Abstract
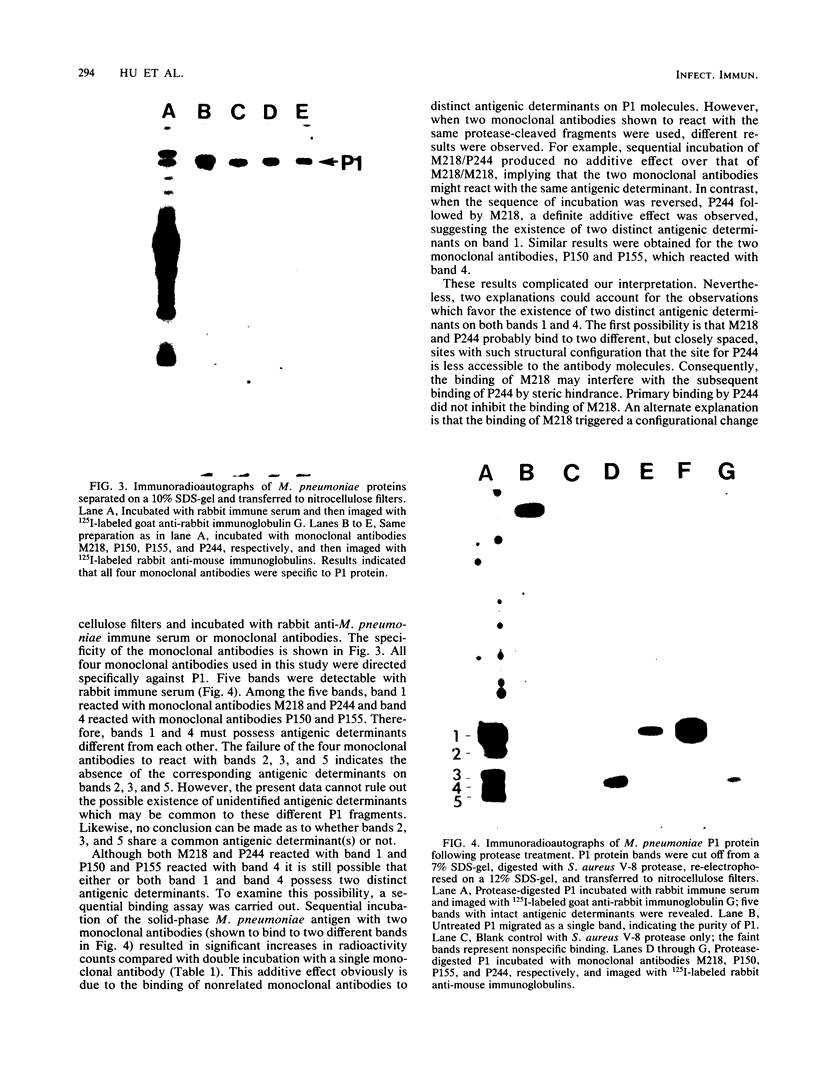
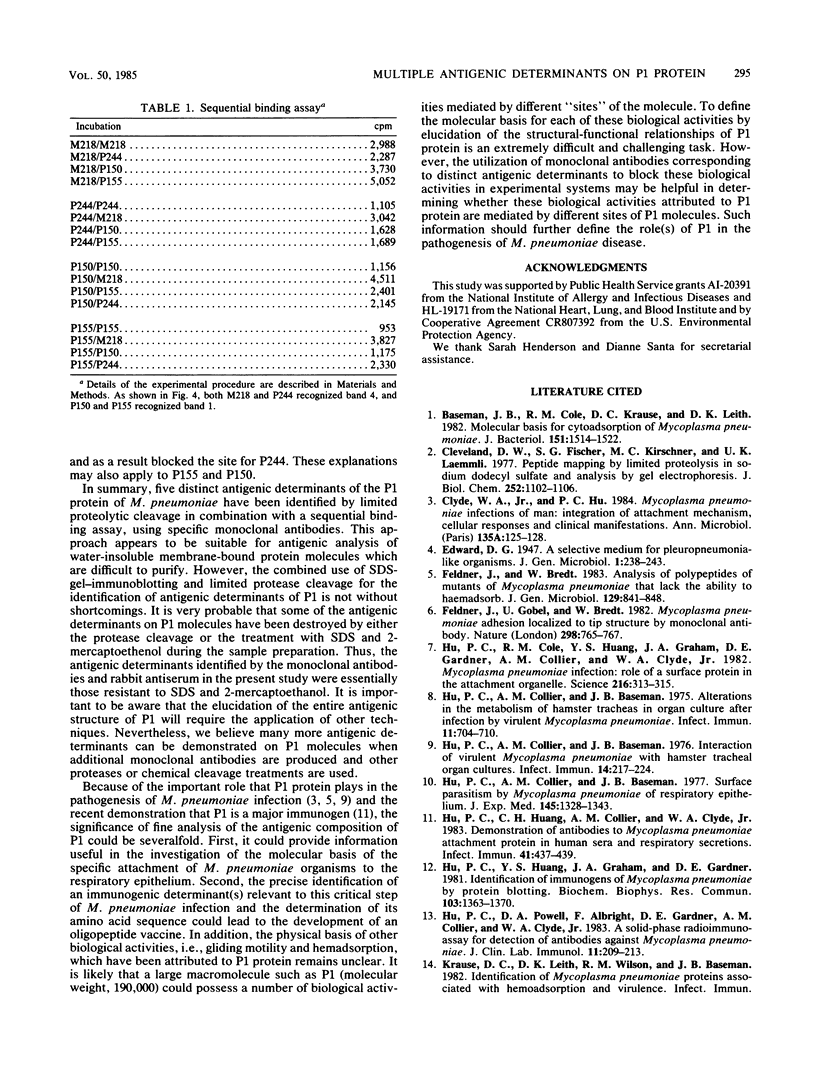
Distinct multiple antigenic determinants of the attachment protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae have been identified by limited proteolytic cleavage, using specific monoclonal antibodies. Western blots prepared from the gels containing the cleaved fragments were probed with antiserum against M. pneumoniae or monoclonal antibodies. Five distinct bands with intact antigenic determinants were detected by the antiserum, of which two bands were each reactable with two monoclonal antibodies. A sequential binding assay suggested that these monoclonal antibodies recognized different antigenic sites of each band. These results demonstrate the existence of multiple antigenic sites on the attachment protein and describe procedures that should prove useful for identifying those antigenic sites critical to the specific attachment of M. pneumoniae.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baseman J. B., Cole R. M., Krause D. C., Leith D. K. Molecular basis for cytadsorption of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1514–1522. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1514-1522.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
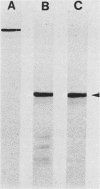
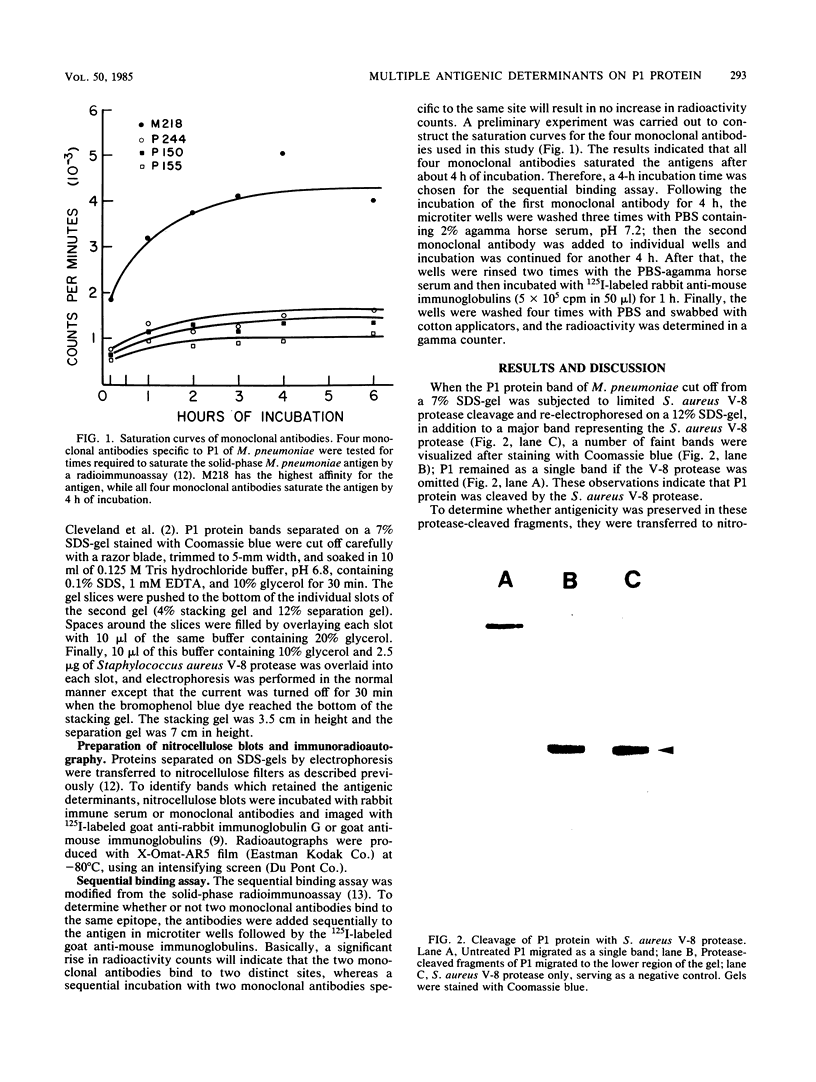
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clyde W. A., Jr, Hu P. C. Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections of man: integration of attachment mechanism, cellular responses and clinical manifestations. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1984 Jan-Feb;135A(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(84)80068-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Bredt W. Analysis of polypeptides of mutants of Mycoplasma pneumoniae that lack the ability to haemadsorb. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Mar;129(3):841–848. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-3-841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldner J., Göbel U., Bredt W. Mycoplasma pneumoniae adhesin localized to tip structure by monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):765–767. doi: 10.1038/298765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Cole R. M., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: role of a surface protein in the attachment organelle. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):313–315. doi: 10.1126/science.6801766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Alterations in the metabolism of hamster tracheas in organ culture after infection by virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):704–710. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.704-710.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Interaction of virulent Mycoplasma pneumoniae with hamster tracheal organ cultures. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):217–224. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.217-224.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Collier A. M., Baseman J. B. Surface parasitism by Mycoplasma pneumoniae of respiratory epithelium. J Exp Med. 1977 May 1;145(5):1328–1343. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.5.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Huang C. H., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr Demonstration of antibodies to Mycoplasma pneumoniae attachment protein in human sera and respiratory secretions. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):437–439. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.437-439.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Huang Y. S., Graham J. A., Gardner D. E. Identification of immunogens of Mycoplasma pneumoniae by protein blotting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Dec 31;103(4):1363–1370. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu P. C., Powell D. A., Albright F., Gardner D. E., Collier A. M., Clyde W. A., Jr A solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of antibodies against Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Clin Lab Immunol. 1983 Aug;11(4):209–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell D. A., Clyde W. A., Jr Opsonin-reversible resistance of Mycoplasma pneumoniae to in vitro phagocytosis by alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1975 Mar;11(3):540–550. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.3.540-550.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radestock U., Bredt W. Motility of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1495–1501. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1495-1501.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M., Wilde C. D., Köhler G. A better cell line for making hybridomas secreting specific antibodies. Nature. 1978 Nov 16;276(5685):269–270. doi: 10.1038/276269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]