Abstract
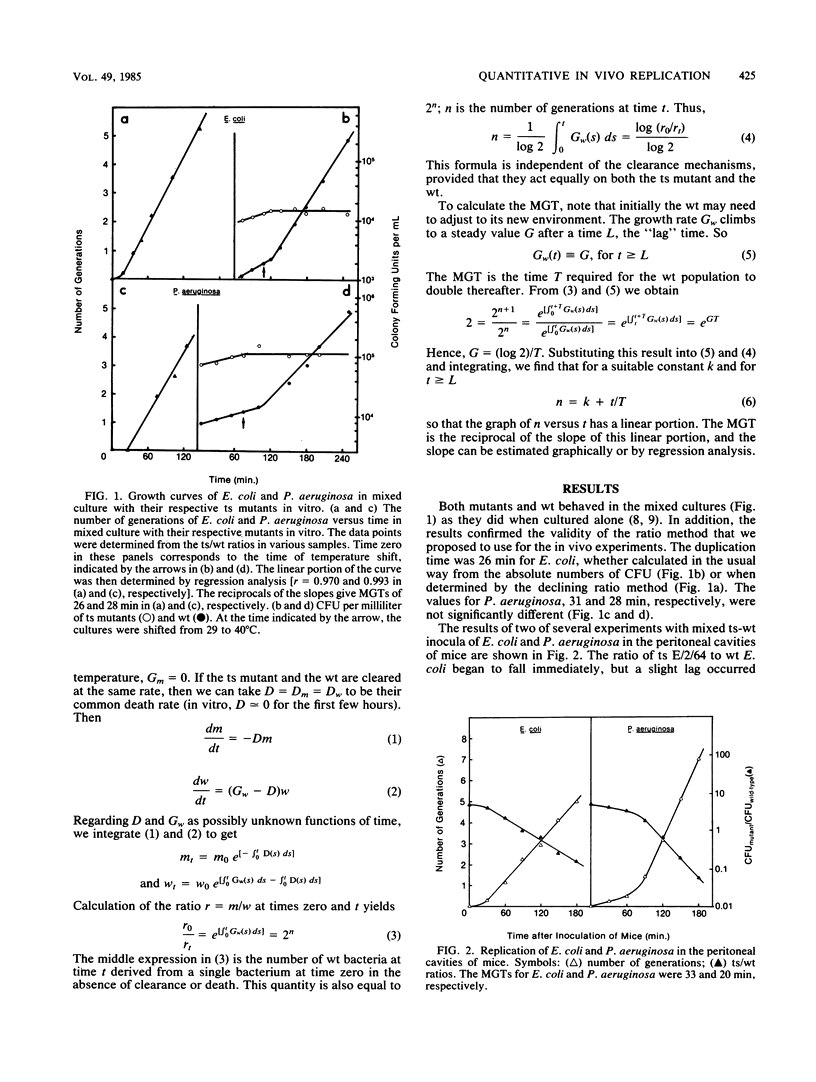
A new methodology which permits the quantitative measurement of absolute bacterial replication in vivo is proposed. Mice were inoculated with mixtures of temperature-sensitive mutants and parental wild types, and the changes in the ratios of the two strains were measured. The number of wild-type generations was calculated from the declining ratios over time with the formula n = log (r0/rt)/log 2; n is the number of generations, and r0 and rt are the ratio of temperature-sensitive mutants to the parental wild type at time zero and at the times sampled throughout the experiment. The replication rate was determined by regression analysis. A mathematical argument for the formula is presented. Using this technique, we determined the mean generation times of Escherichia coli (33 min) and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (20 min) in the peritoneal cavities of mice, in the face of host clearance mechanisms during the first stages of infection.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baselski V. S., Medina R. A., Parker C. D. Survival and multiplication of Vibrio cholerae in the upper bowel of infant mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):435–440. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.435-440.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freter R., O'Brien P. C. Role of chemotaxis in the association of motile bacteria with intestinal mucosa: fitness and virulence of nonchemotactic Vibrio cholerae mutants in infant mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):222–233. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.222-233.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HART P. D., REES R. J. Effect of macrocyclon in acute and chronic pulmonary tuberculous infection in mice as shown by viable and total bacterial counts. Br J Exp Pathol. 1960 Aug;41:414–421. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooke A. M., Arroyo P. J., Oeschger M. P., Bellanti J. A. Temperature-sensitive mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: isolation and preliminary immunological evaluation. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):136–140. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.136-140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooke A. M., Oeschger M. P., Zeligs B. J., Bellanti J. A. Ideal target organism for quantitative bactericidal assays. Infect Immun. 1978 May;20(2):406–411. doi: 10.1128/iai.20.2.406-411.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hormaeche C. E. The in vivo division and death rates of Salmonella typhimurium in the spleens of naturally resistant and susceptible mice measured by the superinfecting phage technique of Meynell. Immunology. 1980 Dec;41(4):973–979. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYNELL G. G., SUBBAIAH T. V. Antibacterial mechanisms of the mouse gut. I. Kinetics of infection by Salmonella typhi-murium in normal and streptomycin-treated mice studied with abortive transductants. Br J Exp Pathol. 1963 Apr;44:197–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maw J., Meynell G. G. The true division and death rates of Salmonella typhimurium in the mouse spleen determined with superinfecting phage P22. Br J Exp Pathol. 1968 Dec;49(6):597–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel S. P., Finkelstein R. A., Parker C. D. Ability of an avirulent mutant of Vibrio cholerae to colonize in the infant mouse upper bowel. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):474–479. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.474-479.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordelli D. O., Cerquetti M. C., Hooke A. M., Bellanti J. A. Enhancement of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lung clearance after local immunization with a temperature-sensitive mutant. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1275–1279. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1275-1279.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


