Abstract
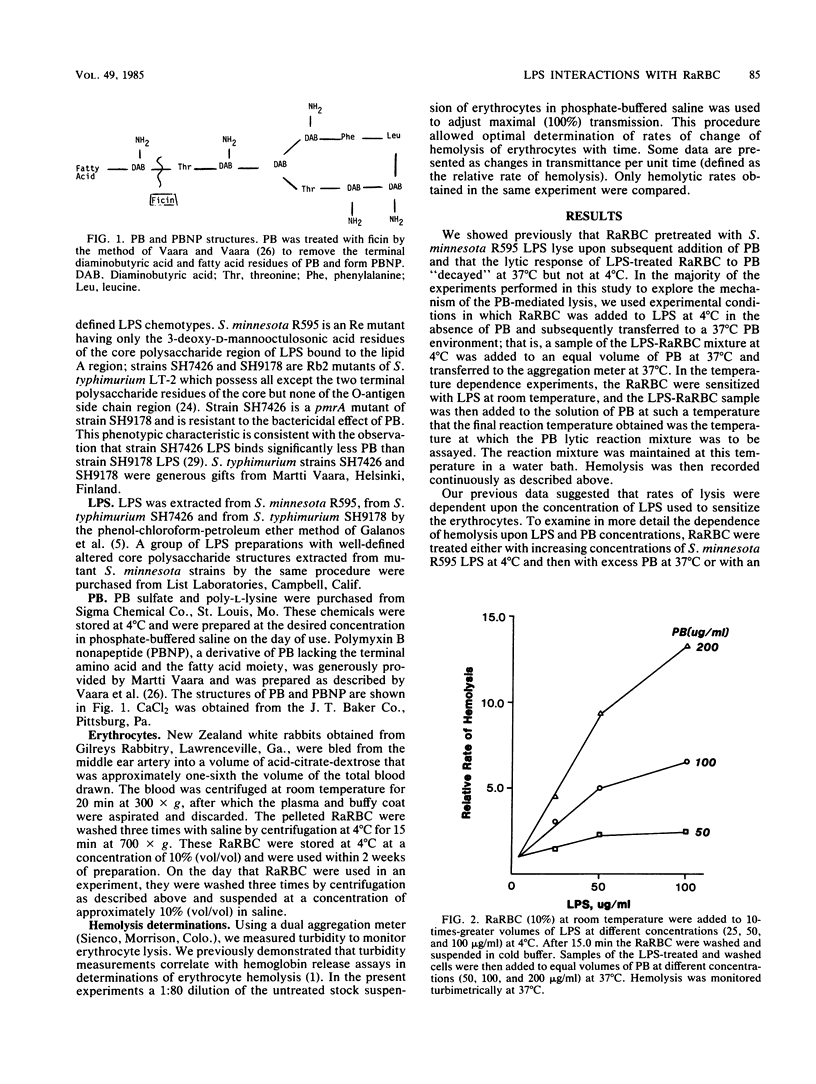
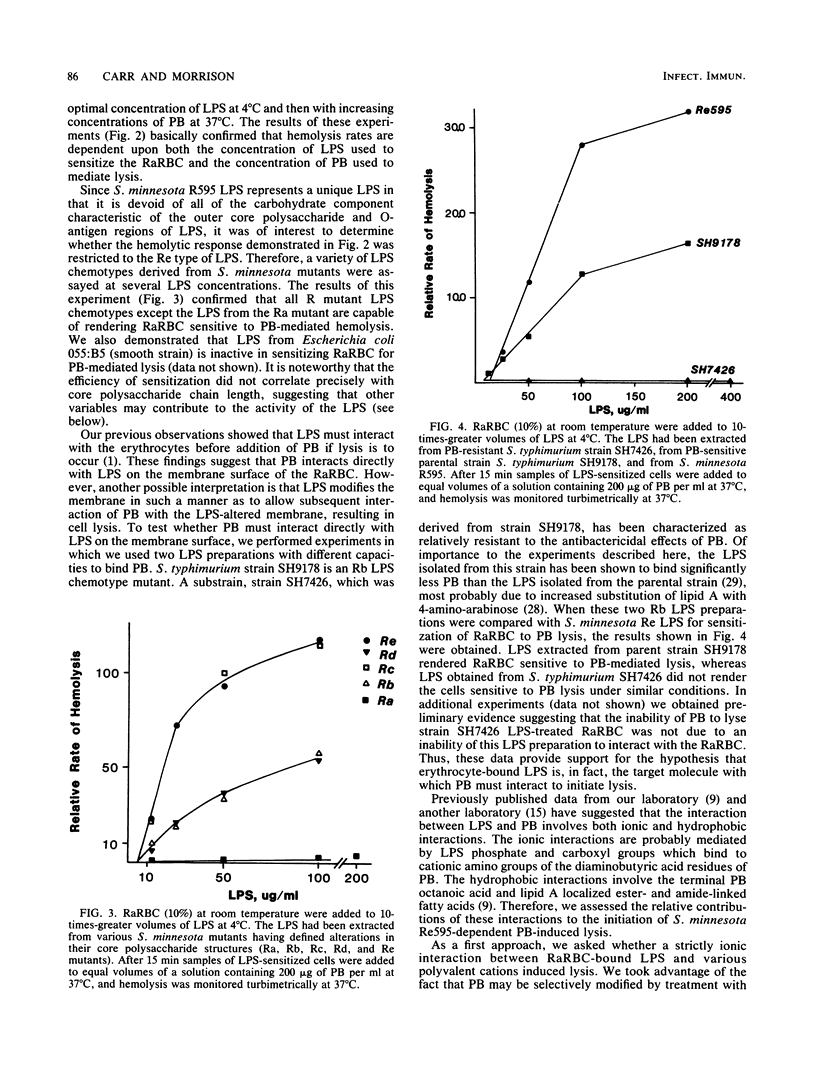
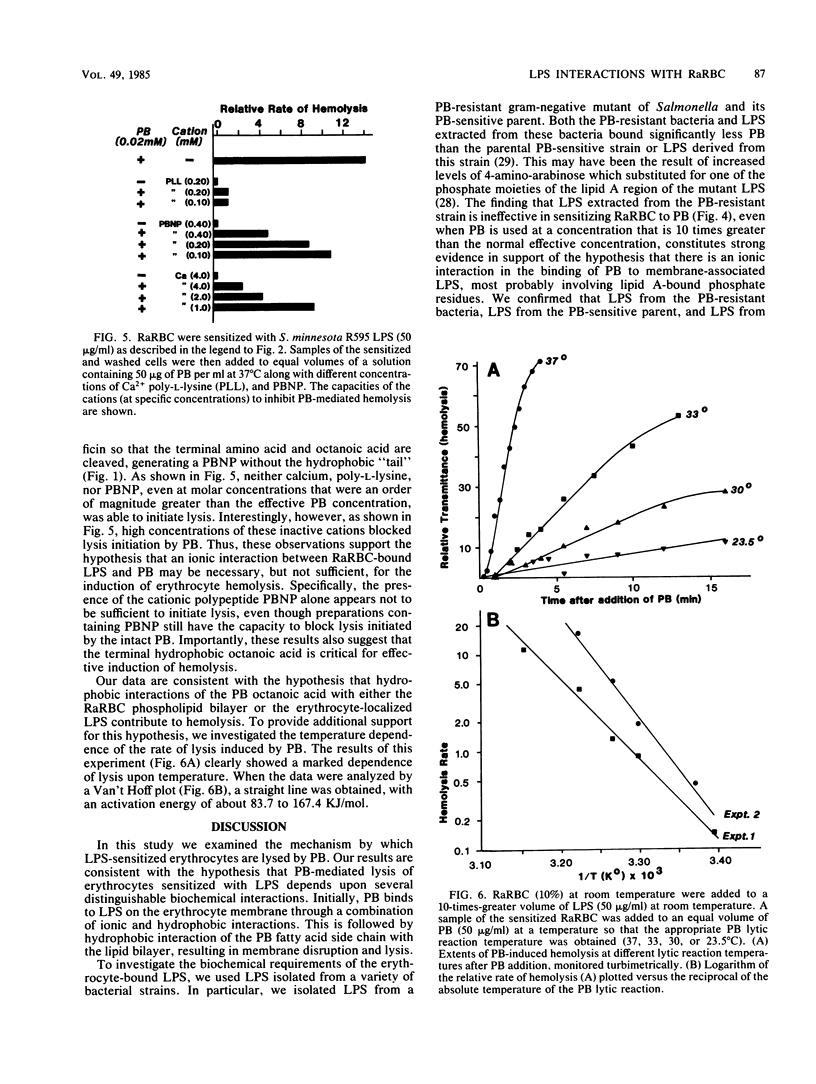
A novel system was used previously to characterize the dynamic interaction of a polysaccharide-deficient, lipid-rich lipopolysaccharide (LPS) with rabbit erythrocytes (RaRBC). Exposure of the RaRBC to the LPS rendered them sensitive to induction of hemolysis by the cationic antibiotic polymyxin B (PB) in a time- and temperature-independent manner. Subsequent decay in the response of LPS-sensitized cells to PB was shown to be critically dependent on both the time and temperature of incubation of RaRBC with LPS and to be independent of a change in LPS binding (Carr and Morrison, Infect. Immun. 43:600-606, 1984). In the present study, we performed experiments designed to define the mechanism by which PB mediates hemolysis of LPS-sensitized RaRBC. Experiments were performed to examine the molecular requirements of the LPS and the PB that were essential for hemolytic activity. The capacity of various cations to mediate hemolysis of LPS-sensitized RaRBC or to block PB-mediated hemolysis and the temperature dependence of the PB lytic reaction were investigated. The results of these experiments suggest that PB-mediated hemolysis of LPS-treated erythrocytes is dependent upon an initial ionic association of PB with erythrocyte membrane-bound LPS, followed by hydrophobic insertion of the PB fatty acid into the erythrocyte membrane lipid bilayer.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carr C., Jr, Morrison D. C. Lipopolysaccharide interaction with rabbit erythrocyte membranes. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):600–606. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.600-606.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutinho A., Forni L., Watanabe T. Genetic and functional characterization of an antiserum to the lipid A-specific triggering receptor on murine B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jan;8(1):63–67. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M., Stewart-Tull D. E., Jackson D. M. The binding of lipopolysaccharide from Escherichia coli to mammalian cell membranes and its effect on liposomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 4;508(2):260–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forni L., Coutinho A. An antiserum which recognizes lipopolysaccharide-reactive B cells in the mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1978 Jan;8(1):56–62. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830080112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. A new method for the extraction of R lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1969 Jun;9(2):245–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1969.tb00601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodate K., Bito Y. Temperature dependence of bactericidal action of polymyxin B. Microbiol Immunol. 