Abstract
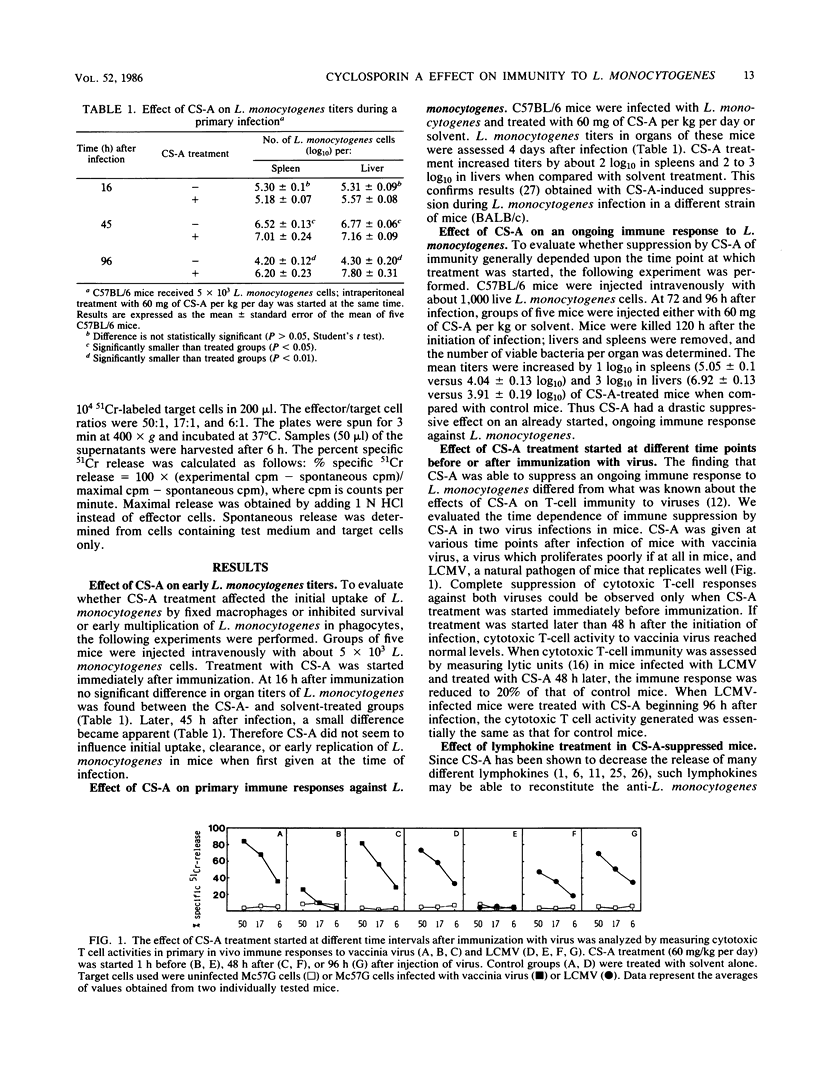
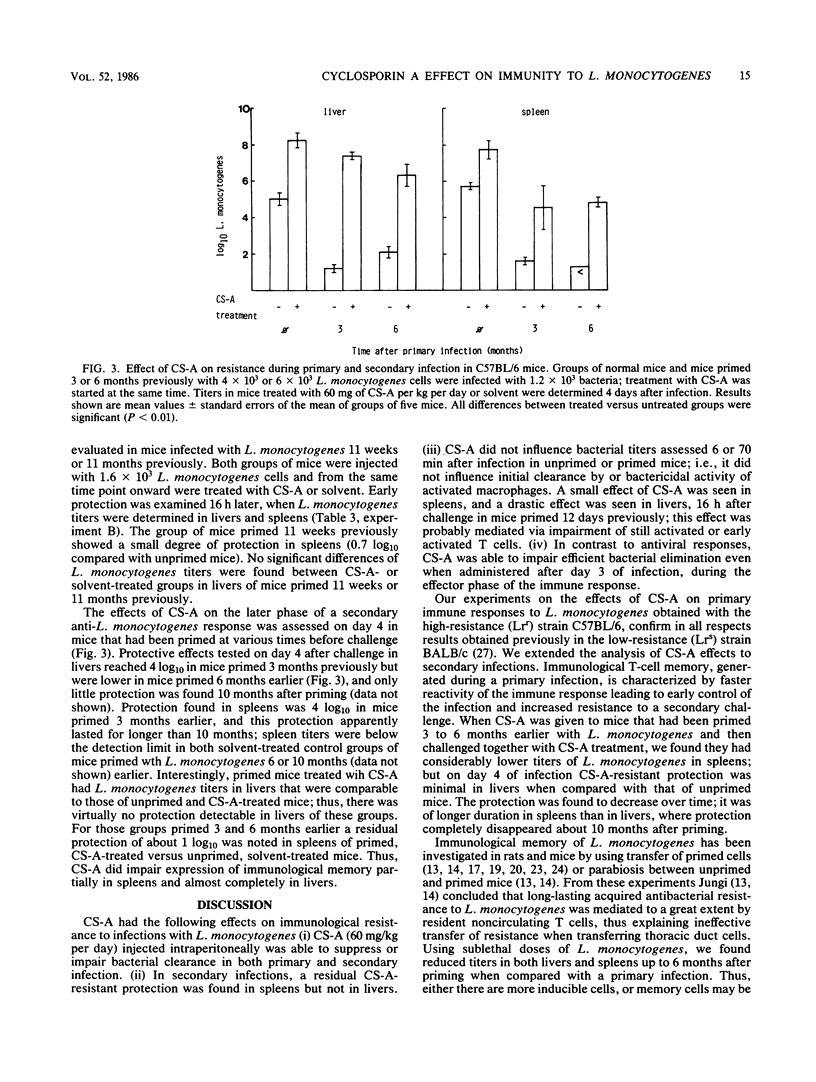
The effect of the immunosuppressive drug cyclosporin A (CS-A) on immunity to the facultative intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes was investigated in unprimed and primed mice. Different treatment protocols were followed to evaluate the time dependence of CS-A-mediated immune suppression and the effect of CS-A on immunological memory to L. monocytogenes. The effect of CS-A was observed only during and after activation of T cell-mediated immunity, whereas early resistance exerted by macrophages assessed 6 and 70 min after challenge remained unaffected. CS-A suppressed efficient elimination of L. monocytogenes even when given after day 3 of a primary infection. This contrasts with findings in other models, including viral infections, where CS-A must be administered very early in an immune response to suppress it. CS-A suppressed antibacterial resistance in mice primed at various times before challenge; suppression of protection was time dependent and was virtually complete in livers, whereas CS-A-resistant memory persisted in spleens for up to 10 months.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abb J., Abb H., Deinhardt F. Effect of cyclosporin A on the production of interferon by human peripheral blood leukocytes in vitro. Antiviral Res. 1982 Dec;2(6):361–367. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(82)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armerding D. Selective induction of immunological tolerance in antiviral T killer cells of inbred mice after treatment with cyclosporin A. Infect Immun. 1981 Jun;32(3):1164–1175. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.3.1164-1175.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanden R. V., Langman R. E. Cell-mediated immunity to bacterial infection in the mouse. Thymus-derived cells as effectors of acquired resistance to Listeria monocytogenes. Scand J Immunol. 1972;1(4):379–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1972.tb03304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F., Feurer C., Gubler H. U., Stähelin H. Biological effects of cyclosporin A: a new antilymphocytic agent. Agents Actions. 1976 Jul;6(4):468–475. doi: 10.1007/BF01973261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borel J. F., Feurer C., Magnée C., Stähelin H. Effects of the new anti-lymphocytic peptide cyclosporin A in animals. Immunology. 1977 Jun;32(6):1017–1025. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunjes D., Hardt C., Röllinghoff M., Wagner H. Cyclosporin A mediates immunosuppression of primary cytotoxic T cell responses by impairing the release of interleukin 1 and interleukin 2. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Aug;11(8):657–661. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne R. Y., White D. J. The use of cyclosporin A in clinical organ grafting. Ann Surg. 1982 Sep;196(3):330–337. