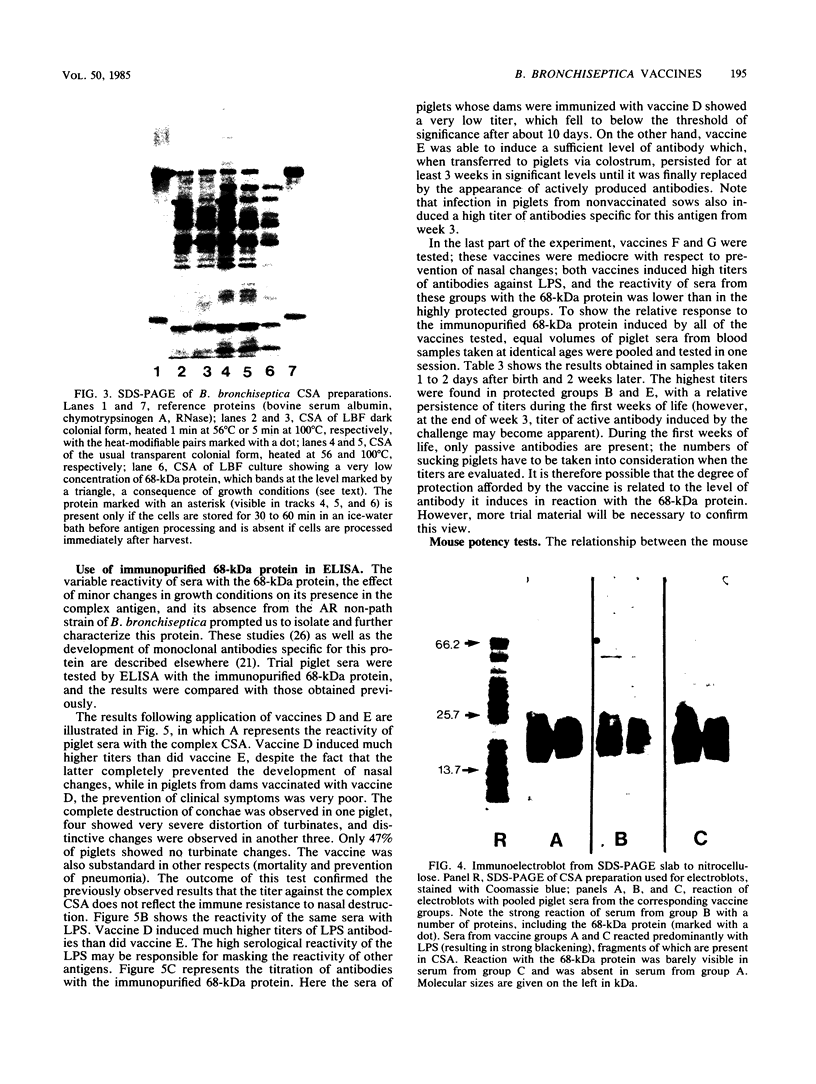
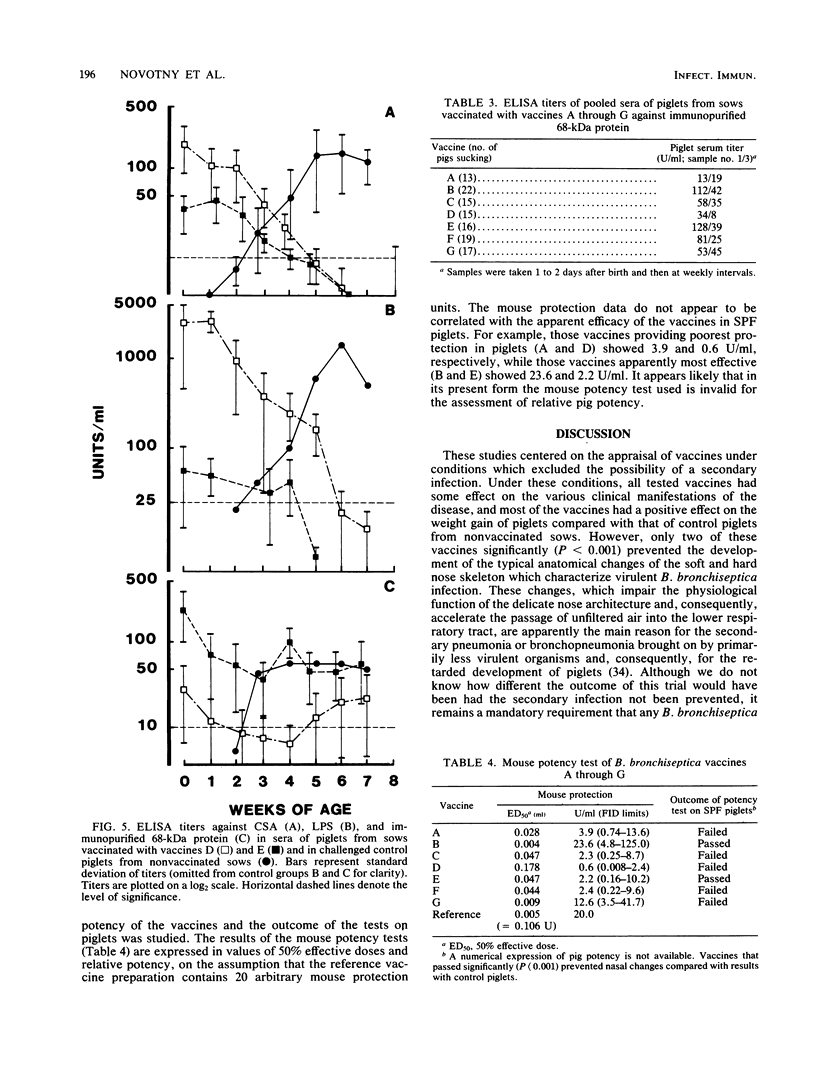
Abstract
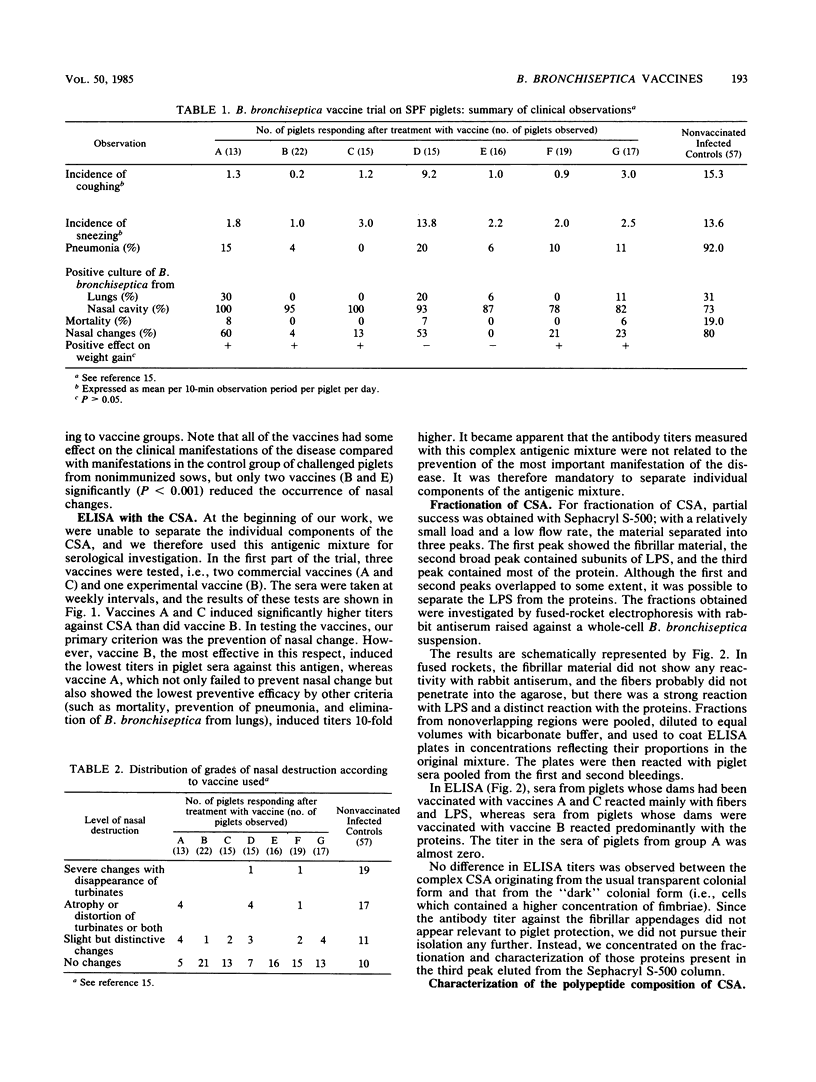
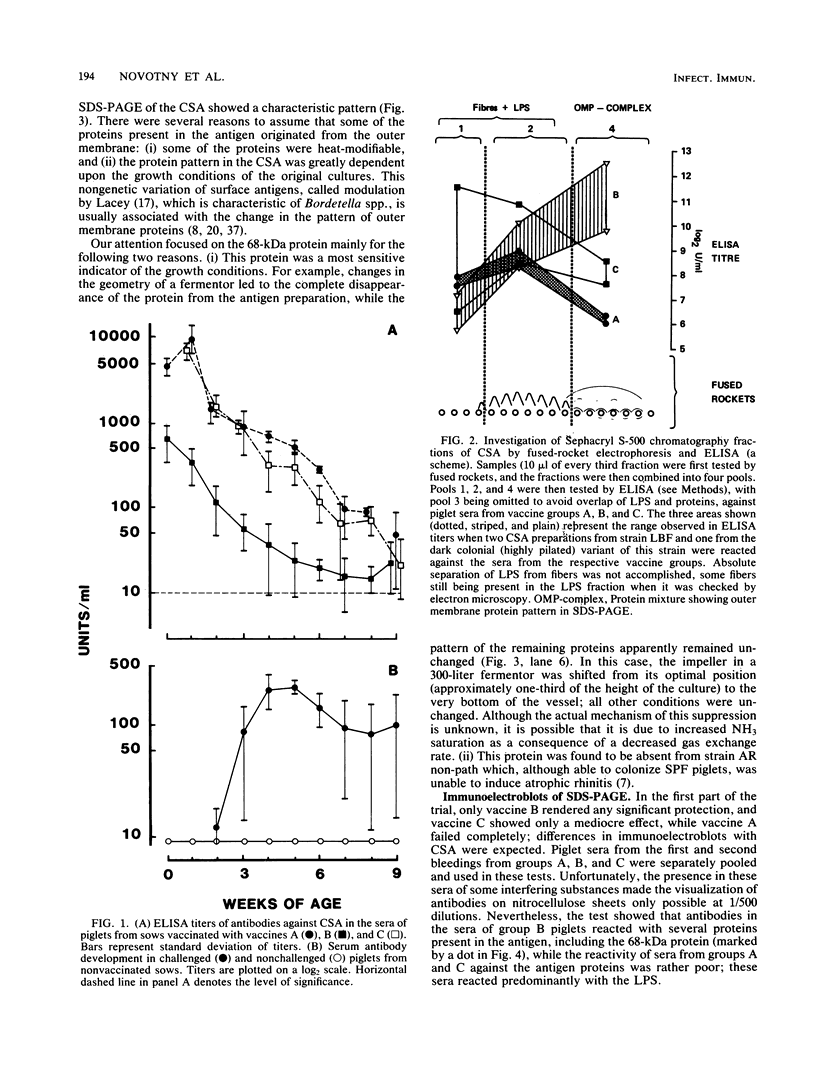
The progenies of specific-pathogen-free sows which had been immunized with Bordetella bronchiseptica vaccines of various origin before parturition were challenged intranasally with B. bronchiseptica within 5 days of birth. Sera of piglets were taken weekly and investigated by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay against a mixture of B. bronchiseptica cell surface antigens containing curled fibers and fimbriae, lipopolysaccharide, and a mixture of proteins mostly derived from the outer membrane. The serological response to this antigenic mixture was paradoxical; the highest titers were obtained with the least effective vaccines. Antibodies which did relate to protection were oriented against the outer-membrane-derived proteins, one of which, of 68,000 molecular weight, appeared to be particularly important for two reasons. First, its concentration within the antigenic mixture was dependent upon cultural conditions; of all the proteins present in virulent strains, it was the first to disappear upon modulation. Second, it was absent from a strain which was unable to induce atrophic rhinitis in specific-pathogen-free piglets. Although all vaccines tested had some beneficial effect on the various clinical manifestations of the disease, only two vaccines were effective (P less than 0.001) in the prevention of nasal pathological changes. These two vaccines also stimulated the highest titers against the 68,000-molecular-weight protein. A mouse protection test utilizing a lethal intraperitoneal challenge failed to monitor the efficacy of vaccines for protection against atrophic rhinitis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bercovich Z., Oosterwoud R. A. Vaccination with Bordetella bronchiseptica vaccine on a farm with atrophic rhinitis: an evaluation of a field experiment. Tijdschr Diergeneeskd. 