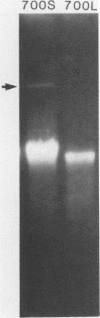
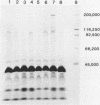
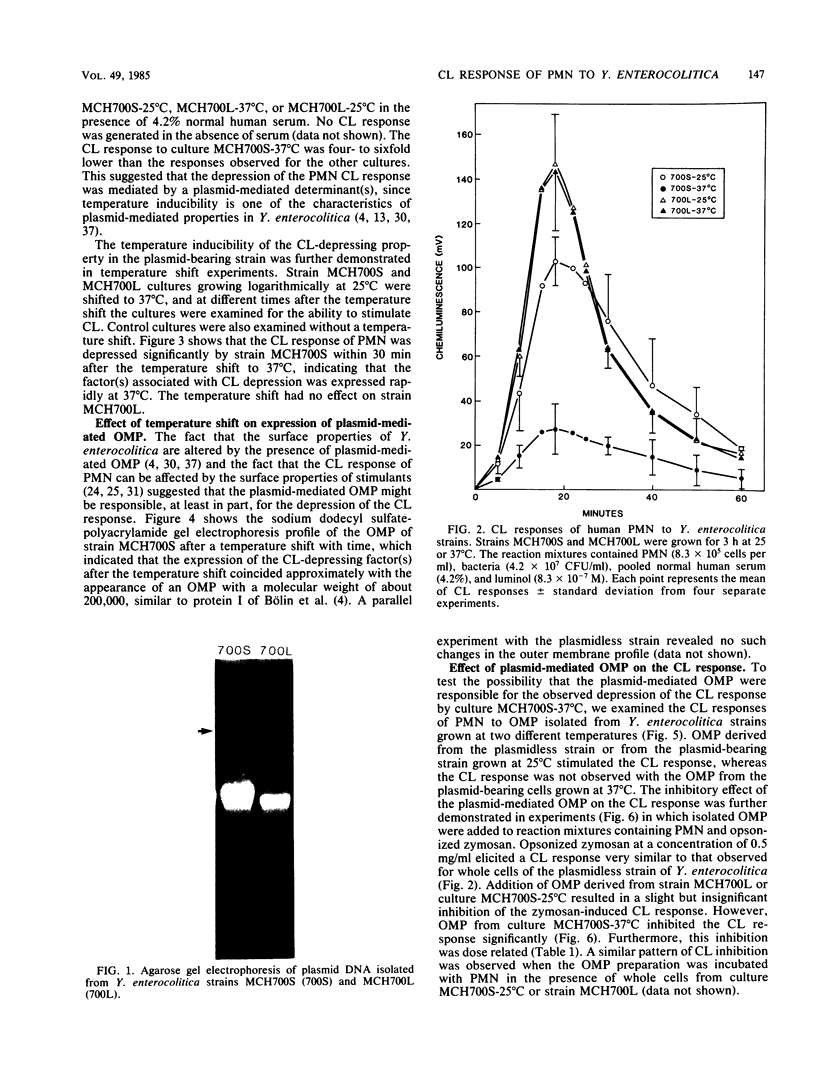
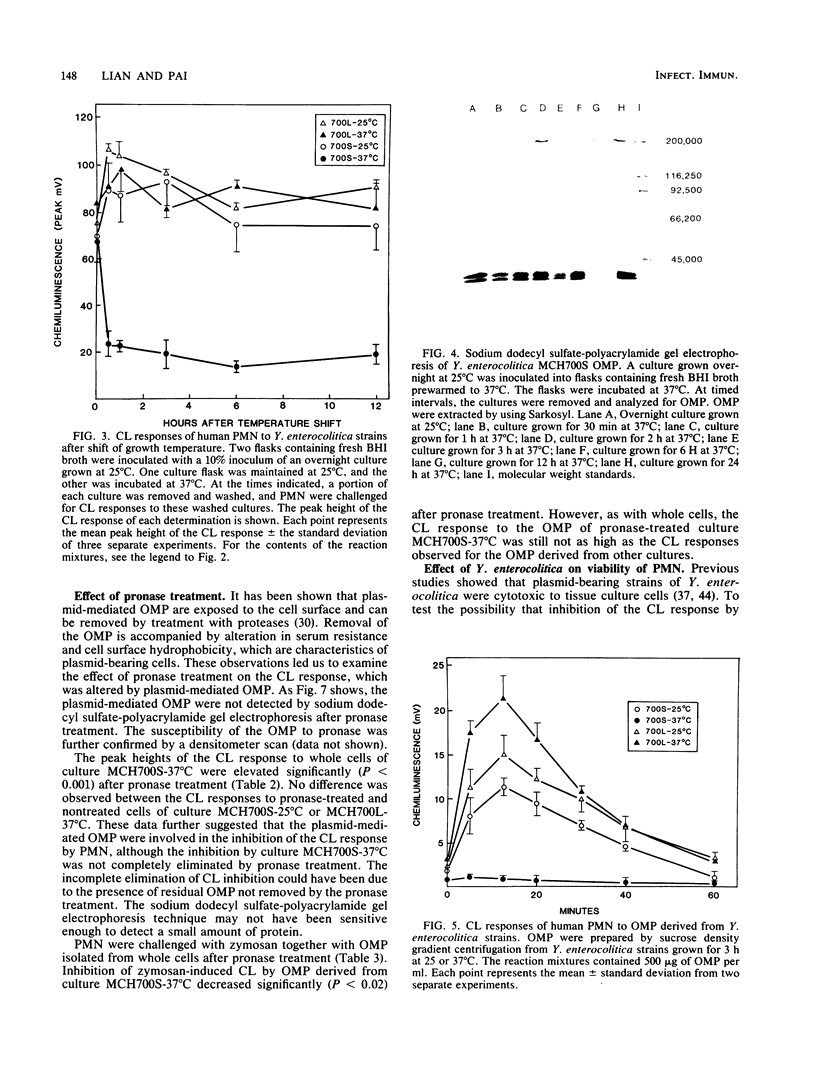
Abstract
Recent studies have shown that the cell surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica are altered by the presence of the virulence plasmid, which mediates temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins (OMP). We investigated the interaction of Y. enterocolitica with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes by monitoring luminol-enhanced chemiluminescence (CL) responses. A plasmid-bearing strain grown at 37 degrees C induced four- to sixfold less CL than did the same strain grown at 25 degrees C or a plasmidless, isogenic strain grown at either temperature. Inhibition of CL responses by whole cells was related to plasmid-mediated expression of OMP. The OMP alone could inhibit the CL response of polymorphonuclear leukocytes stimulated by either opsonized zymosan or whole cells of Y. enterocolitica. Pronase treatment of whole cells, which removed the plasmid-mediated OMP, resulted in partial but significant elimination of CL inhibition by whole cells and by OMP derived from them. Incubation with Y. enterocolitica for 60 min did not affect the viability of polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Our results suggest that the interaction of Y. enterocolitica with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes is directly affected by the plasmid-mediated OMP.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen R. C., Stjernholm R. L., Steele R. H. Evidence for the generation of an electronic excitation state(s) in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes and its participation in bactericidal activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 May 26;47(4):679–684. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90545-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Gurion R., Shafferman A. Essential virulence determinants of different Yersinia species are carried on a common plasmid. Plasmid. 1981 Mar;5(2):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björkstén B., Wadström T. Interaction of Escherichia coli with different fimbriae and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):298–305. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.298-305.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford W. D., Noce P. S., Gutman L. T. Pathologic features of enteric infection with Yersinia enterocolitica. Arch Pathol. 1974 Jul;98(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brubaker R. R. The genus Yersinia: biochemistry and genetics of virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;57:111–158. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65297-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Norlander L., Wolf-Watz H. Temperature-inducible outer membrane protein of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis and Yersinia enterocolitica is associated with the virulence plasmid. Infect Immun. 1982 Aug;37(2):506–512. doi: 10.1128/iai.37.2.506-512.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Wolf-Watz H. Molecular cloning of the temperature-inducible outer membrane protein 1 of Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):72–78. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.72-78.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B. Pathogenecity of Yersinia enterocolitica for mice. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):164–170. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.164-170.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. B., Zahorchak R. J., Brubaker R. R. Plague virulence antigens from Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):638–640. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.638-640.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. T., Doyle M. P. Identification of specific outer membrane polypeptides associated with virulent Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Feb;43(2):472–476. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.2.472-476.