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198209000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F., Pavlov H., Waid C., York J. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: course of listeriosis in resistant or susceptible mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):763–770. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.763-770.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., McKenzie I. F. Resistance and susceptibility of mice to bacterial infection: genetics of listeriosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):755–762. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.755-762.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Waller R. Activated macrophages in congenitally athymic "nude mice" and in lethally irradiate mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Inaba K., Steinman R. M. Stimulation of lymphokine release from T lymphoblasts. Requirement for mRNA synthesis and inhibition by cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1984 Dec 1;160(6):1792–1802. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.6.1792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huegin A. W., Cerny A., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Suppression by cyclosporin A of murine T-cell-mediated immunity against viruses in vivo and in vitro. Cell Immunol. 1985 Feb;90(2):464–473. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90211-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungi T. W. Immunological memory to Listeria monocytogenes in rodents: evidence for protective T lymphocytes outside the recirculating lymphocyte pool. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1980 Oct;28(4):405–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungi T. W. Nonrecirculating memory T lymphocytes in cellular resistance to infection. Cell Immunol. 1980 Oct;55(2):499–505. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiderlen A. F., Kaufmann S. H., Lohmann-Matthes M. L. Protection of mice against the intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes by recombinant immune interferon. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):964–967. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty K., Ryan M., Misko I. An improved system for the assay of stimulation in mouse mixed leucocyte cultures. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Mar;4(2):263–273. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane F. C., Unanue E. R. Requirement of thymus (T) lymphocytes for resistance to listeriosis. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1104–1112. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKANESS G. B. Cellular resistance to infection. J Exp Med. 1962 Sep 1;116:381–406. doi: 10.1084/jem.116.