Abstract
The chemical structure and biologic function of the lipid A portion of lipopolysaccharide are not identical among gram-negative bacteria. This study indicates that antigenically heterogeneous lipid A exists among strains of Haemophilus influenzae. An immunoglobulin G3 murine monoclonal antibody, 3D2, produced against a nontypable H. influenzae strain 3524 has specificity for a site on the lipid A portion of the H. influenzae lipopolysaccharide. With the Western blot and immunodot assay, 3D2 recognized this lipid A determinant on 14 of 24 (58%) of strains of nontypable H. influenzae and in 51 of 95 (54%) strains of H. influenzae type b. This lipid A epitope has a high degree of specificity for H. influenzae, since it is not present on the lipid A of 39 gram-negative strains from 14 non-Haemophilus species. In addition, studies of 36 strains of six Haemophilus species other than H. influenzae and 8 strains of 4 species of Actinobacillus did not contain the 3D2 epitope. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay analysis with a kinetic assay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay inhibition confirmed the antigenic heterogeneity of H. influenzae lipid A. Thin-layer chromatography demonstrated that the 3D2 epitope is associated with a chloroform-soluble lipid moiety in the lipid A. Fluorescent antibody analysis of H. influenzae indicated that the epitope is on the cell surface. The monoclonal antibody was not bactericidal for strain 3524, and it did not inhibit the bactericidal action of normal human serum against the same strain. These studies demonstrate that the lipid As of H. influenzae are antigenically heterogeneous.
Full text
PDF

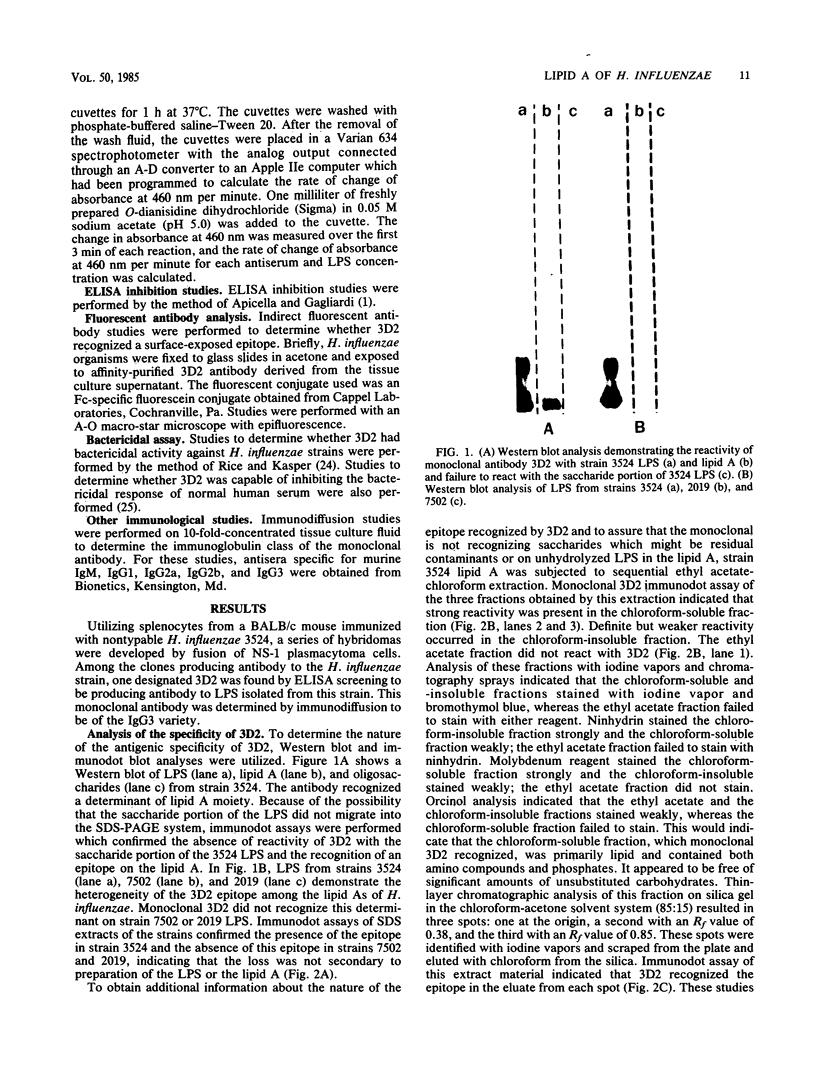


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apicella M. A., Gagliardi N. C. Antigenic heterogeneity of the non-serogroup antigen structure of Neisseria gonorrhoeae lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Dec;26(3):870–874. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.3.870-874.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apicella M. A., Shero M., Dudas K. C., Stack R. R., Klohs W., LaScolea L. J., Murphy T. F., Mylotte J. M. Fimbriation of Haemophilus species isolated from the respiratory tract of adults. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jul;150(1):40–43. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji B., Alving C. R. Lipid A from endotoxin: antigenic activities of purified fractions in liposomes. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2558–2562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Nowotny Relation of structure to function in bacterial O-antigens--VII. Endotoxicity of 'lipid A'. Immunochemistry. 1975 Jan;12(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flesher A. R., Insel R. A. Characterization of lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1978 Dec;138(6):719–730. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.6.719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Freudenberg M. A., Jay F., Nerkar D., Veleva K., Brade H., Strittmatter W. Immunogenic properties of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):546–552. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galanos C., Lüderitz O., Westphal O. Preparation and properties of antisera against the lipid-A component of bacterial lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec 22;24(1):116–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hase S., Rietschel E. T. Isolation and analysis of the lipid A backbone. Lipid A structure of lipopolysaccharides from various bacterial groups. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Mar 16;63(1):101–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inzana T. J. Electrophoretic heterogeneity and interstrain variation of the lipopolysaccharide of Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):492–499. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KASAI N., YAMANO A. STUDIES ON THE LIPIDS OF ENDOTOXINS.(THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF LIPID FRACTIONS). Jpn J Exp Med. 1964 Dec;34:329–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai N. Chemical studies on the lipid component of endotoxin, with special emphasis on its relation to biological activities. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun 30;133(2):486–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb52385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Dimond R. L. Visualization of antigenic proteins on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Gemski P., Alving C. R. Heterogeneity of lipid A. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jul-Aug;6(4):444–448. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.4.444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Gemski P., Alving C. R. Heterogeneity of lipid A: comparison of lipid A types from different gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):900–904. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.900-904.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattsby-Baltzer I., Kaijser B. Lipid A and anti-lipid A. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):758–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.758-763.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Dudas K. C., Mylotte J. M., Apicella M. A. A subtyping system for nontypable Haemophilus influenzae based on outer-membrane proteins. J Infect Dis. 1983 May;147(5):838–846. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.5.838. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myhre E. B. Typing of Haemophilus influenzae by counterimmunoelectrophoresis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1974 Apr;82(2):164–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1974.tb02308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWOTNY A. Relation of structure to function in bacterial O antigens. II. Fractionation of lipids present in Boivin-type endotoxin of Serratia marcescens. J Bacteriol. 1963 Feb;85:427–435. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.2.427-435.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry M. B., Daoust V. The lipopolysaccharides of Neisseria gonorrhoeae colony types 1 and 4. Can J Biochem. 1975 May;53(5):623–629. doi: 10.1139/o75-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raichvarg D., Guenounou M., Brossard C., Agneray J. Characteristics of a lipid preparation (lipid A) from Haemophilus influenzae type a lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):49–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.49-53.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Kasper D. L. Characterization of gonococcal antigens responsible for induction of bactericidal antibody in disseminated infection. J Clin Invest. 1977 Nov;60(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1172/JCI108867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P. A., Kasper D. L. Characterization of serum resistance of Neisseria gonorrhoeae that disseminate. Roles of blocking antibody and gonococcal outer membrane proteins. J Clin Invest. 1982 Jul;70(1):157–167. doi: 10.1172/JCI110589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang V. C., Wilson B. C., Peralta J. M. Quantitative, single-tube, kinetic-dependent enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (k-ELISA). Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:391–403. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]