Abstract
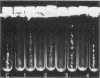
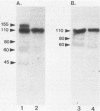
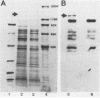
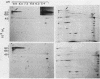
A polypeptide believed to be the monomeric form of the lectin responsible for the coaggregation of Capnocytophaga gingivalis (emended) and Actinomyces israelii has been identified. Denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblot analyses were used to distinguish the protein from other proteins in the outer membrane of C. gingivalis. The subunit of the putative lectin has a pI of 8.6 and a molecular weight of 155,000.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achenbach H., Kohl W., Wachter W., Reichenbach H. Investigations of the pigments from Cytophaga johnsonae Cy jl. New flexirubin-type pigments. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jun 26;117(3):253–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00738543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesk R. A., London J. Attachment of oral Cytophaga species to hydroxyapatite-containing surfaces. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):768–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.768-777.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisar J. O., Kolenbrander P. E., McIntire F. C. Specificity of coaggregation reactions between human oral streptococci and strains of Actinomyces viscosus or Actinomyces naeslundii. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):742–752. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.742-752.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donkersloot J. A., Cisar J. O., Wax M. E., Harr R. J., Chassy B. M. Expression of Actinomyces viscosus antigens in Escherichia coli: cloning of a structural gene (fimA) for type 2 fimbriae. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):1075–1078. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.1075-1078.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dzandu J. K., Deh M. E., Barratt D. L., Wise G. E. Detection of erythrocyte membrane proteins, sialoglycoproteins, and lipids in the same polyacrylamide gel using a double-staining technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1733–1737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagermeier A. S., London J., Kolenbrander P. E. Evidence for the participation of N-acetylated amino sugars in the coaggregation between Cytophaga species strain DR2001 and Actinomyces israelii PK16. Infect Immun. 1984 May;44(2):299–305. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.2.299-305.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King J., Laemmli U. K. Polypeptides of the tail fibres of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 28;62(3):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N. Cell to cell interactions of Capnocytophaga and Bacteroides species with other oral bacteria and their potential role in development of plaque. J Periodontal Res. 1984 Nov;19(6):564–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1984.tb01315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Andersen R. N., Holdeman L. V. Coaggregation of oral Bacteroides species with other bacteria: central role in coaggregation bridges and competitions. Infect Immun. 1985 Jun;48(3):741–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.3.741-746.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolenbrander P. E., Celesk R. A. Coaggregation of human oral Cytophaga species and Actinomyces israelii. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1178–1185. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1178-1185.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell J. P., Lascelles J. Membrane-bound, pyridine nucleotide-independent L-lactate dehydrogenase of Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):593–600. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.593-600.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marucha P. T., Keyes P. H., Wittenberger C. L., London J. Rapid method for identification and enumeration of oral Actinomyces. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):786–791. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.786-791.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., Jacobs T. Cell wall-associated protein antigens of Streptococcus salivarius: purification, properties, and function in adherence. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):233–242. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.233-242.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weerkamp A. H., McBride B. C. Identification of a Streptococcus salivarius cell wall component mediating coaggregation with Veillonella alcalescens V1. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.723-730.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]