Abstract
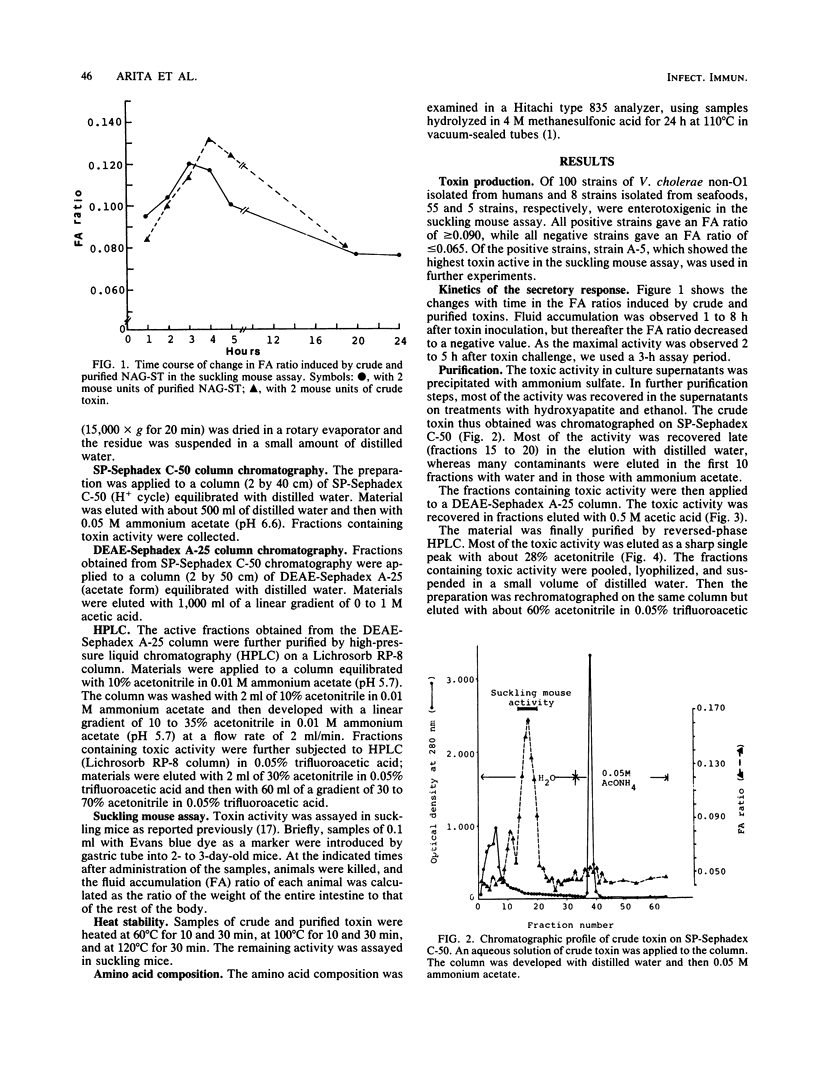
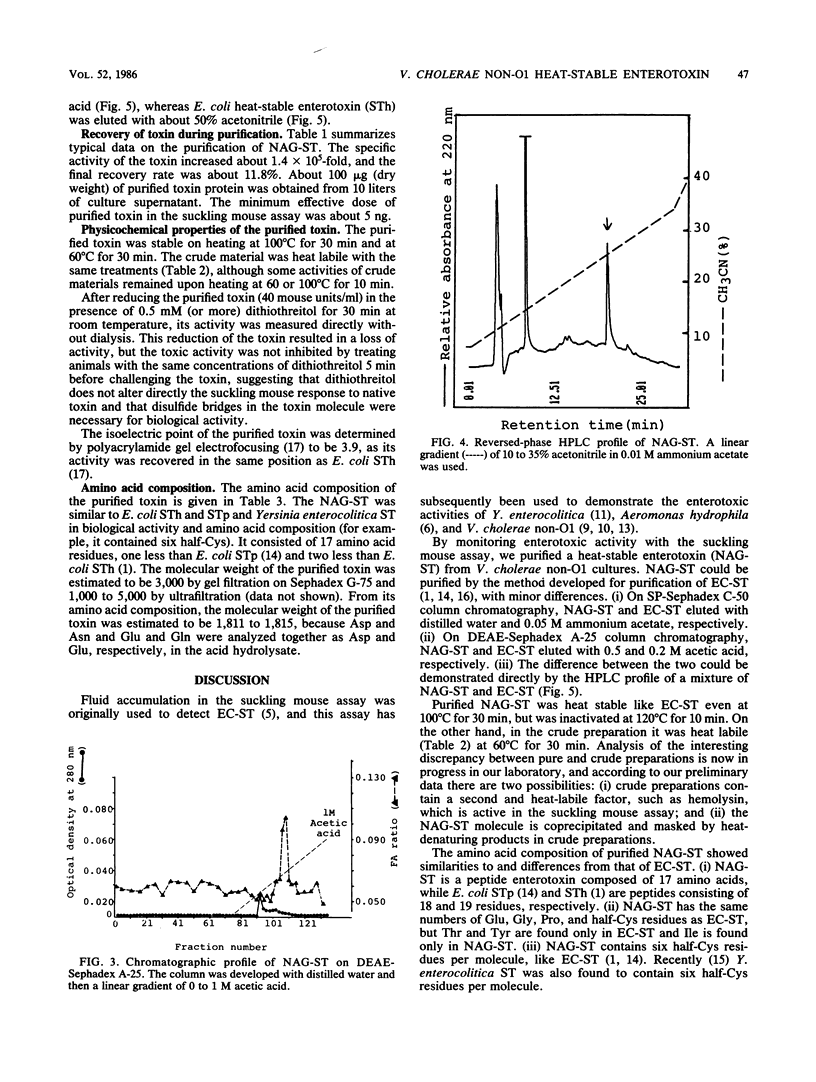
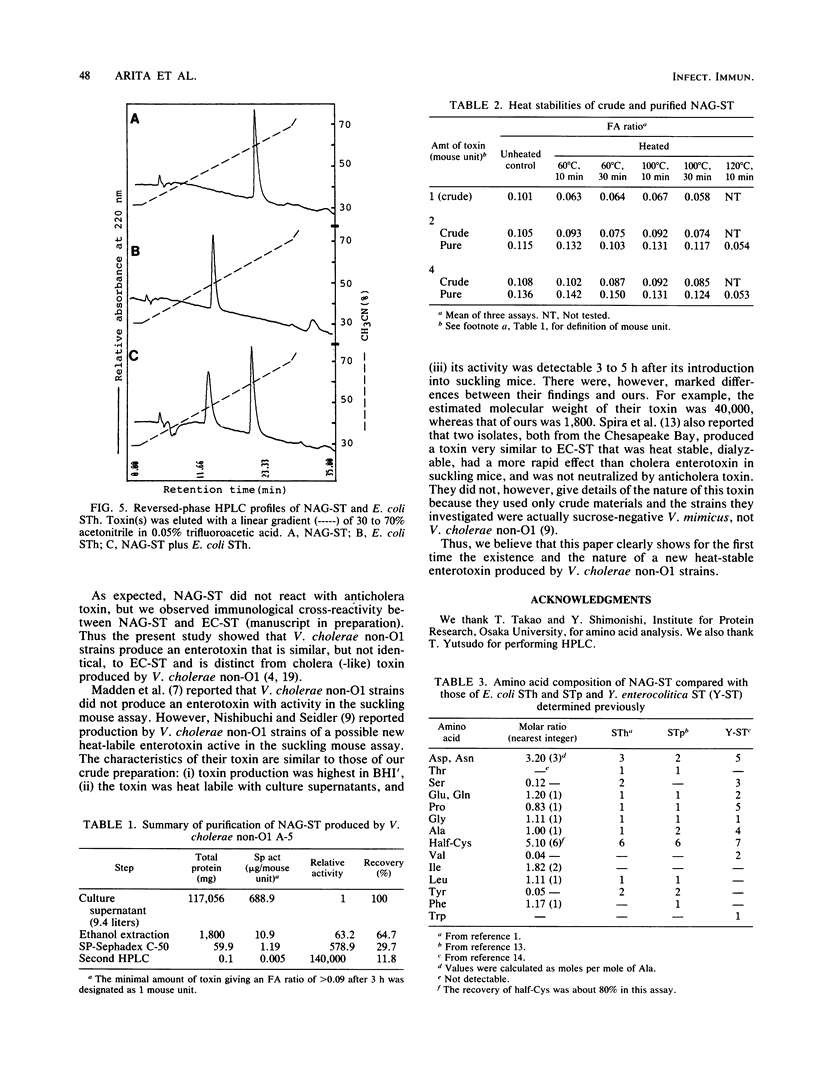
A toxin which causes rapid fluid accumulation in a suckling mouse assay and which was produced by Vibrio cholerae non-O1 was investigated. The toxin was purified from the culture supernatant of V. cholerae non-O1 (strain A-5) by ammonium sulfate fractionation, hydroxyapatite treatment, ethanol extraction, column chromatographies on SP-Sephadex C-50 and DEAE-Sephadex A-25, and high-pressure liquid chromatography on a Lichrosorb RP-8 column. About 1.4 X 10(5)-fold purification was achieved, with a recovery of about 12%. Although the crude preparation was heat labile, the purified toxin was heat stable. The minimum effective dose of purified toxin was about 5 ng in the suckling mouse assay. The amino acid composition of the purified toxin was determined to be Asp(3), Glu(1), Ala(1), half-Cys(6), Ile(2), Leu(1), Phe(1), and Pro(1). These data show the production of a new type of heat-stable enterotoxin (NAG-ST) by V. cholerae non-O1.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aimoto S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino-acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin produced by human enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):257–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldová E., Láznicková K., Stepánková E., Lietava J. Isolation of nonagglutinable vibrios from an enteritis outbreak in Czechoslovakia. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):25–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake P. A., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G. Diseases of humans (other than cholera) caused by vibrios. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1980;34:341–367. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.34.100180.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P., Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Production of cholera-like enterotoxin by a Vibrio cholerae non-O1 strain isolated from the environment. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.90-97.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. M., Lior H. Cytotoxicity and suckling mouse reactivity of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from human sources. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Oct;27(10):1019–1027. doi: 10.1139/m81-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE O. R., FEELEY J. C., GREENOUGH W. B., 3rd, BENENSON A. S., HASSAN S. I., SAAD A. DIARRHEA CAUSED BY NON-CHOLERA VIBRIOS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:412–418. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1965.14.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden J. M., Nematollahi W. P., Hill W. E., McCardell B. A., Twedt R. M. Virulence of three clinical isolates of Vibrio cholerae non-O-1 serogroup in experimental enteric infections in rabbits. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):616–619. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.616-619.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J. Medium-dependent production of extracellular enterotoxins by non-O-1 Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio mimicus, and Vibrio fluvialis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):228–231. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.228-231.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibuchi M., Seidler R. J., Rollins D. M., Joseph S. W. Vibrio factors cause rapid fluid accumulation in suckling mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1083–1091. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1083-1091.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai C. H., Mors V. Production of enterotoxin by Yersinia enterocolitica. Infect Immun. 1978 Mar;19(3):908–911. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.3.908-911.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B. Human diarrheal disease caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:333–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Hitouji T., Aimoto S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin isolated from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain 18D. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 7;152(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Tominaga N., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Inoue T., Miyama A. Primary structure of heat-stable enterotoxin produced by Yersinia enterocolitica. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Dec 28;125(3):845–851. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Evidence that a non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces enterotoxin that is similar but not identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.896-901.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