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth J. A., Hendley J. O., Mandell G. L. Attachment and ingestion of gonococci human neutrophils. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):512–516. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.512-516.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easmon C. S., Cole P. J., Williams A. J., Hastings M. The measurement of opsonic and phagocytic function by Luminol-dependent chemiluminescence. Immunology. 1980 Sep;41(1):67–74. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLEY M. J., WOOD W. B., Jr Studies on the pathogenicity of group A streptococci. II. The antiphagocytic effects of the M protein and the capsular gel. J Exp Med. 1959 Oct 1;110:617–628. doi: 10.1084/jem.110.4.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferber D. M., Brubaker R. R. Plasmids in Yersinia pestis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):839–841. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.839-841.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T. Plasmid associated with pathogenicity and calcium dependency of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):682–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.682-685.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gemski P., Lazere J. R., Casey T., Wohlhieter J. A. Presence of a virulence-associated plasmid in Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1980 Jun;28(3):1044–1047. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.3.1044-1047.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebner J. V., Mills E. L., Gray G. H., Quie P. G. Comparison of phagocytic and chemiluminescence response of human polymorphonuclear neutrophils. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Jan;89(1):153–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria. XIX. Isolation from Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 and use in reconstitution and definition of the permeability barrier. J Bacteriol. 1978 Oct;136(1):381–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.136.1.381-390.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heesemann J., Algermissen B., Laufs R. Genetically manipulated virulence of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):105–110. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.105-110.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapperud G., Namork E., Skarpeid H. J. Temperature-inducible surface fibrillae associated with the virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1985 Feb;47(2):561–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.2.561-566.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kossack R. E., Guerrant R. L., Densen P., Schadelin J., Mandell G. L. Diminished neutrophil oxidative metabolism after phagocytosis of virulent Salmonella typhi. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):674–678. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.674-678.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreger A., DeChatelet L., Shirley P. Interaction of Vibrio vulnificus with human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: association of virulence with resistance to phagocytosis. J Infect Dis. 1981 Sep;144(3):244–248. doi: 10.1093/infdis/144.3.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachica R. V., Zink D. L., Ferris W. R. Association of fibril structure formation with cell surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):272–275. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.272-275.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Davies J., Grundström T., Kihlström E., Normark S. Surface charge and hydrophobicity of Salmonella, E. coli, Gonococci in relation to their tendency to associate with animal cells. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:135–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R. J. Plasmid-mediated and temperature-regulated surface properties of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):921–930. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.921-930.