Abstract
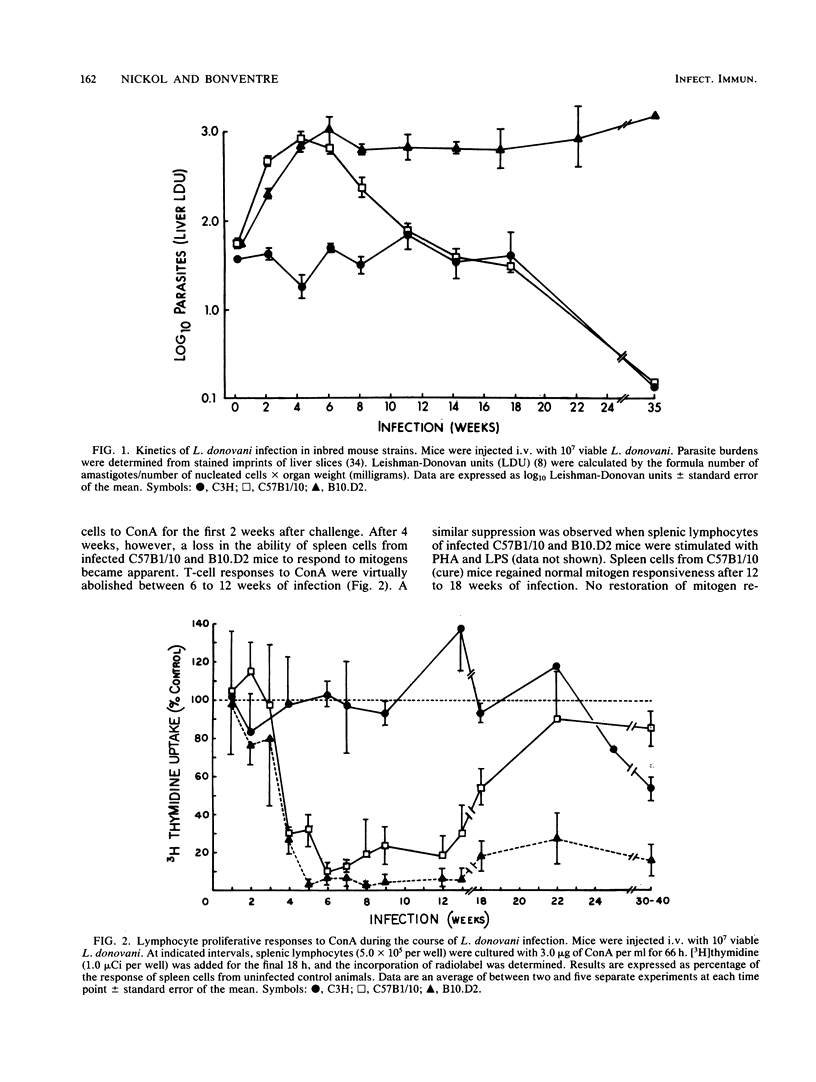
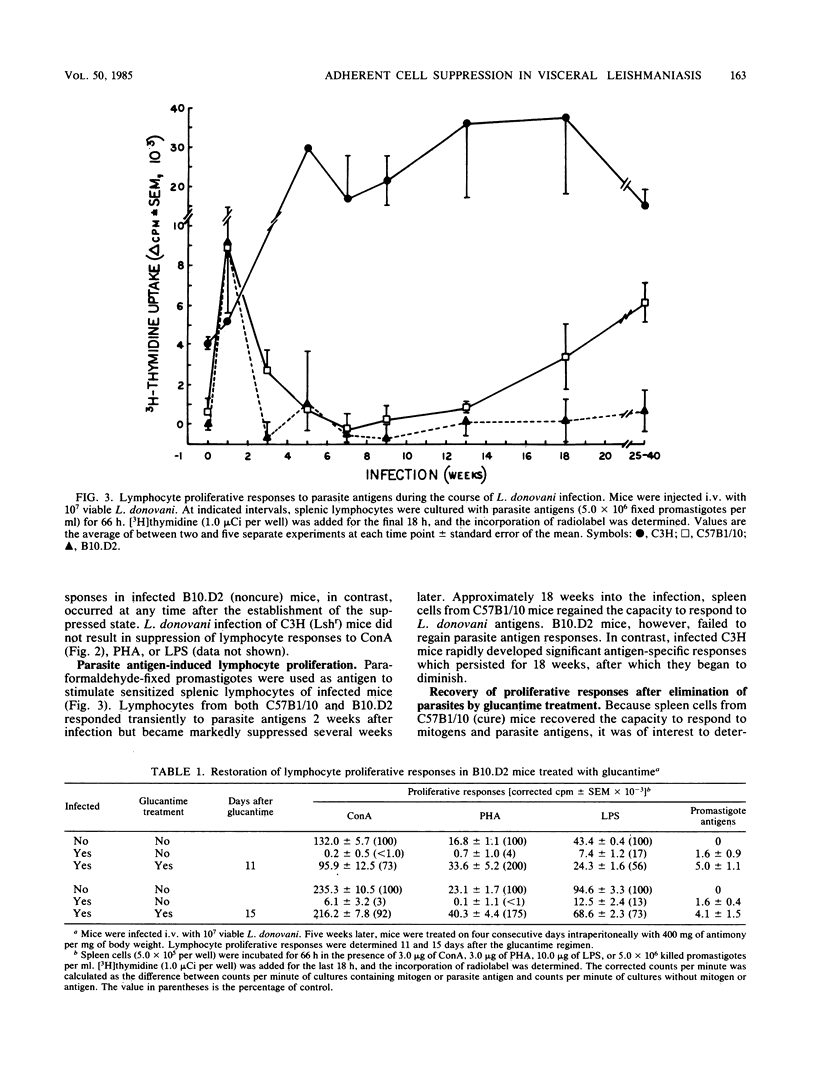
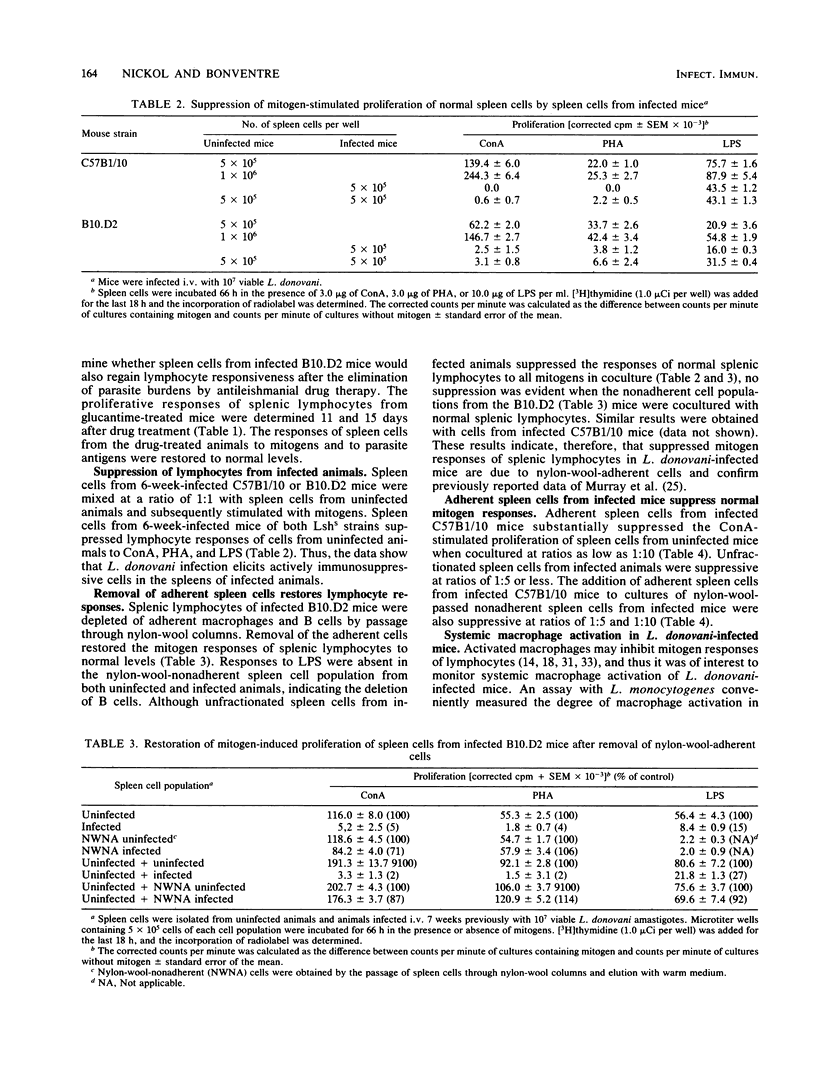
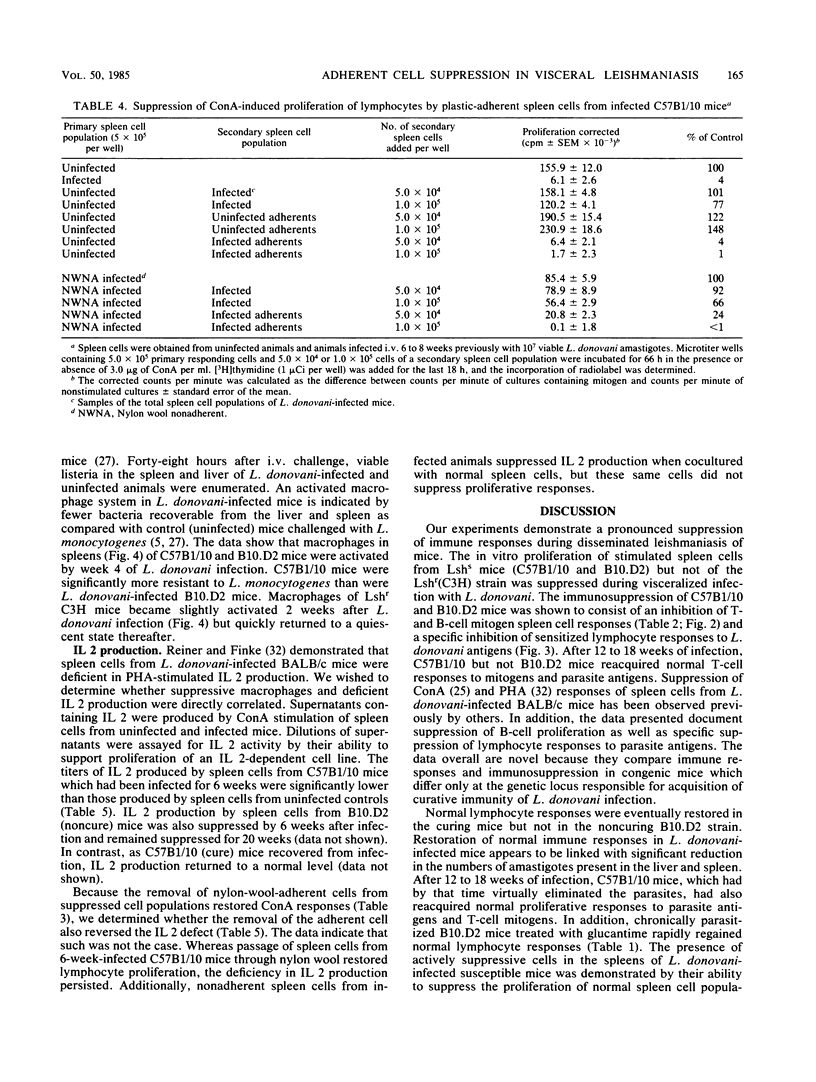
Visceral leishmaniasis is one of several parasitic diseases of humans characterized by immune suppression. A murine model of disseminated leishmaniasis utilizing inbred strains of specific genetic constitution was used to study the mechanisms of immunosuppression elicited during the course of infection. Resistant (Lshr) and susceptible (Lshs) strains of mice were challenged with amastigotes of Leishmania donovani and evaluated as to immune status at intervals between 2 and 40 weeks after challenge. The proliferative responses of splenic lymphocytes to T-cell mitogens, a B-cell mitogen, and parasite antigens were measured to evaluate the relative immune status of parasitized mice and noninfected control mice. Lymphocytes from resistant C3Heb/FeJ (C3H) mice responded normally to concanavalin A and phytohemagglutinin throughout the course of infection. Parasite antigen responses appeared 2 weeks after challenge of C3H mice and remained vigorous for periods up to 6 months. In contrast, immune suppression during infection was profound in both the curing (C57B1/10) and noncuring (B10.D2) phenotypes of Lshs congenic mice. Both Lshs strains developed severe infection as evidenced by high parasite burdens in the liver and spleen 4 to 5 weeks after challenge; splenic lymphocytes taken from these mice between 2 and 8 weeks became increasingly unresponsive to the T-cell mitogens as well as to parasite antigens. The noncuring B10.D2 mice which suffered chronic infection continued to be suppressed for as long as 40 weeks. C57B1/10 (curing) mice, in contrast, cleared infection between 12 and 16 weeks. After spontaneous recovery or elimination of parasites by antimonial drug therapy, the response of spleen cells to T-cell mitogens or parasite antigens were restored to normal. The spleen cells from the Lshs strains of mice obtained during the height of infection suppressed the proliferative responses of spleen cells from their uninfected counterparts upon cocultivation in vitro. Removal of adherent cells from the suppressive spleen cell populations restored normal mitogen responses. On the basis of adherence characteristics, phagocytosis, and morphology, the suppressor was identified as a macrophage population which appears to be responsible for a nonspecific immunosuppression of Lshs mice with significant parasite burdens of L. donovani.