1982;26(8):737–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1982.tb00217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Inoue K., Nojima S. Effect of polymyxin B on liposomal membranes derived from Escherichia coli lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 14;375(1):130–137. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lounatmaa K., Mäkelä P. H., Sarvas M. Effect of polymyxin on the ultrastructure of the outer membrane of wild-type and polymyxin-resistant strain of Salmonella. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1400–1407. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1400-1407.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Jacobs D. M. Binding of polymyxin B to the lipid A portion of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Immunochemistry. 1976 Oct;13(10):813–818. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. C., Rudbach J. A. Endotoxin-cell-membrane interactions leading to transmembrane signaling. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1981;8:187–218. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3917-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NETER E., WESTPHAL O., LUDERITZ O., GORZYNSKI E. A., EICHENBERGER E. Studies of enterobacterial lipopolysaccharides; effects of heat and chemicals on erythrocyte-modifying, antigenic, toxic and pyrogenic properties. J Immunol. 1956 May;76(5):377–385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onji T., Liu M. S. Effect of E coli endotoxin on the leakage of 14C-sucrose from phosphatidylcholine liposomes. Circ Shock. 1981;8(4):403–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pache W., Chapman D., Hillaby R. Interaction of antibiotics with membranes: polymyxin B and gramicidin S. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jan 17;255(1):358–364. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottem S. The effect of lipid A on the fluidity and permeability properties of phospholipid dispersions. FEBS Lett. 1978 Nov 1;95(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler M., Osborn M. J. Interaction of divalent cations and polymyxin B with lipopolysaccharide. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4425–4430. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler P. R., Teuber M. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes: morphological changes in the cytoplasm and in the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli B. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 Jul;8(1):95–104. doi: 10.1128/aac.8.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P., Singer S. J. Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer G. F., Huprikar S. V., Neter E. Specific inhibition of endotoxin coating of red cells by a human erythrocyte membrane component. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):98–108. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.98-108.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons D. B., Clarkson C. A. The binding of LPS to the lymphocyte surface. Immunology. 1979 Nov;38(3):503–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Bader J. Action of polymyxin B on bacterial membranes. Binding capacities for polymyxin B of inner and outer membranes isolated from Salmonella typhimurium G30. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Aug;109(1-2):51–58. doi: 10.1007/BF00425112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teuber M., Miller I. R. Selective binding of polymyxin B to negatively charged lipid monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jun 16;467(3):280–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90305-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truffa-Bachi P., Kaplan J. G., Bona C. The mitogenic effect of lipopolysaccharide. Metabolic processing of lipopolysaccharide by mouse lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1977 Apr;30(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M. Increased outer membrane resistance to ethylenediaminetetraacetate and cations in novel lipid A mutants. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):426–434. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.426-434.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Jensen M., Helander I., Nurminen M., Rietschel E. T., Mäkelä P. H. Characterization of the lipopolysaccharide from the polymyxin-resistant pmrA mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jun 29;129(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80777-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations as outer membrane-disorganizing agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Polycations sensitize enteric bacteria to antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983 Jul;24(1):107–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.24.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T., Sarvas M. Decreased binding of polymyxin by polymyxin-resistant mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Aug;139(2):664–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.2.664-667.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Sensitization of Gram-negative bacteria to antibiotics and complement by a nontoxic oligopeptide. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):526–528. doi: 10.1038/303526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