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackaness G. B. The influence of immunologically committed lymphoid cells on macrophage activity in vivo. J Exp Med. 1969 May 1;129(5):973–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.129.5.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGregor D. D., Koster F. T., Mackaness G. B. The mediator of cellular immunity. I. The life-span and circulation dynamics of the immunologically committed lymphocyte. J Exp Med. 1971 Feb 1;133(2):389–399. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.2.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W., Spitalny G. L., Nathan C. F. Activation of mouse peritoneal macrophages in vitro and in vivo by interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1619–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Importance of thymus-derived lymphocytes in cell-mediated immunity to infection. Cell Immunol. 1973 Apr;7(1):166–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(73)90193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. Nature of "memory" in T-cell-mediated antibacterial immunity: anamnestic production of mediator T cells. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):754–760. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.754-760.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. J. The action of cortisone acetate on cell-mediated immunity to infection. Suppression of host cell proliferation and alteration of cellular composition of infective foci. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1485–1500. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Martinez-Maza O., De Ley M. Production of human immune interferon (Hu IFN-gamma) studied at the single cell level. Origin, evidence for spontaneous secretion and effect of cyclosporin A. Eur J Immunol. 1983 Mar;13(3):221–225. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reem G. H., Cook L. A., Vilcek J. Gamma interferon synthesis by human thymocytes and T lymphocytes inhibited by cyclosporin A. Science. 1983 Jul 1;221(4605):63–65. doi: 10.1126/science.6407112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner A., Douglas H., Davis C. E. Models of T cell deficiency in listeriosis: the effects of cortisone and cyclosporin A on normal and nude BALB/c mice. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):450–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber R. D., Hicks L. J., Celada A., Buchmeier N. A., Gray P. W. Monoclonal antibodies to murine gamma-interferon which differentially modulate macrophage activation and antiviral activity. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1609–1618. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Blanden R. V. Macrophage activation in mice lacking thymus-derived (T) cells. Experientia. 1975 May 15;31(5):591–593. doi: 10.1007/BF01932477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



