Abstract
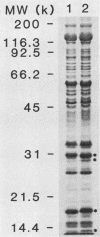
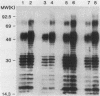
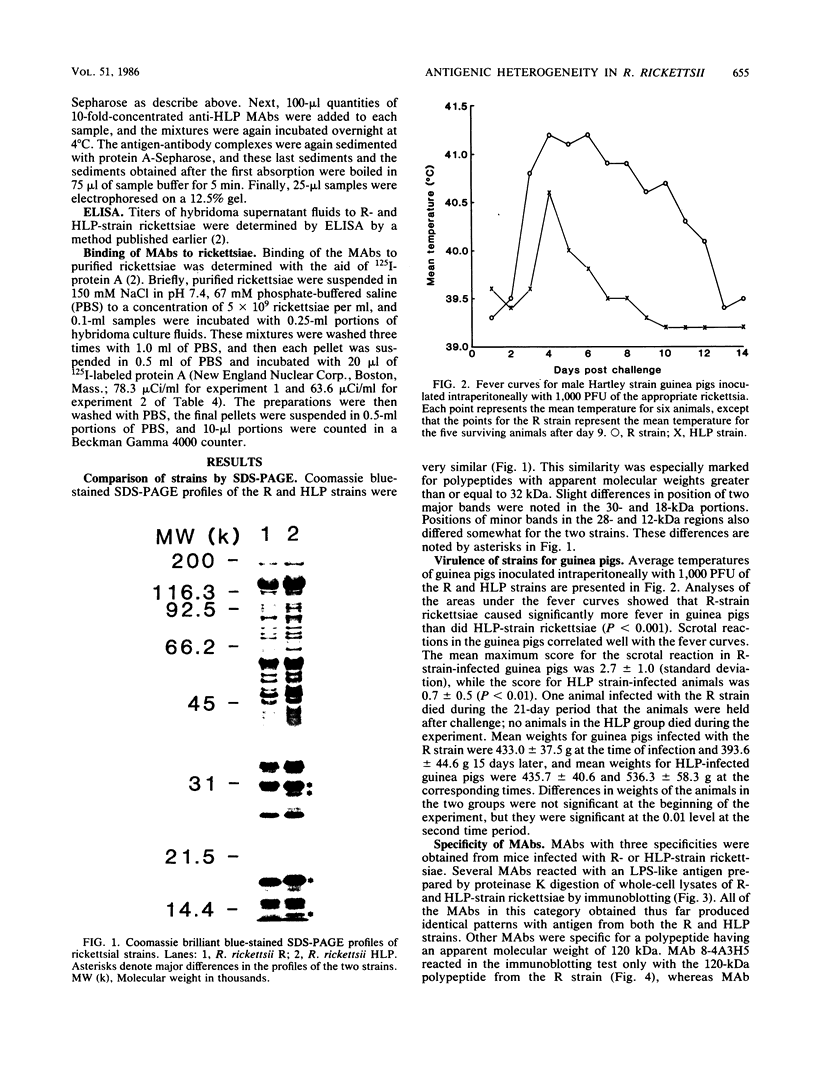
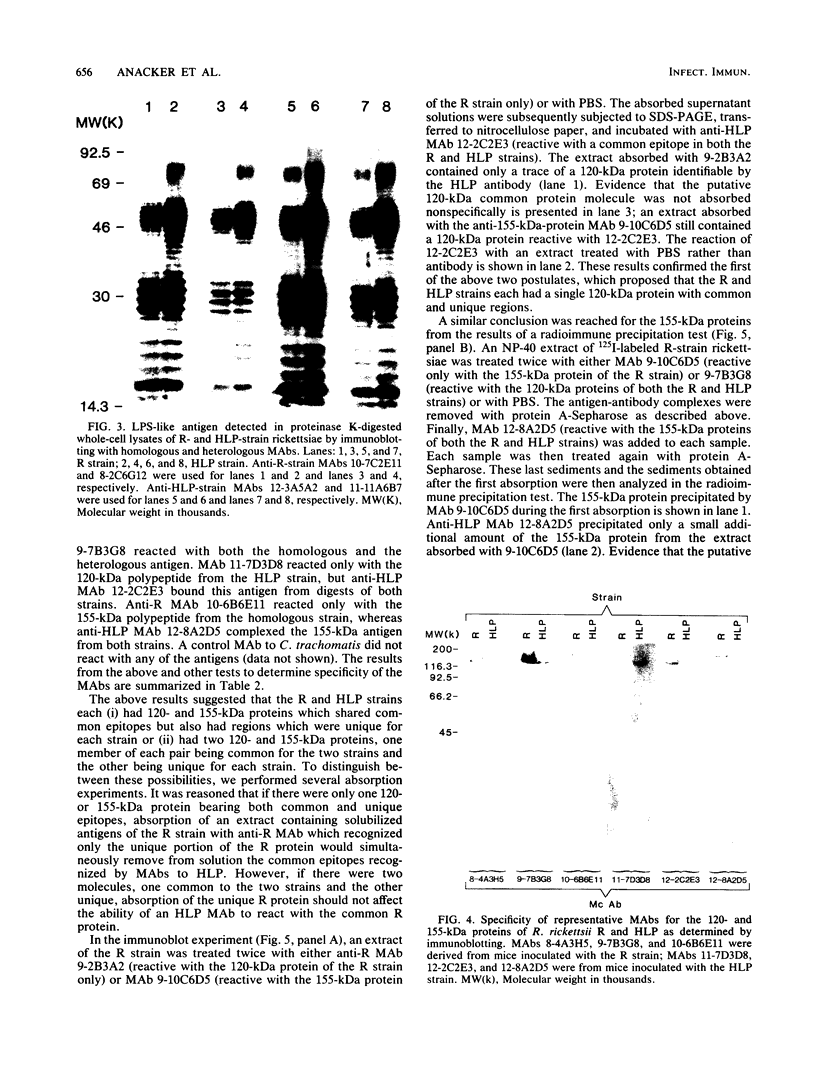
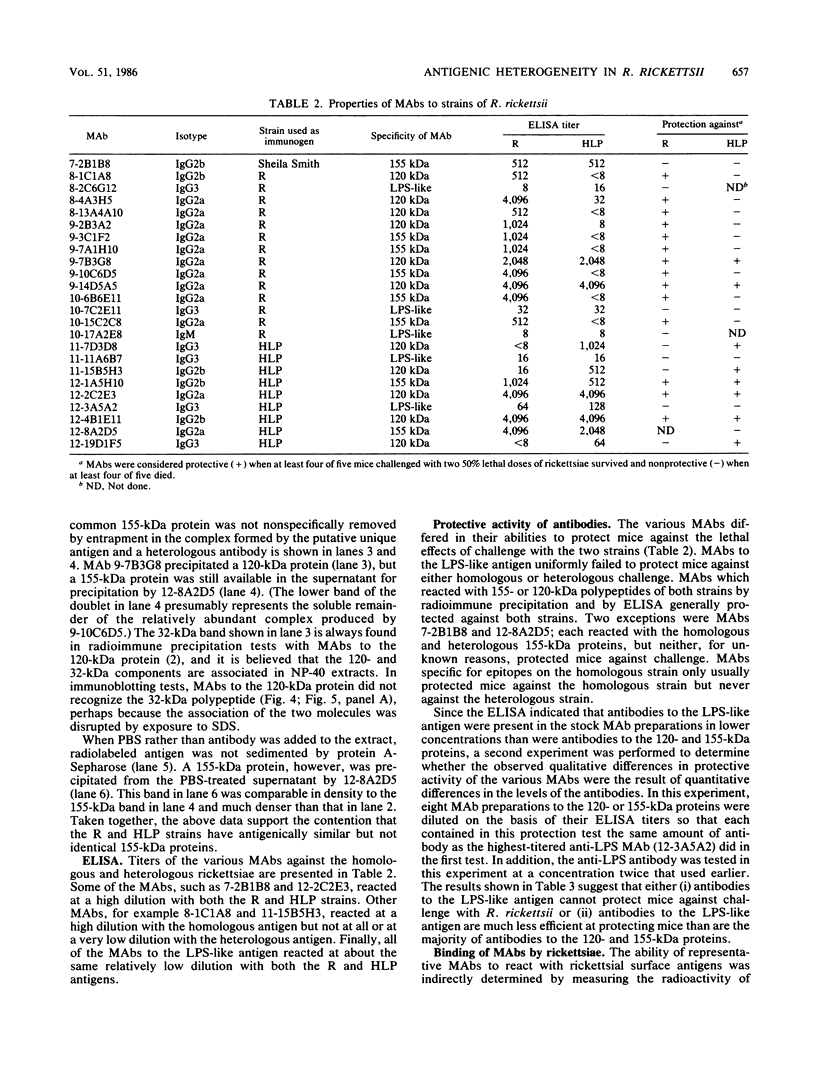
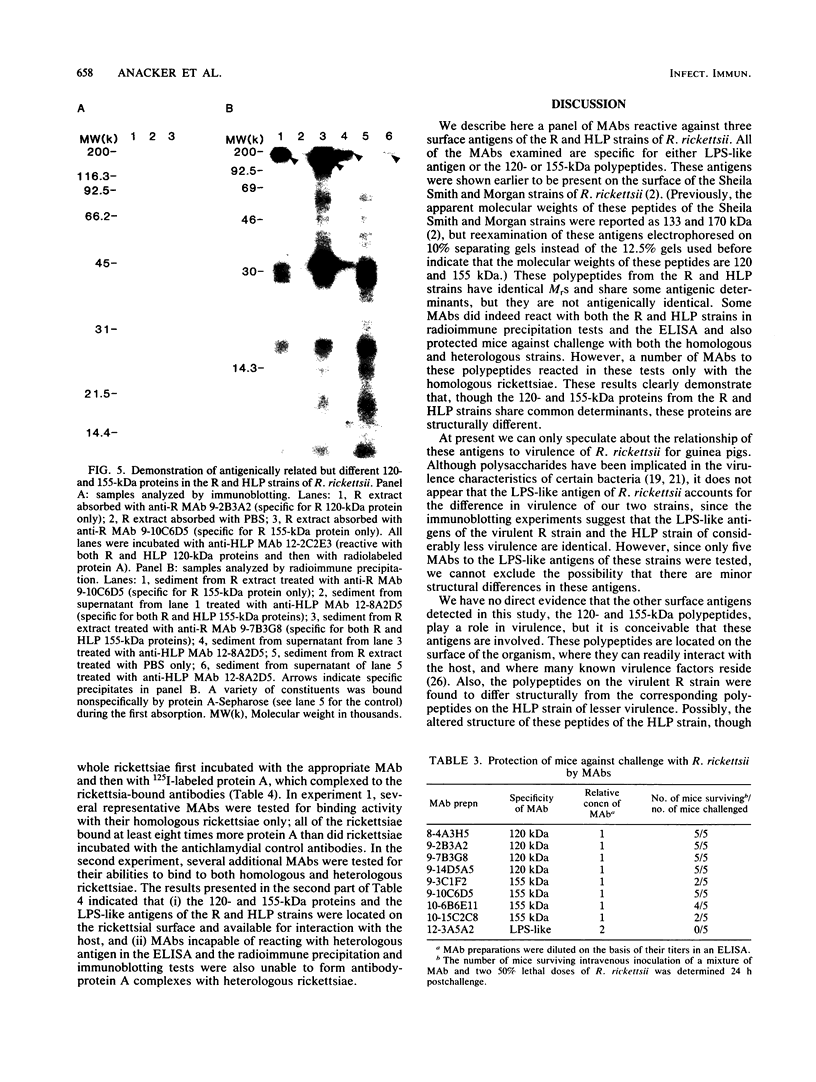
Previously it has been reported that strains of Rickettsia rickettsii that differ greatly in their ability to cause disease in guinea pigs are similar by serological and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analyses. In this study, we used monoclonal antibodies to the virulent R and the relatively avirulent HLP strains to investigate strain differences which might account for the disparate behavior of the strains in guinea pigs. Coomassie blue-stained sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis profiles of the R and HLP strains were nearly identical for polypeptides with apparent molecular weights greater than 32 kilodaltons (kDa). All of the monoclonal antibodies to a lipopolysaccharide-like antigen reacted equally well with antigen from both strains by immunoblotting. None of the antibodies to the lipopolysaccharide-like antigen protected mice against challenge with viable rickettsiae. Some antibodies reacted with both 120- and 155-kDa polypeptides of both strains in radioimmune precipitation and immunoblotting tests, and other antibodies reacted only with the homologous strain. The monoclonal antibodies cross-reacted with the heterologous strain in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay essentially either completely or not at all. The ability of the monoclonal antibodies to the 120- and 155-kDa polypeptides to protect mice against the two strains was correlated with the ability of the antibodies to react with the antigens in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and radioimmune precipitation or immunoblotting tests. These results demonstrate that R and HLP antigens which appear identical in molecular weight differ in their compositions of antigenic determinants.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anacker R. L., Gerloff R. K., Thomas L. A., Mann R. E., Bickel W. D. Immunological properties of Rickettsia rickettsii purified by zonal centrifugation. Infect Immun. 