Abstract
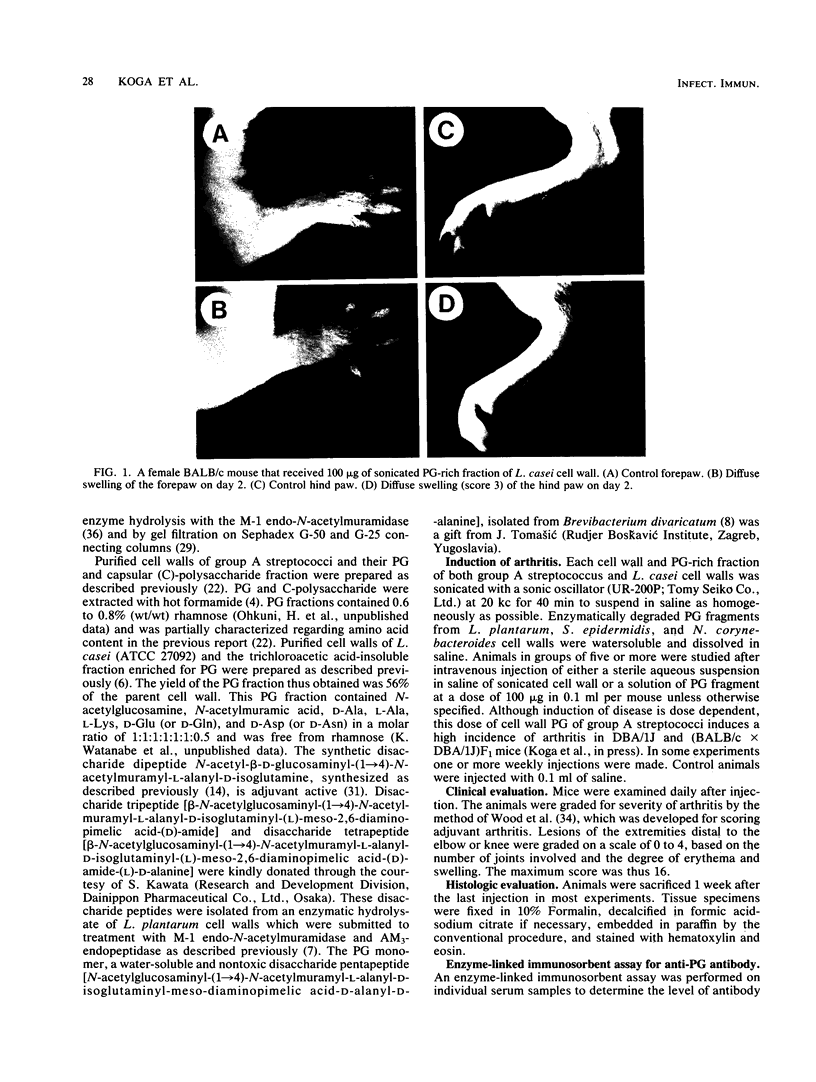
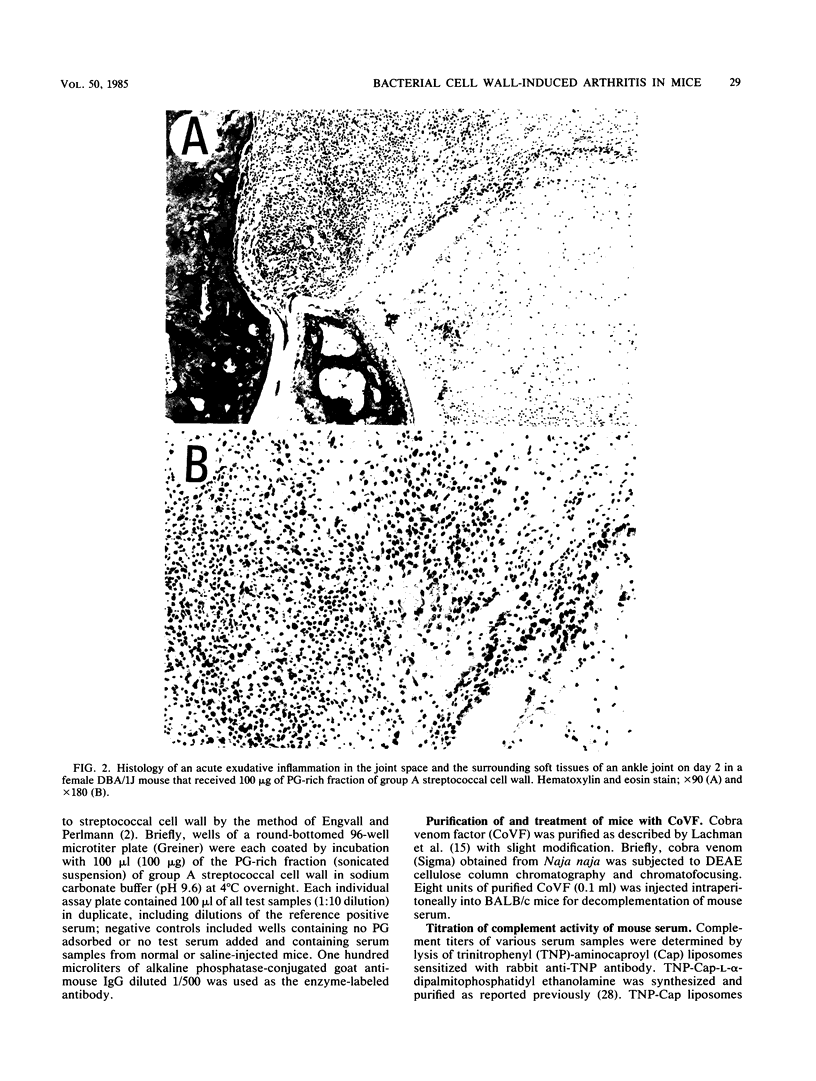
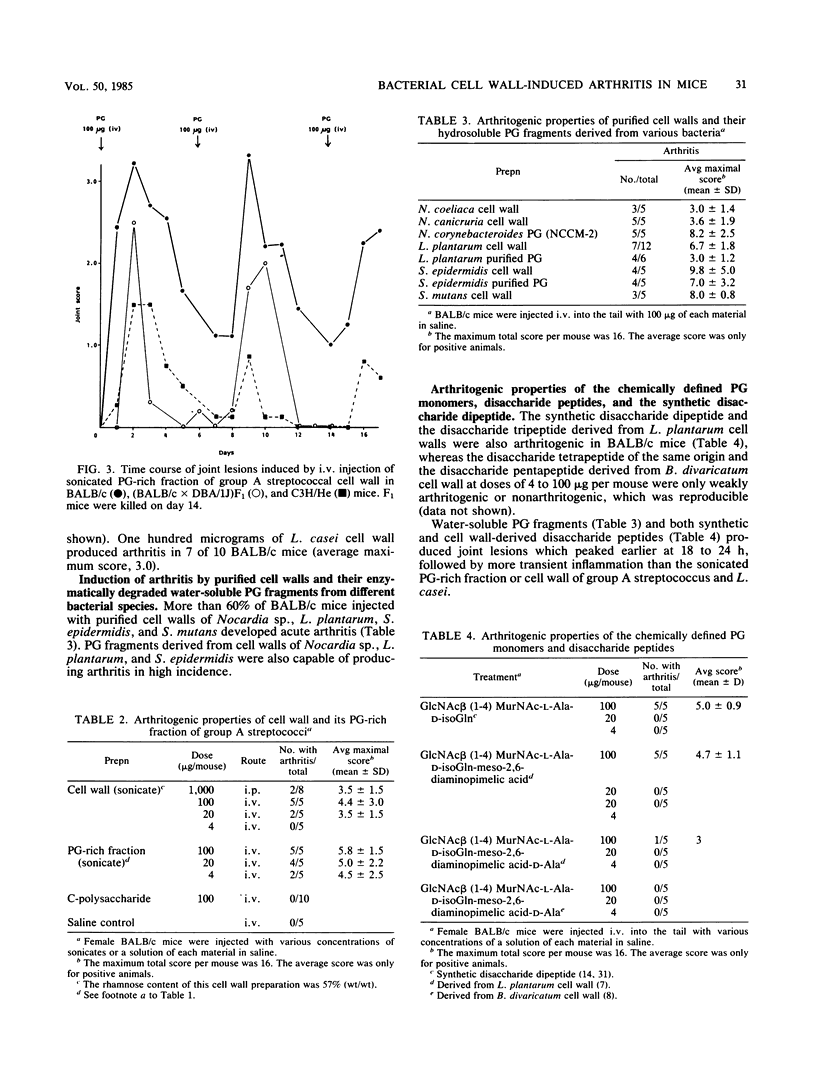
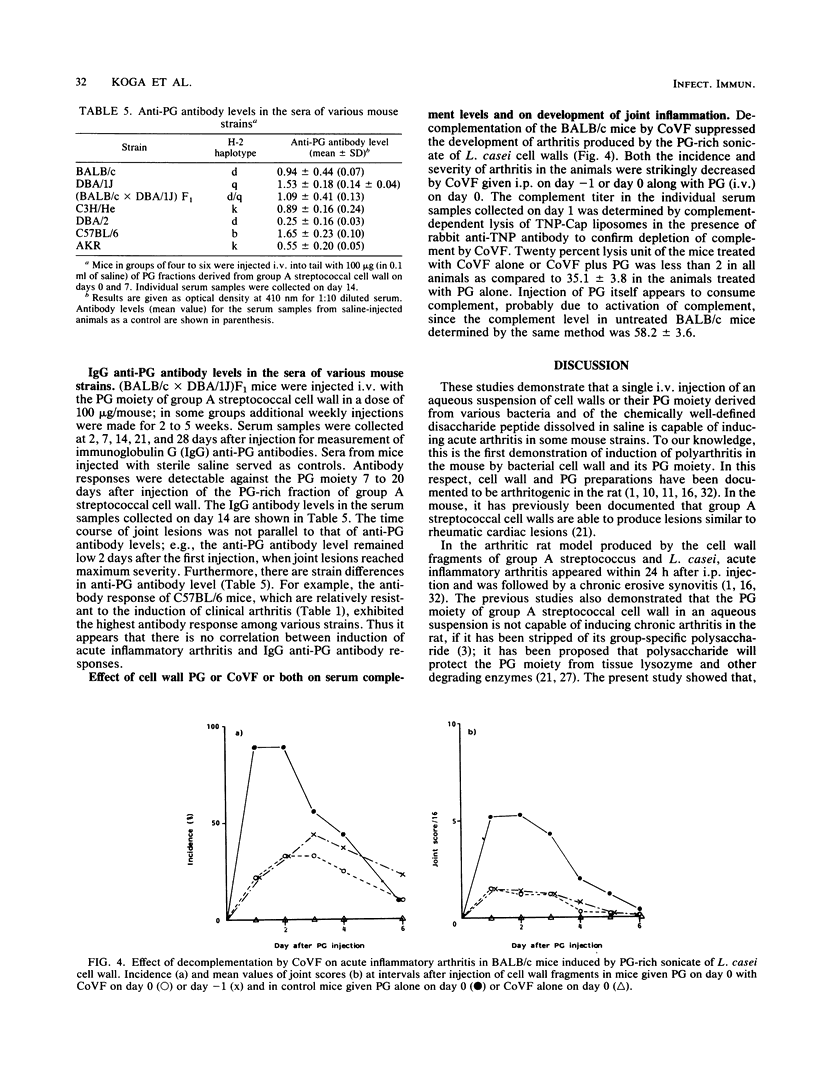
The systemic injection of an aqueous suspension of cell wall or its peptidoglycan (PG)-rich sonicate derived from group A streptococcus and Lactobacillus casei induced acute joint lesions in BALB/c, DBA/1J, (BALB/c X DBA/1J)F1, and C3H/He mouse strains, but not in C57BL/6, DBA/2, and AKR strains. Cell walls and their enzymatically degraded PG fragments from other bacteria as well as the synthetic disaccharide dipeptide and Lactobacillus plantarum cell wall-derived disaccharide tripeptide produced similar acute inflammation in susceptible BALB/c mice. Acute swelling and erythema of the ankles and wrists were observed as early as 3 h, reached maximum severity by day 2, and generally subsided by days 4 to 6 after injection. Histological studies showed synovial proliferation, marked infiltration of many mononuclear cells and a few polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the soft tissues, and extensive deposition of fibrinous exudate in the joint space. Antibody response was detectable against the PG fraction. However, anti-PG antibody does not seem to be responsible for the pathogenesis of this disease. On the other hand, experiments on decomplementation by cobra venom factor suggest that complement components are involved in the early phase of this arthritic model.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cromartie W. J., Craddock J. G., Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Yang C. H. Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1585–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A., Brown R. R., Anderle S. K., Chetty C., Cromartie W. J., Gooder H., Schwab J. H. Arthropathic properties related to the molecular weight of peptidoglycan-polysaccharide polymers of streptococcal cell walls. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1003-1010.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keglević D., Ladesić B., Tomasić J., Valinger Z., Naumski R. Isolation procedure and properties of monomer unit from lysozyme digest of peptidoglycan complex excreted into the medium by penicillin-treated Brevibacterium divaricatum mutant. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jun 12;585(2):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(79)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Maeda K., Onoue K., Kato K., Kotani S. Chemical structure required for immunoadjuvant and arthritogenic activities of cell wall peptidoglycans. Mol Immunol. 1979 Mar;16(3):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90140-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Pearson C. M., Narita T., Kotani S. Polyarthritis induced in the rat with cell walls from several bacteria and two Streptomyces species. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973 Jul;143(3):824–827. doi: 10.3181/00379727-143-37421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Pearson C. M., Watanabe Y., Kotani S., Koga T. Structural requirements for arthritogenicity of peptidoglycans from Staphylococcus aureus and Lactobacillus plant arum and analogous synthetic compounds. J Immunol. 1976 Jun;116(6):1635–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohashi O., Tanaka A., Kotani S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S., Yokogawa K., Kawata S., Ozawa A. Arthritis-inducing ability of a synthetic adjuvant, N-acetylmuramyl peptides, and bacterial disaccharide peptides related to different oil vehicles and their composition. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):70–75. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.70-75.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Narita T., Stewart-Tull D. E., Shimono T., Watanabe Y. Immunoadjuvant activities of cell walls and their water-soluble fractions prepared from various gram-positive bacteria. Biken J. 1975 Jun;18(2):77–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Halbwachs L., Gewurz A., Gewurz H. Purification of cobra venom factor from phospholipase A contaminant. Immunology. 1976 Dec;31(6):961–968. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. J., Allen J. B., Plotz P. H., Wilder R. L. Lactobacillus casei cell wall-induced arthritis in rats: cell wall fragment distribution and persistence in chronic arthritis-susceptible LEW/N and -resistant F344/N rats. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Aug;27(8):939–942. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehman T. J., Allen J. B., Plotz P. H., Wilder R. L. Polyarthritis in rats following the systemic injection of Lactobacillus casei cell walls in aqueous suspension. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Oct;26(10):1259–1265. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J. The ecology and taxonomic status of the lactobacilli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:279–301. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao S., Tanaka A. Muramyl dipeptide-induced adjuvant arthritis. Infect Immun. 1980 May;28(2):624–626. doi: 10.1128/iai.28.2.624-626.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson U. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Deficiency of the fifth component of complement in mice with an inherited complement defect. J Exp Med. 1967 Jan 1;125(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohanian S. H., Schwab J. H., Cromartie W. J. Relation of rheumatic-like cardiac lesions of the mouse to localization of group A streptococcal cell walls. J Exp Med. 1969 Jan 1;129(1):37–49. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuni H., Kimura Y. Increased capillary permeability in guinea pigs and rats by peptidoglycan fraction extracted from Group A streptococcal cell walls. Exp Cell Biol. 1976;44(2):83–94. doi: 10.1159/000163102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Yasuda T., Tsumita T., Okada H. Activation of the alternative complement pathway of guinea-gip by liposomes incorporated with trinitrophenylated phosphatidylethanolamine. Immunology. 1982 Jan;45(1):115–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Yasuda T., Tsumita T., Okada H. Differing reactivities of human and guinea-pig complement on haptenized liposomes via the alternative pathway. Mol Immunol. 1983 Aug;20(8):857–864. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Allen J. B., Anderle S. K., Dalldorf F., Eisenberg R., Cromartie W. J. Relationship of complement to experimental arthritis induced in rats with streptococcal cell walls. Immunology. 1982 May;46(1):83–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab J. H., Ohanian S. H. Degradation of streptococcal cell wall antigens in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1346–1352. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1346-1352.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Six H. R., Uemura K. I., Kinsky S. C. Effect of immunoglobulin class and affinity on the initiation of complement-dependent damage to liposomal model membranes sensitized with dinitrophenylated phospholipids. Biochemistry. 