Abstract
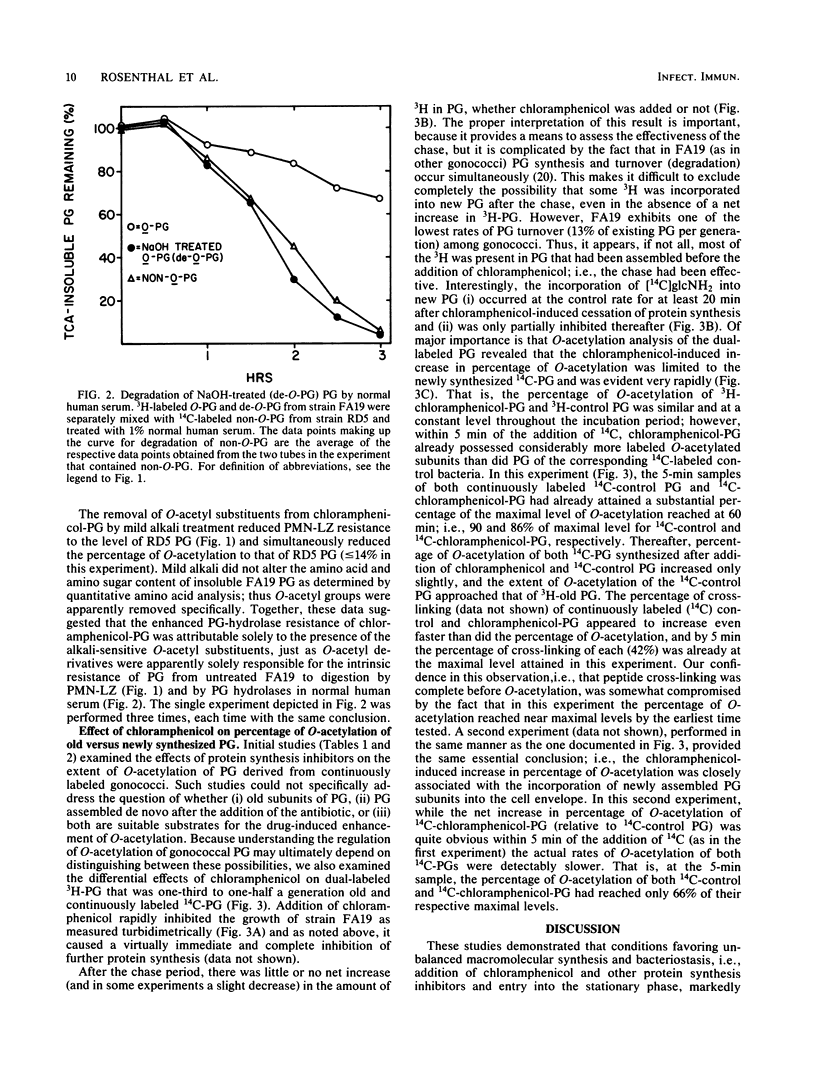
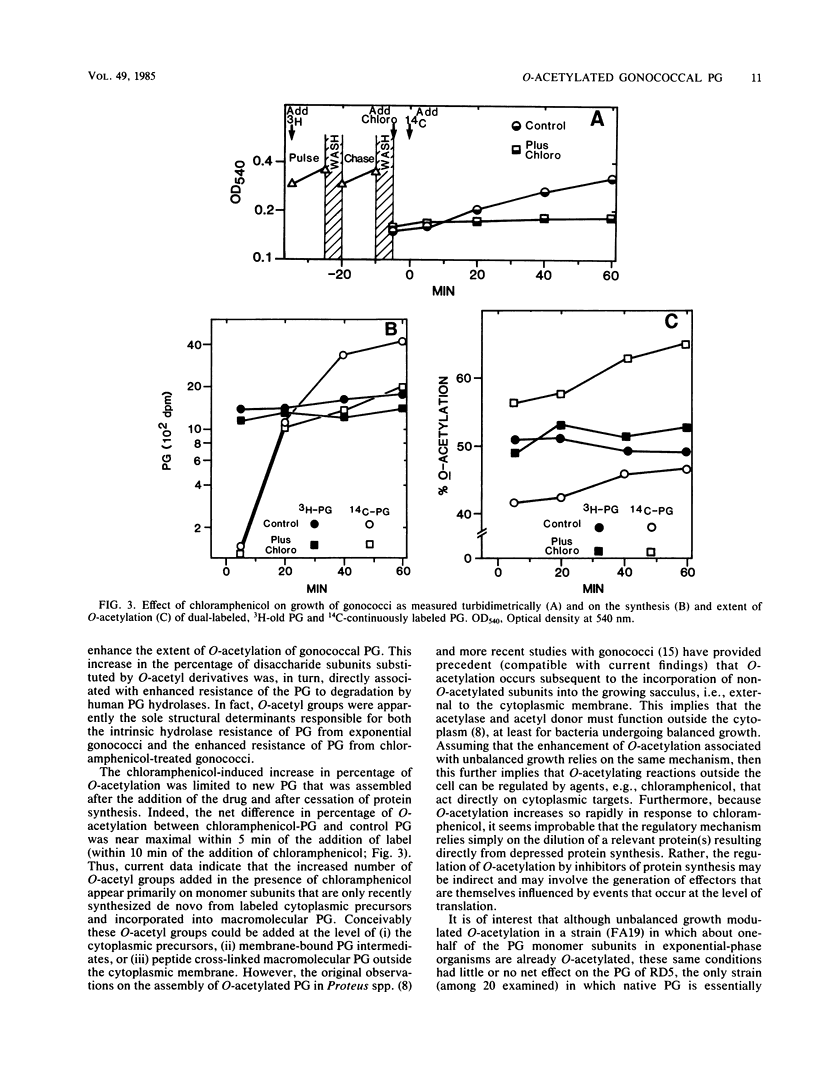
The effects of protein synthesis inhibitors on the extent of O-acetylation of Neisseria gonorrhoeae peptidoglycan (PG) and on the resistance of PG to degradation by human PG hydrolases were examined. Addition of chloramphenicol, tetracycline, and streptomycin (in amounts equal to approximately twice their respective MICs) rapidly increased the level of O-acetylation of [3H]glucosamine-labeled N. gonorrhoeae FA19 PG from 46% to about 70% and simultaneously enhanced the resistance of the PG to degradation by human polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysozyme. Entry into the stationary phase also enhanced O-acetylation of FA19 PG, but neither protein synthesis inhibitors nor the stationary phase had a detectable effect on the O-acetyl-deficient, lysozyme-sensitive PG of N. gonorrhoeae RD5. Mild alkali treatment of PG derived from chloramphenicol-treated FA19 specifically removed O-acetyl groups and simultaneously reduced the extents of O-acetylation and polymorphonuclear leukocyte lysozyme resistance to the level of RD5 PG, suggesting that the O-acetyl substituents were solely responsible for the increased PG hydrolase resistance of PG from chloramphenicol-treated FA19. Pulse-chase experiments indicated that the drug-mediated enhancement of O-acetylation was limited to newly assembled PG. In summary, conditions favoring unbalanced macromolecular synthesis and bacteriostasis increased the level of O-acetylation and the PG hydrolase resistance of gonococcal PG. Similar conditions encountered by gonococci in vivo might potentiate the pathobiological consequences of PG-host interactions.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dalldorf F. G., Cromartie W. J., Anderle S. K., Clark R. L., Schwab J. H. The relation of experimental arthritis to the distribution of streptococcal cell wall fragments. Am J Pathol. 1980 Aug;100(2):383–402. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R., Fox A., Greenblatt J. J., Anderle S. K., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Measurement of bacterial cell wall in tissues by solid-phase radioimmunoassay: correlation of distribution and persistence with experimental arthritis in rats. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):127–135. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.127-135.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg I., Sela M. N. The role of leukocytes and their hydrolases in the persistence, degradation, and transport of bacterial constituents in tissues: relation to chronic inflammatory processes in staphylococcal, streptococcal, and mycobacterial infections and in chronic periodontal disease. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1976 Mar;4(3):249–322. doi: 10.3109/10408417609106944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glick A. D., Ranhand J. M., Cole R. M. Degradation of group A streptococcal cell walls by egg-white lysozyme and human lysosomal enzymes. Infect Immun. 1972 Sep;6(3):403–413. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.3.403-413.