Abstract
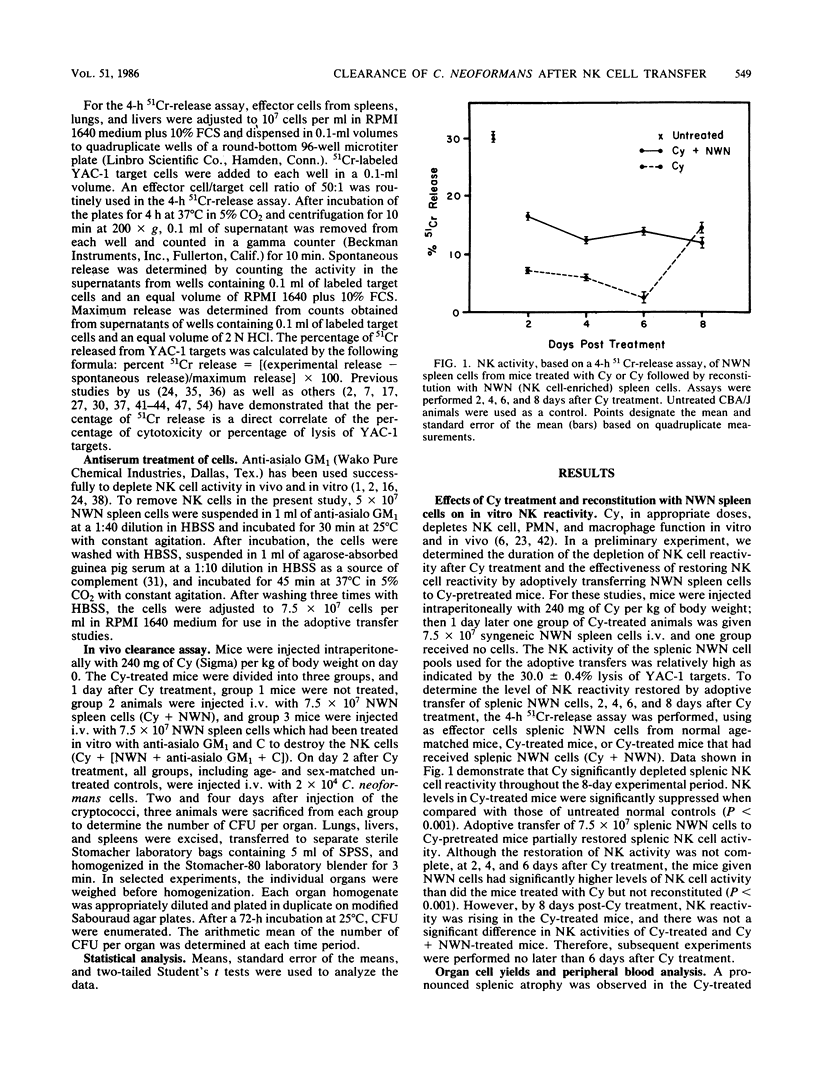
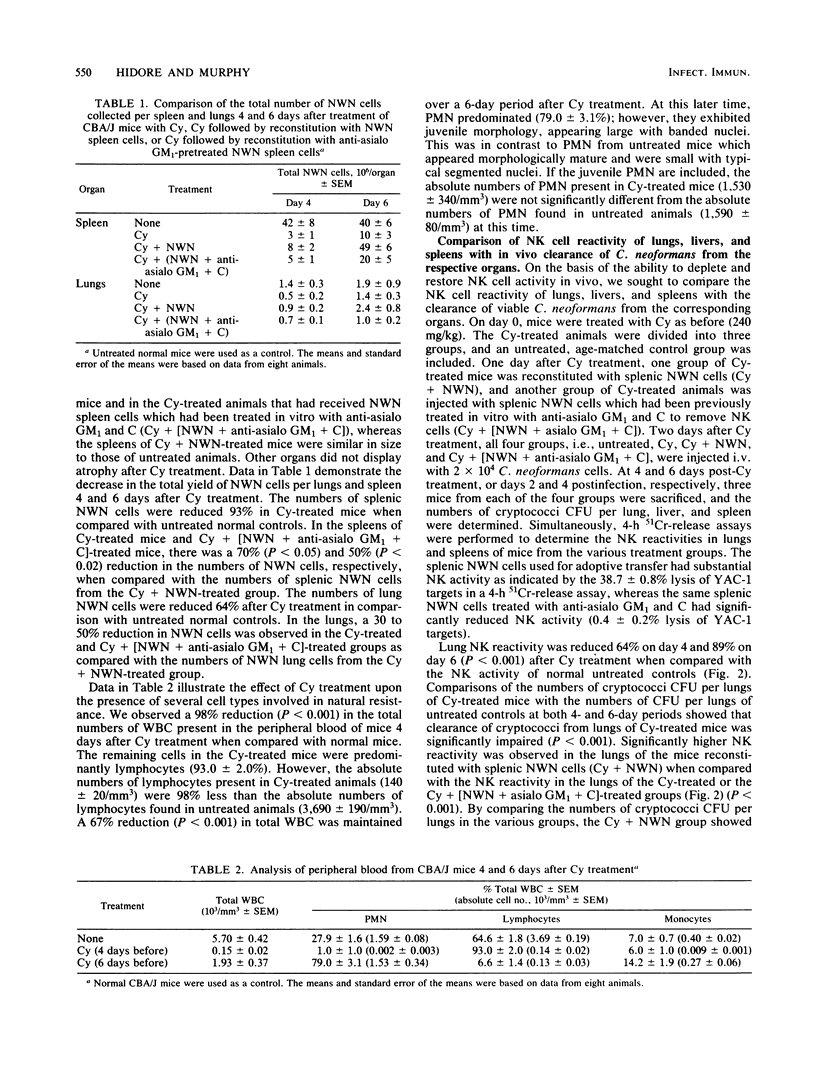
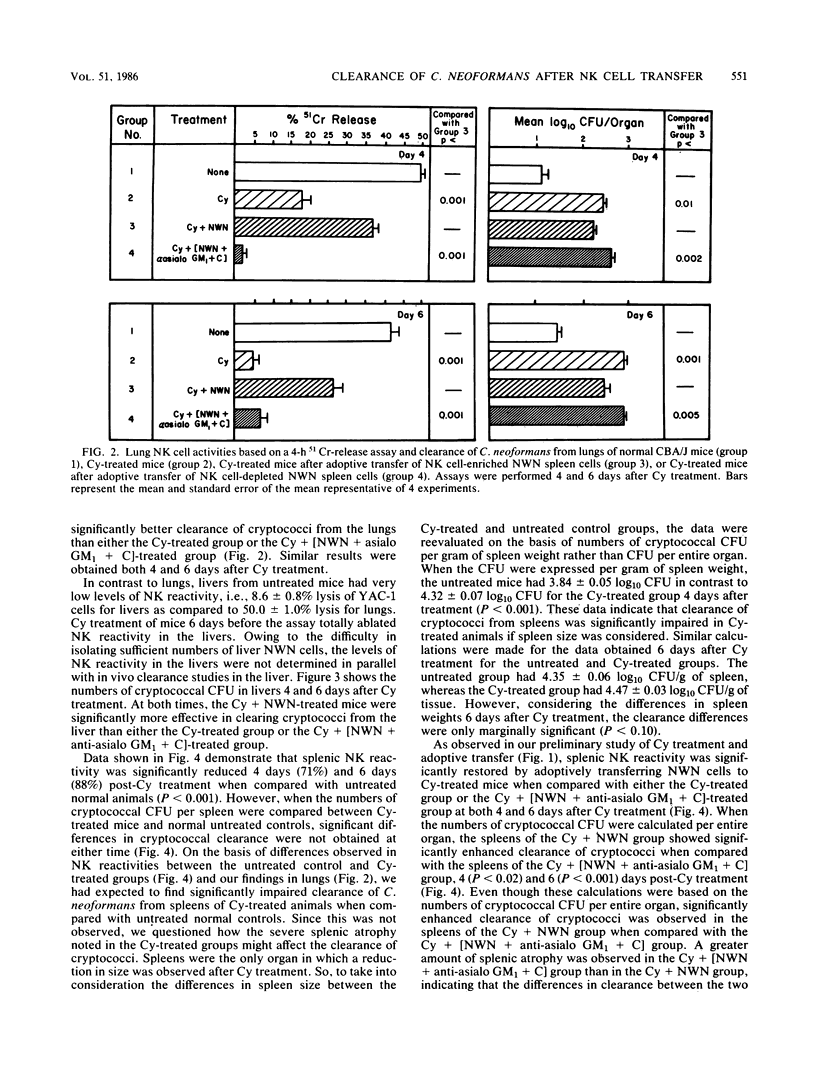
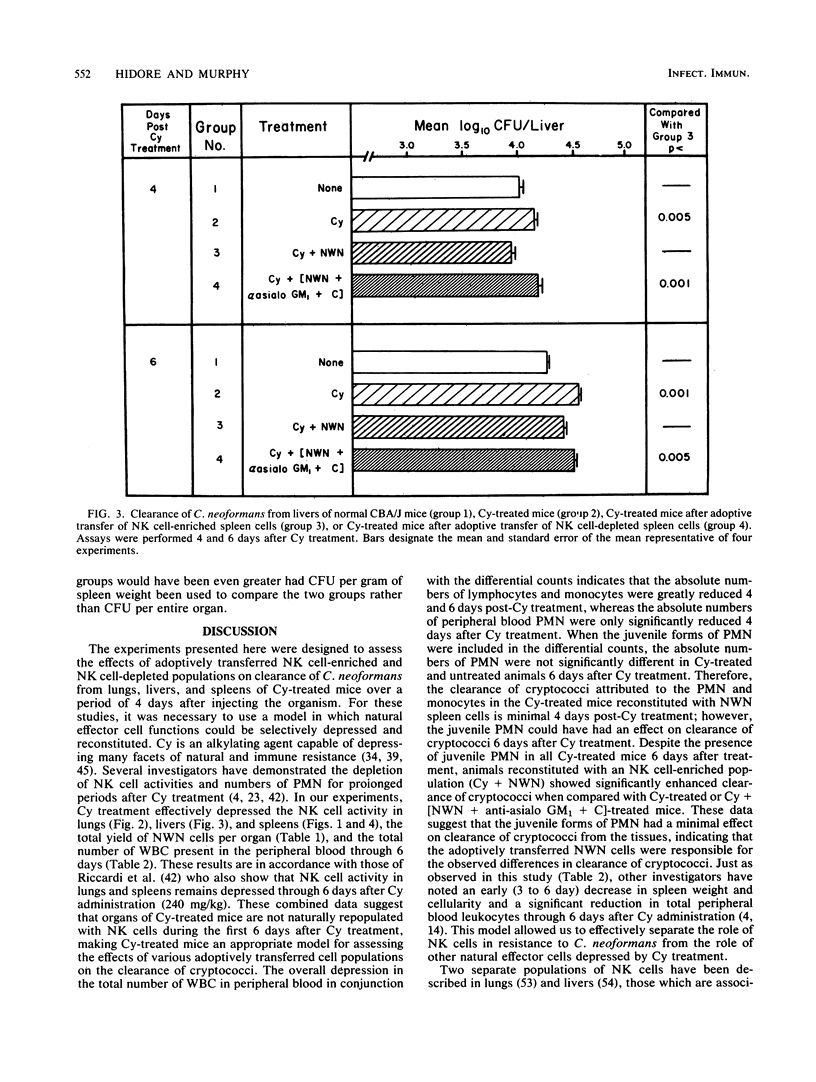
Previous reports demonstrate that natural killer (NK) cells inhibit the growth of Cryptococcus neoformans in vitro, but conclusive evidence supporting the effectiveness of NK cells in host resistance to cryptococci is not available. The objective of these studies was to assess the ability of NK cells to clear C. neoformans from the lungs, livers, and spleens of infected mice. CBA/J mice were depleted of NK cells, as well as other natural effector cells, by an intraperitoneal injection of cyclophosphamide (Cy), 240 mg/kg of body weight. One day later, 7.5 X 10(7) nylon wool-nonadherent (NWN) spleen cells, either untreated or treated with anti-asialo GM1 and complement to remove NK cells, were adoptively transferred to Cy-pretreated mice. On day 2 after Cy treatment, the mice were injected intravenously with 2 X 10(4) cryptococci. At 4 and 6 days after Cy treatment, tissues were assayed for NK reactivity, using a 4-h 51Cr-release assay, and for in vivo clearance of cryptococci as reflected by mean log10 CFU per organ. We observed that Cy treatment depleted NK activity against YAC-1 targets and reduced in vivo clearance of C. neoformans from the tissues of infected mice. Additionally, Cy treatment depleted the total lung and spleen cellularity and the total number of peripheral blood lymphocytes when compared with those in normal untreated control mice. Also, spleen weights were significantly decreased in comparison with those of untreated animals 4 days after Cy treatment. Adoptive transfer of untreated NWN spleen cells into Cy-depressed mice restored the NK cell activity which correlated with enhanced clearance of cryptococci from lungs, livers, and spleens. In contrast, treatment of NWN spleen cells with anti-asialo GM1 and complement before adoptive transfer abrogated the ability of these cells to restore NK activity or reduce the numbers of cryptococci present in tissues of infected mice. Taken together, these data indicate that NK cells are the cells effective in diminishing the numbers of cryptococci in tissues of infected mice. Consequently, NK cells may play a role in first-line host resistance against C. neoformans.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlozzari T., Reynolds C. W., Herberman R. B. In vivo role of natural killer cells: involvement of large granular lymphocytes in the clearance of tumor cells in anti-asialo GM1-treated rats. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):1024–1027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron C. A., Welsh R. M. Activation and role of natural killer cells in virus infections. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1982;170(3):155–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02298196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistoni F., Baccarini M., Blasi E., Marconi P., Puccetti P., Garaci E. Correlation between in vivo and in vitro studies of modulation of resistance to experimental Candida albicans infection by cyclophosphamide in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):46–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.46-55.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Warner J. F., Dennert G., Welsh R. M. Adoptive transfer studies demonstrating the antiviral effect of natural killer cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):40–52. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulmer G. S., Tacker J. R. Phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by alveolar macrophages. Infect Immun. 1975 Jan;11(1):73–79. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.1.73-79.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauley L. K., Murphy J. W. Response of congenitally athymic (nude) and phenotypically normal mice to Cryptococcus neoformans infection. Infect Immun. 1979 Mar;23(3):644–651. doi: 10.1128/iai.23.3.644-651.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheers C., Waller R. Activated macrophages in congenitally athymic "nude mice" and in lethally irradiate mice. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):844–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond R. D., Root R. K., Bennett J. E. Factors influencing killing of Cryptococcus neoformans by human leukocytes in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):367–376. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentry L. O., Remington J. S. Resistance against Cryptococcus conferred by intracellular bacteria and protozoa. J Infect Dis. 1971 Jan;123(1):22–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/123.1.22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybill J. R., Mitchell L. Cyclophosphamide effects on murine cryptococcosis. Infect Immun. 1978 Aug;21(2):674–677. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.2.674-677.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habu S., Akamatsu K., Tamaoki N., Okumura K. In vivo significance of NK cell on resistance against virus (HSV-1) infections in mice. J Immunol. 