1975 Jun;11(6):1203–1209. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.6.1203-1209.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., List R. H., Mann R. E., Hayes S. F., Thomas L. A. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies protecting mice against Rickettsia rickettsii. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jun;151(6):1052–1060. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.6.1052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., McCaul T. F., Burgdorfer W., Gerloff R. K. Properties of selected rickettsiae of the spotted fever group. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):468–474. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.468-474.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., Philip R. N., Williams J. C., List R. H., Mann R. E. Biochemical and immunochemical analysis of Rickettsia rickettsii strains of various degrees of virulence. Infect Immun. 1984 Jun;44(3):559–564. doi: 10.1128/iai.44.3.559-564.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anacker R. L., Smith R. F., Mann R. E., Hamilton M. A. New assay of protective activity of Rocky Mountain spotted fever vaccines. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Sep;4(3):309–311. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.3.309-311.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. J., KOHLS G. M., STOENNER H. G., LACKMAN D. B. NONPATHOGENIC RICKETTSIAS RELATED TO THE SPOTTED FEVER GROUP ISOLATED FROM TICKS, DERMACENTOR VARIABILIS AND DERMACENTOR ANDERSONI FROM EASTERN MONTANA. J Immunol. 1963 May;90:770–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. J., PICKENS E. G. A toxic substance associated with the rickettsias of the spotted fever group. J Immunol. 1953 May;70(5):461–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. J., STOENNER H. G. Immunologic relationships among the spotted fever group of rickettsias determined by toxin neutralization tests in mice with convalescent animal serums. J Immunol. 