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gmeiner J., Kroll H. P. Murein biosynthesis and O-acetylation of N-acetylmuramic acid during the cell-division cycle of Proteus mirabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):171–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenblatt J., Boackle R. J., Schwab J. H. Activation of the alternate complement pathway by peptidoglycan from streptococcal cell wall. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):296–303. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.296-303.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebeler B. H., Young F. E. Chemical composition and turnover of peptidoglycan in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1180–1185. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1180-1185.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Pearson C. M., Watanabe Y., Kotani S., Koga T. Structural requirements for arthritogenicity of peptidoglycans from Staphylococcus aureus and Lactobacillus plant arum and analogous synthetic compounds. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1635–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladesić B., Tomasić J., Kveder S., Hrsak I. The metabolic fate of 14C-labeled immunoadjuvant peptidoglycan monomer. II. In vitro studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 18;678(1):12–17. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear A. L., Perkins H. R. Degrees of O-acetylation and cross-linking of the peptidoglycan of Neisseria gonorrhoeae during growth. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):885–888. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. P., Fleck J., Mock M., Ghuysen J. M. The wall peptidoglycans of Neisseria perflava, Moraxella glucidolytica, Pseudomonas alcaligenes and Proteus vulgaris strain P18. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Oct 5;38(2):301–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03062.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melly M. A., McGee Z. A., Rosenthal R. S. Ability of monomeric peptidoglycan fragments from Neisseria gonorrhoeae to damage human fallopian-tube mucosa. J Infect Dis. 1984 Mar;149(3):378–386. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.3.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oken M. M., Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J. Endogenous pyrogen production by human blood monocytes stimulated by staphylococcal cell wall components. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):208–213. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.208-213.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen B. H., Rosenthal R. S. Complement consumption gonococcal peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):442–448. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.442-448.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Blundell J. K., Perkins H. R. Strain-related differences in lysozyme sensitivity and extent of O-acetylation of gonococcal peptidoglycan. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):826–829. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.826-829.