1973 Sep 25;12(20):4003–4011. doi: 10.1021/bi00744a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Kato K., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Inage M., Shiba T., Yano I., Kawata S., Yokogawa K. Macrophage activation by bacterial cell walls and related synthetic compounds. Infect Immun. 1979 Jul;25(1):48–53. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.1.48-53.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada H., Tsujimoto M., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Inage M., Shiba T., Nagao S., Yano I., Kawata S., Yokogawa K. Mitogenic effects of bacterial cell walls, their fragments, and related synthetic compounds on thymocytes and splenocytes of guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1979 Aug;25(2):645–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.2.645-652.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto M., Kinoshita F., Okunaga T., Kotani S., Kusumoto S., Yamamoto K., Shiba T. Higher immunoadjuvant activities of N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminyl-(1-4)-N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine in comparison with N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanyl-D-isoglutamine. Microbiol Immunol. 1979;23(9):933–936. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1979.tb02828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Wahl L. M., Calandra G. B., Wahl S. M. The pathogenesis of group A streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Comparative studies in arthritis resistant and susceptible inbred rat strains. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1442–1451. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Calandra G. B., Garvin A. J., Wright K. D., Hansen C. T. Strain and sex variation in the susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1064–1072. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood F. D., Pearson C. M., Tanaka A. Capacity of mycobacterial wax D and its subfractions to induce adjuvant arthritis in rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1969;35(5):456–467. doi: 10.1159/000230198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda T., Naito Y., Tsumita T., Tadakuma T. A simple method to measure anti-glycolipid antibody by using complement-mediated immune lysis of fluorescent dye-trapped liposomes. J Immunol Methods. 1981;44(2):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]