Abstract
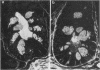
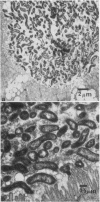
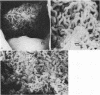
Human isolates of the intestinal pathogen Campylobacter jejuni have been shown to colonize mucus on the outer surface and deep within the intestinal crypts of gnotobiotic or germfree mice. The cecal crypts are preferentially colonized. A model of mucus colonization by C. jejuni in the mouse cecum has been developed, using antibiotic- and magnesium sulfate-treated specific-pathogen-free animals. These spiral-shaped bacteria colonize the mucus in a similar manner to the normal spiral-shaped microbiota. No evidence of adhesion to the intestinal surface was found with a wide variety of microscopic techniques. The campylobacters were seen to be highly motile in living preparations of gut tissue and rapidly tracked along intestinal mucus. Just as many of the normal spiral-shaped bacteria of intestinal surfaces can achieve close association with the epithelium through mucus association and do not adhere to the surface, C. jejuni colonizes the intestinal mucosa via mucus colonization. Thus, a major determinant of pathogenicity in intestinal infection with C. jejuni is proposed to be an ability to colonize intestinal mucus. The possession of specific adhesins is unlikely to be a significant determinant of pathogenicity. Better understanding of the mechanism of mucus association and the properties of the bacterium that are responsible will provide a basis for the rational selection of preventative measures. The model of mucus association in adult antibiotic-treated mice provides an opportunity for colonization studies with variant organisms and immunization studies.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chase D. G., Erlandsen S. L. Evidence for a complex life cycle and endospore formation in the attached, filamentous, segmented bacterium from murine ileum. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):572–583. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.572-583.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Underwood J. L., Pope L. M., Berry L. J. Intestinal colonization of neonatal animals by Campylobacter fetus subsp. jejuni. Infect Immun. 1981 Sep;33(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.3.884-892.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrell B. R., Walker R. I., Coolbaugh J. C. Campylobacter fetus ss. Jejuni, a newly recognized enteric pathogen: morphology and intestinal colonization. Scan Electron Microsc. 1981;4:125–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newell D. G., Pearson A. The invasion of epithelial cell lines and the intestinal epithelium of infant mice by Campylobacter jejuni/coli. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1984 Mar;2(1):19–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M., Lee A., Leach W. D. The mucosa-associated microflora of the rat intestine: a study of normal distribution and magnesium sulphate induced diarrhoea. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1978 Dec;56(6):649–662. doi: 10.1038/icb.1978.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price A. B., Jewkes J., Sanderson P. J. Acute diarrhoea: Campylobacter colitis and the role of rectal biopsy. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;32(10):990–997. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.10.990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozee K. R., Cooper D., Lam K., Costerton J. W. Microbial flora of the mouse ileum mucous layer and epithelial surface. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1451–1463. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1451-1463.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAEDLER R. W., DUBOS R., COSTELLO R. THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE BACTERIAL FLORA IN THE GASTROINTESTINAL TRACT OF MICE. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:59–66. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Morphological diversity among members of the gastrointestinal microflora. Int Rev Cytol. 1983;82:305–334. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60827-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suegara N., Morotomi M., Watanabe T., Kawal Y., Mutai M. Behavior of microflora in the rat stomach: adhesion of lactobacilli to the keratinized epithelial cells of the rat stomach in vitro. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):173–179. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.173-179.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]