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artz R. P., Bullock W. E. Immunoregulatory responses in experimental disseminated histoplasmosis: depression of T-cell-dependent and T-effectory responses by activation of splenic suppressor cells. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):893–902. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.893-902.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird L. G., Kaplan A. M. Macrophage regulation of mitogen-induced blastogenesis. I. Demonstration of inhibitory cells in the spleens and peritoneal exudates of mice. Cell Immunol. 1977 Jan;28(1):22–35. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(77)80003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell J., Freeman J., Bradley D. Influence of H-2 complex on acquired resistance to Leishmania donovani infection in mice. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):72–74. doi: 10.1038/283072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Bubel H. C., Michael J. G., Nickol A. D. Effects of solid tumors on the resistance of mice to viral and bacterial infections. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1982 Feb;169(2):165–174. doi: 10.3181/00379727-169-41327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonventre P. F., Nickol A. D. Leishmania donovani infection in athymic mice derived from parental strains of the susceptible (Lshs) or resistant (Lshr) phenotype. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Nov;36(5):651–658. doi: 10.1002/jlb.36.5.651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Kirkley J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. I. the variable course of Leishmania donovani infections in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):119–129. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. II. genetic control of acute susceptibility of mice to Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Oct;30(1):130–140. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Taylor B. A., Blackwell J., Evans E. P., Freeman J. Regulation of Leishmania populations within the host. III. Mapping of the locus controlling susceptibility to visceral leishmaniasis in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):7–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa M., Narayanan P. R., Miller H. C. Suppressive activity of splenic adherent cells from Plasmodium chabaudi-infected mice. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):749–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crocker P. R., Blackwell J. M., Bradley D. J. Transfer of innate resistance and susceptibility to Leishmania donovani infection in mouse radiation bone marrow chimaeras. Immunology. 1984 Jul;52(3):417–422. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Good D. L. X-linked hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta: a case report. Dent Dimens. 1980 Jun;13(2):21–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidaris C. G., Bonventre P. F. Elimination of Leishmania donovani amastigotes by activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):918–926. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.918-926.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel-Bellan A., Joskowicz M., Fradelizi D., Eisen H. Modification of T-cell proliferation and interleukin 2 production in mice infected with Trypanosoma cruzi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3466–3469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockmeyer W. T., Walters D., Gore R. W., Williams J. S., Fortier A. H., Nacy C. A. Intracellular destruction of Leishmania donovani and Leishmania tropica amastigotes by activated macrophages: dissociation of these microbicidal effector activities in vitro. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3120–3125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum F. Immunologic deficiency during experimental Chagas' disease (Trypanosoma cruzi infection): role of adherent, nonspecific esterase-positive splenic cells. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2202–2205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Holden H. T., Herberman Splenic suppressor macrophages induced in mice by injection of Corynebacterium parvum. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1212–1216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Muchmore A. V., Chused T. M., Holden H. T., Herberman R. B. Inhibition of proliferation of lymphoma cells and T lymphocytes by suppressor cells from spleens of tumor-bearing mice. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):206–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung J. T., Brooks S. B., Jakway J. P., Leonard L. L., Talmage D. W. Suppression of in vitro cytotoxic response by macrophages due to induced arginase. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):665–672. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason U. G., 3rd, Greenberg L. E., Yen S. S., Kirkpatrick C. H. Indomethacin-responsive mononuclear cell dysfunction in "atypical" mycobacteriosis. Cell Immunol. 1982 Jul 15;71(1):54–65. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger Z., Hoffeld J. T., Oppenheim J. J. Macrophage-mediated suppression. I. Evidence for participation of both hdyrogen peroxide and prostaglandins in suppression of murine lymphocyte proliferation. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):983–988. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Masur H., Keithly J. S. Cell-mediated immune response in experimental visceral leishmaniasis. I. Correlation between resistance to Leishmania donovani and lymphokine-generating capacity. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickol A. D., Bonventre P. F. Visceral leishmaniasis in congenic mice of susceptible and resistant phenotypes: T-lymphocyte-mediated immunosuppression. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):169–174. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.169-174.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. T cell dependence of macrophage activation and mobilization during infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1974 Jul;10(1):66–71. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.1.66-71.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opitz H. G., Niethammer D., Jackson R. C., Lemke H., Huget R., Flad H. D. Biochemical characterization of a factor released by macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1975 Jul;18(1):70–75. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(75)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Collins F. M. Immune response to atypical mycobacteria: immunocompetence of heavily infected mice measured in vivo fails to substantiate immunosuppression data obtained in vitro. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):32–37. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.32-37.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant J. E., Blackwell J. M., O'Brien A. D., Bradley D. J., Glynn A. A. Are the Lsh and Ity disease resistance genes at one locus on mouse chromosome 1? Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):510–511. doi: 10.1038/297510a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope B. L., Whitney R. B., Levy J. G., Kilburn D. G. Suppressor cells in the spleens of tumor-bearing mice: enrichment by centrifugation on hypaque-ficoll and characterization of the suppressor population. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1342–1346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner N. E., Finke J. H. Interleukin 2 deficiency in murine Leishmaniasis donovani and its relationship to depressed spleen cell responses to phytohemagglutinin. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1487–1491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAUBER L. A. IMMUNITY TO LEISHMANIA. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Dec 30;113:409–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb40679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöberg O. Effect of allogeneic cell interaction on the primary immune response in vitro. Cell types involved in suppression and stimulation of antibody synthesis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Nov;12(3):365–375. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland G. T., Ahmed A., Sell K. W. Blastogenic response of Toxoplasma-infected mouse spleen cells to T- and B-cell mitogens. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):167–176. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youdim S. Enhancing and suppressive effects of macrophages on T-lymphocyte stimulation in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1979 Jul;45(2):377–388. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(79)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