1960 Feb;84:171–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL E. J., STOENNER H. G. Spotted fever vaccine; potency assay by direct challenge of vaccinated mice with toxin of Rickettsia rickettsii. J Immunol. 1961 Dec;87:737–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batteiger B., Newhall W. J., 5th, Jones R. B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Dec 30;55(3):297–307. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90089-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W. A review of Rocky Mountain spotted fever (tick-borne typhus), its agent, and its tick vectors in the United States. J Med Entomol. 1975 Sep 25;12(3):269–278. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/12.3.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Sexton D. J., Gerloff R. K., Anacker R. L., Philip R. N., Thomas L. A. Rhipicephalus sanguineus: vector of a new spotted fever group rickettsia in the United States. Infect Immun. 1975 Jul;12(1):205–210. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.1.205-210.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitchcock P. J., Brown T. M. Morphological heterogeneity among Salmonella lipopolysaccharide chemotypes in silver-stained polyacrylamide gels. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):269–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.269-277.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes L. E., Clifford C. M., Gresbrink R., Thomas L. A., Keirans J. E. Isolation of a spotted fever group rickettsia from the Pacific Coast tick, Ixodes pacificus, in Oregon. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1976 May;25(3):513–516. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1976.25.513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON E. B., SMADEL J. E. Immunization against scrub typhus. II. Preparation of lyophilized living vaccine. Am J Hyg. 1951 May;53(3):326–331. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. J., Nicholson-Weller A., Baker C. J., Kasper D. L. Potentiation of virulence by group B streptococcal polysaccharides. J Infect Dis. 1984 Jun;149(6):851–860. doi: 10.1093/infdis/149.6.851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orskov F. Virulence factors of the bacterial cell surface. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):630–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER R. R., PICKENS E. G., LACKMAN D. B., BELLE E. J., THRAIKILL F. B. Isolation and characterization of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever Rickettsiae from the rabbit tick Haemaphysalis leporis-palustris Packard. Public Health Rep. 1951 Apr 13;66(15):455–463. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRICE W. H. The epidemiology of Rocky Mountain spotted fever. I. The characterization of strain virulence of Rickettsia rickettsii. Am J Hyg. 1953 Sep;58(2):248–268. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A., Burgdorfer W., Gerloff R. K., Hughes L. E., Bell E. J. Serologic typing of rickettsiae of the spotted fever group by microimmunofluorescence. J Immunol. 1978 Nov;121(5):1961–1968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip R. N., Casper E. A. Serotypes of spotted fever group rickettsiae isolated from Dermacentor andersoni (Stiles) ticks in western Montana. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981 Jan;30(1):230–238. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOENNER H. G., LACKMAN D. B., BELL E. J. Factors affecting the growth of rickettsias of the spotted fever group in fertile hens' eggs. J Infect Dis. 1962 Mar-Apr;110:121–128. doi: 10.1093/infdis/110.2.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. Microbial surfaces in relation to pathogenicity. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):475–500. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.475-500.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Coolbaugh J. C., Williams J. C. Separation of viable Rickettsia typhi from yolk sac and L cell host components by renografin density gradient centrifugation. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Sep;30(3):456–463. doi: 10.1128/am.30.3.456-463.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]