Abstract
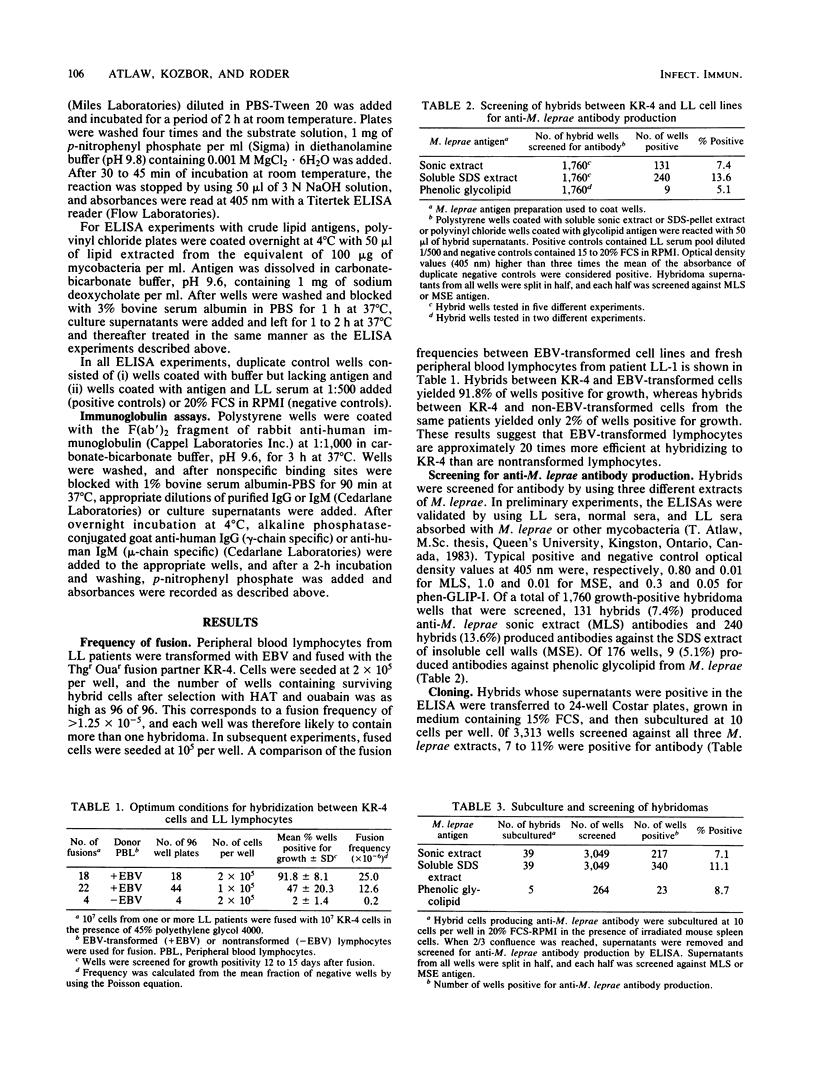
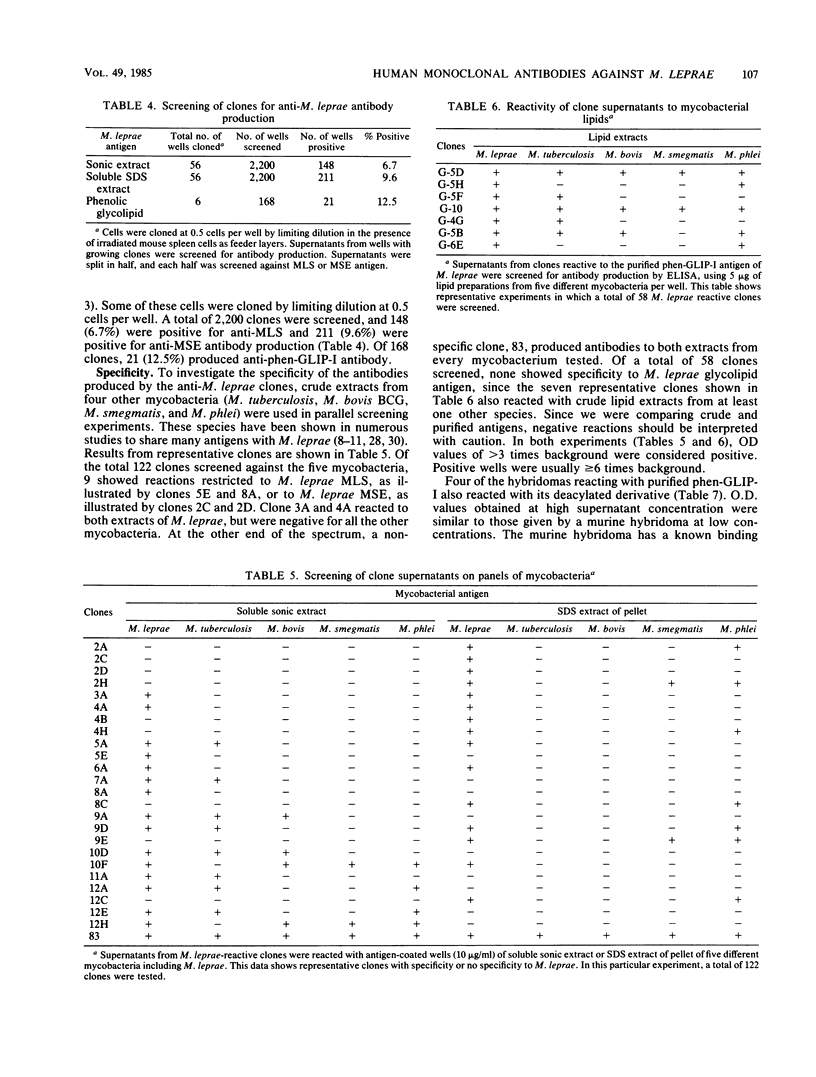
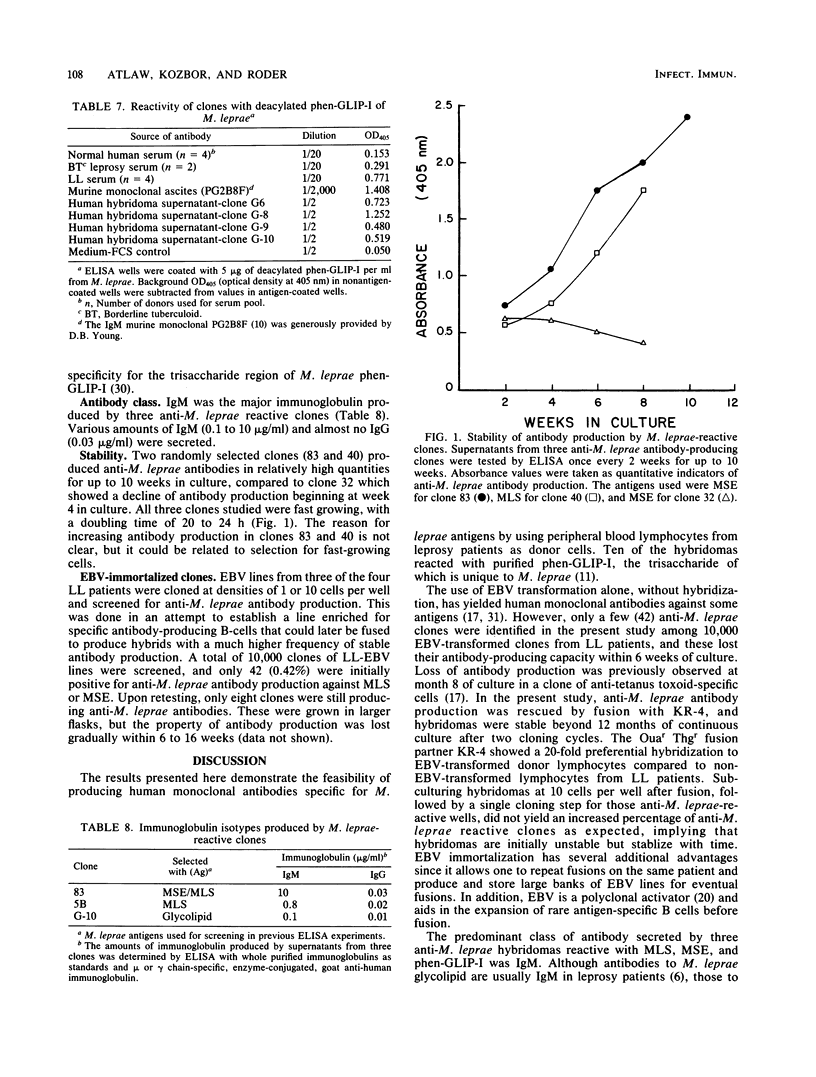
Human hybridomas were constructed which produce antibodies against three different extracts of Mycobacterium leprae. A thioguanine-resistant (Thgr), ouabain-resistant (Ouar), human lymphoblastoid cell line, KR-4, was hybridized with Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cell lines from lepromatous leprosy patients with fusion frequencies of greater than 10(-5). Non-Epstein-Barr virus-transformed donor cells fused at much lower rates (less than 2 X 10(-7]. Hybrids were selected in medium containing hypoxanthine aminopterin thymidine and 10(-5) M ouabain. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to screen for antibodies against three crude extracts of armadillo-derived M. leprae, including (i) a soluble sonic extract preparation, (ii) sodium dodecyl sulfate extract of insoluble sonicated M. leprae, and (iii) a purified phenolic glycolipid antigen. Of a total of 2,200 final clones screened, 359 were found to secrete antibody which bound to soluble sonic extracts and the sodium dodecyl sulfate extract (6.7 and 9.6%, respectively), whereas 12.5% (21 out of 168) showed positivity to the glycolipid antigen. Four selected hybridomas also reacted with the deacylated derivative of M. leprae phenolic-glycolipid antigen. The specificity of these monoclonal antibodies was partially determined by screening on a panel of crude extracts from four other mycobacteria. Nine clones of 122 showed reactivity to M. leprae only. The predominant immunoglobulin was immunoglobulin M, and quantities up to 10 micrograms/ml were produced. Antibody production by hybrid clones was stable in more than 75% of the clones grown in continuous culture. By comparison, 10,000 Epstein-Barr virus-transformed lymphocyte clones from lepromatous leprosy patients were screened for anti-M. leprae antibody production, and all of the 42 clones that were initially positive in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay lost their antibody-producing capabilities within 6 weeks in culture. These results suggest that a combination of Epstein-Barr virus transformation and hybridization may be an optimal method in producing human monoclonal antibodies from leprosy patients.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe M., Minagawa F., Yoshino Y., Okamura K. Studies on the antigenic specificity of Mycobacterium leprae. II. Purification and immunological characterization of the soluble antigen in leprosy nodules. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1972 Apr-Jun;40(2):107–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan P. J., Barrow W. W. Evidence for species-specific lipid antigens in Mycobacterium leprae. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1980 Dec;48(4):382–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett S. J., Draper P., Payne S. N., Rees R. J. Serological activity of a characteristic phenolic glycolipid from Mycobacterium leprae in sera from patients with leprosy and tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 May;52(2):271–279. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell H. D., Kirchheimer W. F., Buchanan T. M. Identification of a Mycobacterium leprae specific protein antigen(s) and its possible application for the serodiagnosis of leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1979 Sep;47(3):477–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. K., Maire M. A., Lambert P. H. SDS-PAGE analysis of M. leprae protein antigens reacting with antibodies from sera from lepromatous patients and infected armadillos. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Sep;49(3):523–531. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho S. N., Yanagihara D. L., Hunter S. W., Gelber R. H., Brennan P. J. Serological specificity of phenolic glycolipid I from Mycobacterium leprae and use in serodiagnosis of leprosy. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.1077-1083.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs O., Mshana R. N., Harboe M. Antigenic analysis of Mycobacterium leprae. Scand J Immunol. 1979 Mar;9(3):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb02735.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis T. P., Buchanan T. M. Production and partial characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1982 Jul;37(1):172–178. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.1.172-178.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Closs O., Bjorvatn B., Kronvall G., Axelsen N. H. Antibody response in rabbits to immunization with Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1977 Dec;18(3):792–805. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.3.792-805.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Closs O., Bjune G., Kronvall G., Axelsen N. H. Mycobacterium leprae specific antibodies detected by radioimmunoassay. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(2):111–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harboe M., Closs O., Reitan L. J., Draper P. Demonstration of antibodies reacting with different determinants on Mycobacterium leprae antigen 7. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1981 Jun;49(2):147–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harte P. G., Cooke A., Playfair J. H. Specific monoclonal IgM is a potent adjuvant in murine malaria vaccination. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):256–258. doi: 10.1038/302256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Brennan P. J. A novel phenolic glycolipid from Mycobacterium leprae possibly involved in immunogenicity and pathogenicity. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):728–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.728-735.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter S. W., Fujiwara T., Brennan P. J. Structure and antigenicity of the major specific glycolipid antigen of Mycobacterium leprae. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15072–15078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanyi J., Sinha S., Aston R., Cussell D., Keen M., Sengupta U. Definition of species specific and cross-reactive antigenic determinants of Mycobacterium leprae using monoclonal antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Jun;52(3):528–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer W. F., Storrs E. E. Attempts to establish the armadillo (Dasypus novemcinctus Linn.) as a model for the study of leprosy. I. Report of lepromatoid leprosy in an experimentally infected armadillo. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1971 Jul-Sep;39(3):693–702. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Tosato G., Blaese R. M., Broder S., Magrath I. T. Polyclonal immunoglobulin secretion by human B lymphocytes exposed to Epstein-Barr virus in vitro. J Immunol. 1979 Apr;122(4):1310–1313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Lagarde A. E., Roder J. C. Human hybridomas constructed with antigen-specific Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6651–6655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Roder J. C. Requirements for the establishment of high-titered human monoclonal antibodies against tetanus toxoid using the Epstein-Barr virus technique. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1275–1280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronvall G., Stanford J. L., Walsh G. P. Studies of mycobacterial antigens, with special reference to Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1132–1138. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1132-1138.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R., Miller R. A. Tumor therapy with monoclonal antibodies. Fed Proc. 1983 Jun;42(9):2650–2656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. N., Draper P., Rees R. J. Serological activity of purified glycolipid from Mycobacterium leprae. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1982 Jun;50(2):220–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks D. L., Esser K. M., Sher A. Immunization of mice against African trypanosomiasis using anti-idiotypic antibodies. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1108–1119. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanford J. L., Rook G. A., Convit J., Godal T., Kronvall G., Rees R. J., Walsh G. P. Preliminary taxonomic studies on the leprosy bacillus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1975 Dec;56(6):579–585. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touw J., Langendijk E. M., Stoner G. L., Belehu A. Humoral immunity in leprosy: immunoglobulin G and M antibody responses to Mycobacterium leprae in relation to various disease patterns. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):885–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.885-892.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widebäck K., Kronvall G., Bjorvatn B., Closs O., Harboe M. Comparative studies of antigen 21 in Mycobacterium and Nocardia species: possible taxonomic relationships with Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1980 Nov;30(2):413–420. doi: 10.1128/iai.30.2.413-420.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Buchanan T. M. A serological test for leprosy with a glycolipid specific for Mycobacterium leprae. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1057–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.6348948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Khanolkar S. R., Barg L. L., Buchanan T. M. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the phenolic glycolipid of Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):183–188. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.183-188.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski V. R., Jr, Spedden S. E., Black P. H., Haber E. Clones of human lymphoblastoid cell lines producing antibody to tetanus toxoid. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:152–155. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