1977 Apr 15;102(8):485–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROSS R. F. Bordetella bronchiseptica-induced porcine atrophic rhinitis. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1962 Dec 15;141:1467–1468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaby R., Szabó L. 3-Deoxy-2-octulosonic acid 5-phosphate: a component of the endotoxin of Bordetella pertussis. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 1;59(1):277–280. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezzell J. W., Dobrogosz W. J., Kloos W. E., Manclark C. R. Phase-shift markers in Bordetella: alterations in envelope proteins. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):562–569. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow R. A. Biology of Bordetella bronchiseptica. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):722–738. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.722-738.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow R. A., Lehr C. D., Shade F. J., Wisecarver J. L. Mouse potency assay for Bordetella bronchiseptica bacterins. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Oct;6(4):337–339. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.4.337-339.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOREJSI J., SMETANA R. The isolation of gamma globulin from blood-serum by rivanol. Acta Med Scand. 1956 Jun 30;155(1):65–70. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1956.tb14351.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. L., Switzer W. P. Turbinate atrophy in young pigs exposed to Bordetella bronchiseptica, Pasteurella multocida, and combined inoculum. Am J Vet Res. 1968 Apr;29(4):777–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartree E. F. Determination of protein: a modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Anal Biochem. 1972 Aug;48(2):422–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90094-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., Van Alphen L. Molecular architecture and functioning of the outer membrane of Escherichia coli and other gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Mar 21;737(1):51–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPheat W. L., Wardlaw A. C., Novotny P. Modulation of Bordetella pertussis by nicotinic acid. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):516–522. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.516-522.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
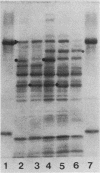
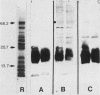
- Montaraz J. A., Novotny P., Ivanyi J. Identification of a 68-kilodalton protective protein antigen from Bordetella bronchiseptica. Infect Immun. 1985 Mar;47(3):744–751. doi: 10.1128/iai.47.3.744-751.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Brookes J. E. The use of Bordetella pertussis preserved in liquid nitrogen as a challenge suspension in the Kendrick mouse protection test. J Biol Stand. 1975;3(1):11–29. doi: 10.1016/0092-1157(75)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novotny P., Chubb A. P., Cownley K., Montaraz J. A. Adenylate cyclase activity of a 68,000-molecular-weight protein isolated from the outer membrane of Bordetella bronchiseptica. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):199–206. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.199-206.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov I., Orskov F., Jann B., Jann K. Serology, chemistry, and genetics of O and K antigens of Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):667–710. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.667-710.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B. The serology of Bordetella bronchiseptica isolated from pigs compared with strains from other animal species. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1975 Dec;83(6):590–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1975.tb00142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman J. T., Hopman C. T., Zanen H. C. Immunochemical characterization of Neisseria meningitidis serotype antigens by immunodiffusion and SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis immunoperoxidase techniques and the distribution of serotypes among cases and carriers. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 Feb;116(2):465–473. doi: 10.1099/00221287-116-2-465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiya K., Kawahira M., Nakase Y. Protection against experimental Bordetella bronchiseptica infection in mice by active immunization with killed vaccine. Infect Immun. 1983 Aug;41(2):598–603. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.2.598-603.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Nakagawa M., Shibata S., Suzuki K. Atrophic rhinitis produced by intranasal inoculation of Bordetella bronchiseptica in hysterectomy produced colostrum-deprived pigs. Cornell Vet. 1971 Oct;61(4):696–705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith I. M., Baskerville A. J., Brothwell E., Oliphant J. Immunogenicity of killed Bordetella bronchiseptica vaccines in the mouse. Res Vet Sci. 1982 Mar;32(2):248–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. Studies on gonococcus infection. XIV. Cell wall protein differences among color/opacity colony variants of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):292–302. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.292-302.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw A. C., Parton R., Hooker M. J. Loss of protective antigen, histamine-sensitising factor and envelope polypeptides in cultural variants of Bordetella pertussis. J Med Microbiol. 1976 Feb;9(1):89–100. doi: 10.1099/00222615-9-1-89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]