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Folkening W. J., Miller D. R., Swim S. C. Resistance of O-acetylated gonococcal peptidoglycan to human peptidoglycan-degrading enzymes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):903–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.903-911.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Fulbright R. S., Eads M. E., Sawyer W. D. Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid-sensitive antiphagocytic activity of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):817–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.817-827.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S. Release of soluble peptidoglycan from growing gonococci: hexaminidase and amidase activities. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):869–878. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.869-878.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal R. S., Wright R. M., Sinha R. K. Extent of peptide cross-linking in the peptidoglycan of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):867–875. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.867-875.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Cromartie W. J., Ohanian S. H., Craddock J. G. Association of experimental chronic arthritis with the persistence of group A streptococcal cell walls in the articular tissue. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1728–1735. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1728-1735.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Ohanian S. H. Degradation of streptococcal cell wall antigens in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1346–1352. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1346-1352.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha R. K., Rosenthal R. S. Effect of penicillin G on release of peptidoglycan fragments by Neisseria gonorrhoeae: characterization of extracellular products. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Jul;20(1):98–103. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha R. K., Rosenthal R. S. Release of soluble peptidoglycan from growing conococci: demonstration of anhydro-muramyl-containing fragments. Infect Immun. 1980 Sep;29(3):914–925. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.3.914-925.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smialowicz R. J., Schwab J. H. Cytotoxicity of rat macrophages activated by persistent or biodegradable bacterial cell walls. Infect Immun. 1977 Sep;17(3):599–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.3.599-606.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XII. Colony color and opacity varienats of gonococci. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):320–331. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.320-331.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swim S. C., Gfell M. A., Wilde C. E., 3rd, Rosenthal R. S. Strain distribution in extents of lysozyme resistance and O-acetylation of gonococcal peptidoglycan determined by high-performance liquid chromatography. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):446–452. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.446-452.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