1984 Nov;133(5):2743–2747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habu S., Fukui H., Shimamura K., Kasai M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tamaoki N. In vivo effects of anti-asialo GM1. I. Reduction of NK activity and enhancement of transplanted tumor growth in nude mice. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatcher F. M., Kuhn R. E. Destruction of Trypanosoma cruzi by Natural killer cells. Science. 1982 Oct 15;218(4569):295–296. doi: 10.1126/science.6812218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Natural cell-mediated immunity. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:305–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Nunn M. E., Lavrin D. H. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic acid allogeneic tumors. I. Distribution of reactivity and specificity. Int J Cancer. 1975 Aug 15;16(2):216–229. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtrel B., Lagrange P. H., Michel J. C. Systemic candidiasis in mice. II.--Main role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in resistance to infection. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1980 Jan-Feb;131C(1):105–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez B. E., Murphy J. W. In vitro effects of natural killer cells against Paracoccidioides brasiliensis yeast phase. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):552–558. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.552-558.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tada T. A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitz D. J., Johnson C. R., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G., Little J. R. Growth inhibition of Cryptococcus neoformans by cloned cultured murine macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1984 Oct 15;88(2):489–500. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo G. C., Jacobson J. B., Hammerling G. J., Hammerling U. Antigenic profile of murine natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1003–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luini W., Boraschi D., Alberti S., Aleotti A., Tagliabue A. Morphological characterization of a cell population responsible for natural killer activity. Immunology. 1981 Aug;43(4):663–668. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell T. G., Friedman L. In vitro phagocytosis and intracellular fate of variously encapsulated strains of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1972 Apr;5(4):491–498. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.4.491-498.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuoka A., Baba M., Morikawa S. Enhancement of delayed hypersensitivity by depletion of suppressor T cells with cyclophosphamide in mice. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):77–78. doi: 10.1038/262077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. W., McDaniel D. O. In vitro reactivity of natural killer (NK) cells against Cryptococcus neoformans. J Immunol. 1982 Apr;128(4):1577–1583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nencioni L., Villa L., Boraschi D., Berti B., Tagliabue A. Natural and antibody-dependent cell-mediated activity against Salmonella typhimurium by peripheral and intestinal lymphoid cells in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):903–907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okumura K., Habu S., Kasai M. The role of NK cells in resistance of in vivo tumors. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;155:773–784. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4394-3_85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer H., Cowens J. W., Colvin M., Nussbaum-Blumenson A., Sheedy D. In vitro effects of 4-hydroperoxycyclophosphamide on human immunoregulatory T subset function. I. Selective effects on lymphocyte function in T-B cell collaboration. J Exp Med. 1982 Jan 1;155(1):276–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.1.276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Denn A. C., 3rd, Barlozzari T., Wiltrout R. H., Reichardt D. A., Herberman R. B. Natural killer activity in the rat. IV. Distribution of large granular lymphocytes (LGL) following intravenous and intraperitoneal transfer. Cell Immunol. 1984 Jul;86(2):371–380. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90392-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Natural killer (NK) cell activity in the rat. I. Isolation and characterization of the effector cells. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riccardi C., Barlozzari T., Santoni A., Herberman R. B., Cesarini C. Transfer to cyclophosphamide-treated mice of natural killer (NK) cells and in vivo natural reactivity against tumors. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1284–1289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C., Lohmann-Matthes M. L., Domzig W., Wigzell H. The beige mutation in the mouse. II. Selectivity of the natural killer (NK) cell defect. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2174–2181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roder J. C. The beige mutation in the mouse. I. A stem cell predetermined impairment in natural killer cell function. J Immunol. 1979 Nov;123(5):2168–2173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shand F. L. The immunopharmacology of cyclophosphamide. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1979;1(3):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(79)90038-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shellam G. R., Allan J. E., Papadimitriou J. M., Bancroft G. J. Increased susceptibility to cytomegalovirus infection in beige mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5104–5108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein-Streilein J., Bennett M., Mann D., Kumar V. Natural killer cells in mouse lung: surface phenotype, target preference, and response to local influenza virus infection. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2699–2704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson F. J., Kozel T. R. Phagocytosis of Cryptococcus neoformans by normal and thioglycolate-activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):714–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.714-720.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tacker J. R., Farhi F., Bulmer G. S. Intracellular fate of Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1972 Aug;6(2):162–167. doi: 10.1128/iai.6.2.162-167.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timonen T., Ortaldo J. R., Herberman R. B. Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 1981 Mar 1;153(3):569–582. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.3.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weindruch R., Devens B. H., Raff H. V., Walford R. L. Influence of dietary restriction and aging on natural killer cell activity in mice. J Immunol. 1983 Feb;130(2):993–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M. Natural cell-mediated immunity during viral infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;92:83–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68069-4_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiltrout R. H., Herberman R. B., Zhang S. R., Chirigos M. A., Ortaldo J. R., Green K. M., Jr, Talmadge J. E. Role of organ-associated NK cells in decreased formation of experimental metastases in lung and liver. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4267–4275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiltrout R. H., Mathieson B. J., Talmadge J. E., Reynolds C. W., Zhang S. R., Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Augmentation of organ-associated natural killer activity by biological response modifiers. Isolation and characterization of large granular lymphocytes from the liver. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1431–1449. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