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musher D. M., Verbrugh H. A., Verhoef J. Suppression of phagocytosis and chemotaxis by cell wall components of Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):84–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., DeStephano L. Serum resistance associated with virulence in Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):605–611. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.605-611.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V., Seemayer T. A. Experimental Yersinia enterocolitica enteritis in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1980 Apr;28(1):238–244. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.1.238-244.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Brubaker R. R. Vwa+ phenotype of Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):166–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.166-171.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Blank H. F., Kingsbury D. T., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of essential plasmid determinants of pathogenicity in Yersinia pestis. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):297–304. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Falkow S. Virulence-associated plasmids from Yersinia enterocolitica and Yersinia pestis. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):877–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.877-883.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Characterization of plasmids and plasmid-associated determinants of Yersinia enterocolitica pathogenesis. Infect Immun. 1981 Feb;31(2):775–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.2.775-782.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H., Bolin I., Beeder A. B., Falkow S. Characterization of common virulence plasmids in Yersinia species and their role in the expression of outer membrane proteins. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):108–114. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.108-114.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinnan G. V., Schooley R., Dolin R., Ennis F. A., Gross P., Gwaltney J. M. Serologic responses and systemic reactions in adults after vaccination with monovalent A/USSR/77 and trivalent A/USSR/77, A/Texas/77, B/Hong Kong/72 influenza vaccines. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):748–757. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M., Bölin I., Heikkinen H., Piha S., Wolf-Watz H. Virulence plasmid-associated autoagglutination in Yersinia spp. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1033–1036. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1033-1036.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skurnik M. Expression of antigens encoded by the virulence plasmid of Yersinia enterocolitica under different growth conditions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jan;47(1):183–190. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.1.183-190.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straley S. C., Brubaker R. R. Cytoplasmic and membrane proteins of yersiniae cultivated under conditions simulating mammalian intracellular environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1224–1228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Une T. Studies on the pathogenicity of Yersinia enterocolitica. I. Experimental infection in rabbits. Microbiol Immunol. 1977;21(7):341–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Sundqvist C., Mäki M. Adherence and toxicity of Yersinia enterocolitica 0:3 and 0:9 containing virulence-associated plasmids for various cultured cells. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1983 Apr;91(2):121–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1983.tb00020.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zink D. L., Feeley J. C., Wells J. G., Vanderzant C., Vickery J. C., Roof W. D., O'Donovan G. A. Plasmid-mediated tissue invasiveness in Yersinia enterocolitica. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):224–226. doi: 10.1038/283224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Oss C. J. Phagocytosis as a surface phenomenon. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1978;32:19–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.32.100178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]