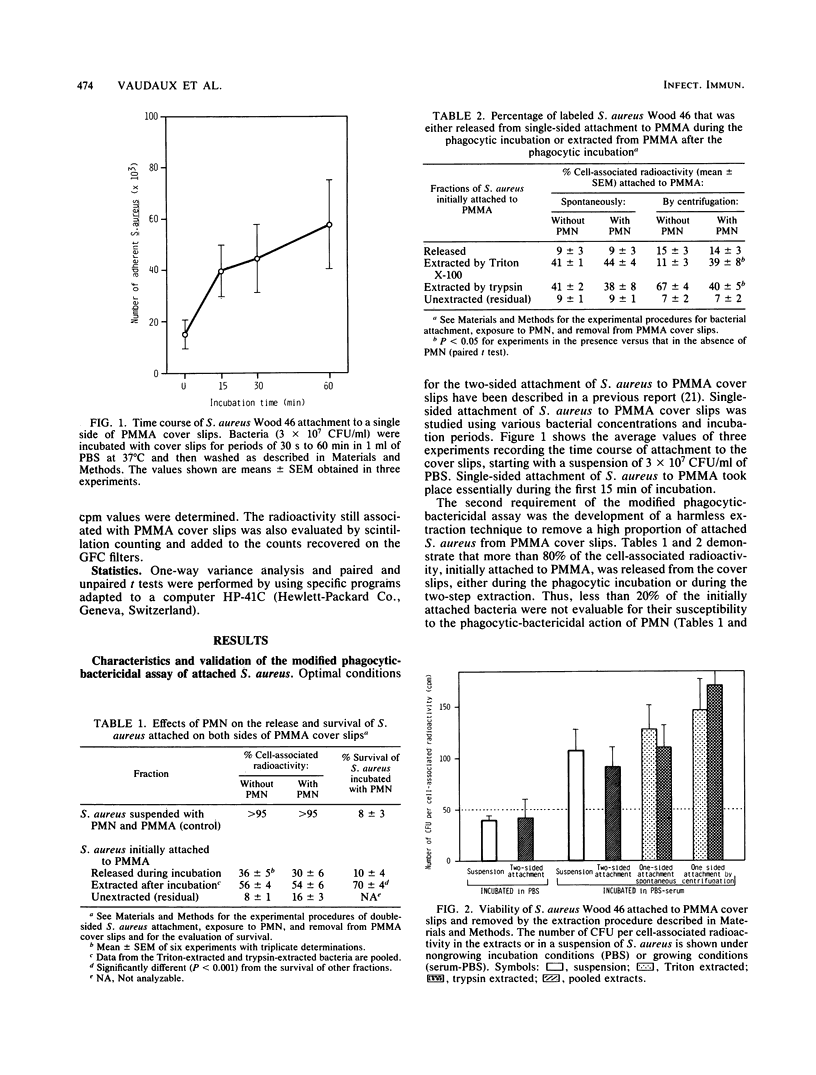
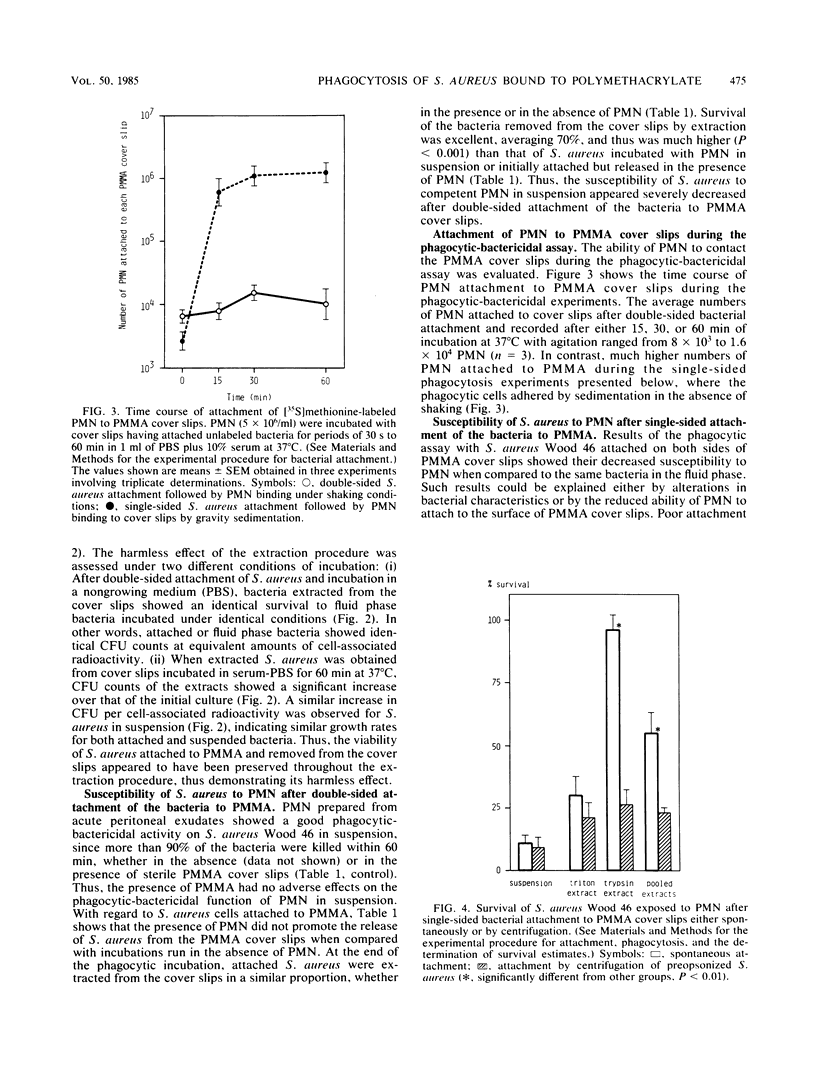
The mechanisms responsible for the development of a pyogenic infection (most commonly due to staphylococci) in the vicinity of an implanted foreign body have been studied recently by several investigators. Thus, we have been able to demonstrate that the phagocytic function of residential polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMN) is deficient in the presence of a foreign body. Others have shown that in the presence of foreign surfaces, microorganisms produce extracellular amorphous material, the pathogenic role of which is still to be defined. In the present study we use a novel assay system to demonstrate that Staphylococcus aureus Wood 46, after attachment to polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA), shows increased resistance to the phagocytic-bactericidal action of normal PMN. The first step of this assay involves the reproducible attachment of [3H]thymidine-labeled bacteria to PMMA cover slips. During the second step, attached bacteria were exposed to guinea pig peritoneal exudate PMN. In the third and final step, attached S. aureus cells were removed from the cover slips using a procedure harmless to the bacteria. The extent of bacterial detachment was estimated by radioactive counts and their viability by standard colony counts. Whereas bacteria that were attached artificially and rapidly by centrifugation and immediately exposed to PMN were killed in the phagocytic assay, bacteria adhering spontaneously to the cover slips for a prolonged period of time were more resistant to the killing action of the phagocytes. The spontaneous adherence of S. aureus to PMMA renders it poorly susceptible to the killing action of PMN.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayston R., Penny S. R. Excessive production of mucoid substance in staphylococcus SIIA: a possible factor in colonisation of Holter shunts. Dev Med Child Neurol Suppl. 1972;27:25–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8749.1972.tb09769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Simpson W. A., Bisno A. L., Beachey E. H. Adherence of slime-producing strains of Staphylococcus epidermidis to smooth surfaces. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):318–326. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.318-326.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The bacterial glycocalyx in nature and disease. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:299–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.001503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Irvin R. T., Cheng K. J. The role of bacterial surface structures in pathogenesis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1981;8(4):303–338. doi: 10.3109/10408418109085082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELEK S. D., CONEN P. E. The virulence of Staphylococcus pyogenes for man; a study of the problems of wound infection. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Dec;38(6):573–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald R. H., Jr, Peterson L. F., Washington J. A., 2nd, Van Scoy R. E., Coventry M. B. Bacterial colonization of wounds and sepsis in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973 Sep;55(6):1242–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inman R. D., Gallegos K. V., Brause B. D., Redecha P. B., Christian C. L. Clinical and microbial features of prosthetic joint infection. Am J Med. 1984 Jul;77(1):47–53. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES R. C., MACLEOD C. J. Induction of staphylococcal infections in mice with small inocula introduced on sutures. Br J Exp Pathol. 1961 Jun;42:266–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloster F. E. Complications of artificial heart valves. JAMA. 1979 May 18;241(20):2201–2203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Quie P. G., Williams R. C., Jr Quantitation of staphylococcal protein A: Determination of equilibrium constant and number of protein A residues on bacteria. J Immunol. 1970 Feb;104(2):273–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew P. D., Zubler R., Vaudaux P., Farquet J. J., Waldvogel F. A., Lambert P. H. Decreased heat-labile opsonic activity and complement levels associated with evidence of C3 breakdown products in infected pleural effusions. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):326–334. doi: 10.1172/JCI109306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble W. C. The production of subcutaneous staphylococcal skin lesions in mice. Br J Exp Pathol. 1965 Jun;46(3):254–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Adherence and growth of coagulase-negative staphylococci on surfaces of intravenous catheters. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):479–482. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Locci R., Pulverer G. Microbial colonization of prosthetic devices. II. Scanning electron microscopy of naturally infected intravenous catheters. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg B. 1981;173(5):293–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters G., Saborowski F., Locci R., Pulverer G. Investigations on staphylococcal infection of transvenous endocardial pacemaker electrodes. Am Heart J. 1984 Aug;108(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(84)90625-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarzmann S., Boring J. R. Antiphagocytic Effect of Slime from a Mucoid Strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1971 Jun;3(6):762–767. doi: 10.1128/iai.3.6.762-767.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P. E., Waldvogel F. A., Morgenthaler J. J., Nydegger U. E. Adsorption of fibronectin onto polymethylmethacrylate and promotion of Staphylococcus aureus adherence. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):768–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.768-774.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaudaux P., Suzuki R., Waldvogel F. A., Morgenthaler J. J., Nydegger U. E. Foreign body infection: role of fibronectin as a ligand for the adherence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1984 Oct;150(4):546–553. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Lew P. D., Waldvogel F. A. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection. Evidence for a local granulocyte defect. J Clin Invest. 1984 Apr;73(4):1191–1200. doi: 10.1172/JCI111305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerli W., Waldvogel F. A., Vaudaux P., Nydegger U. E. Pathogenesis of foreign body infection: description and characteristics of an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1982 Oct;146(4):487–497. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.4.487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


