Abstract
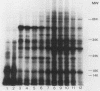
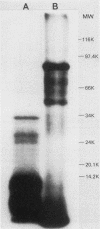
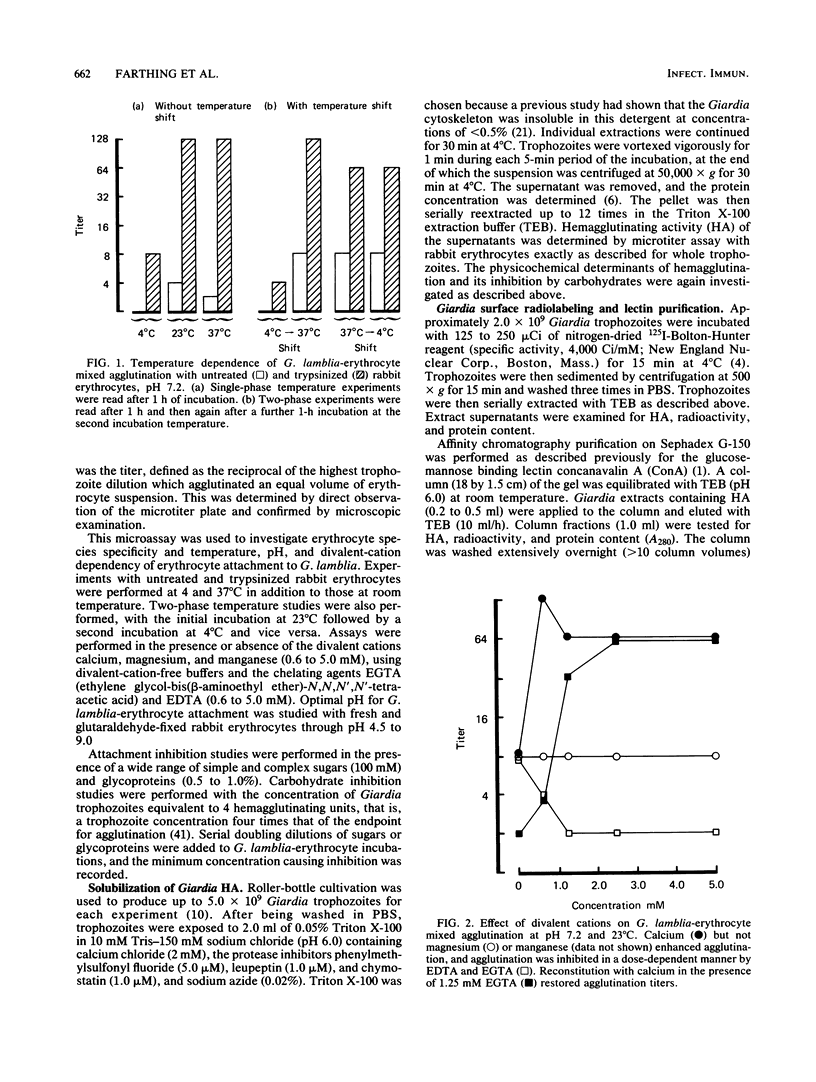
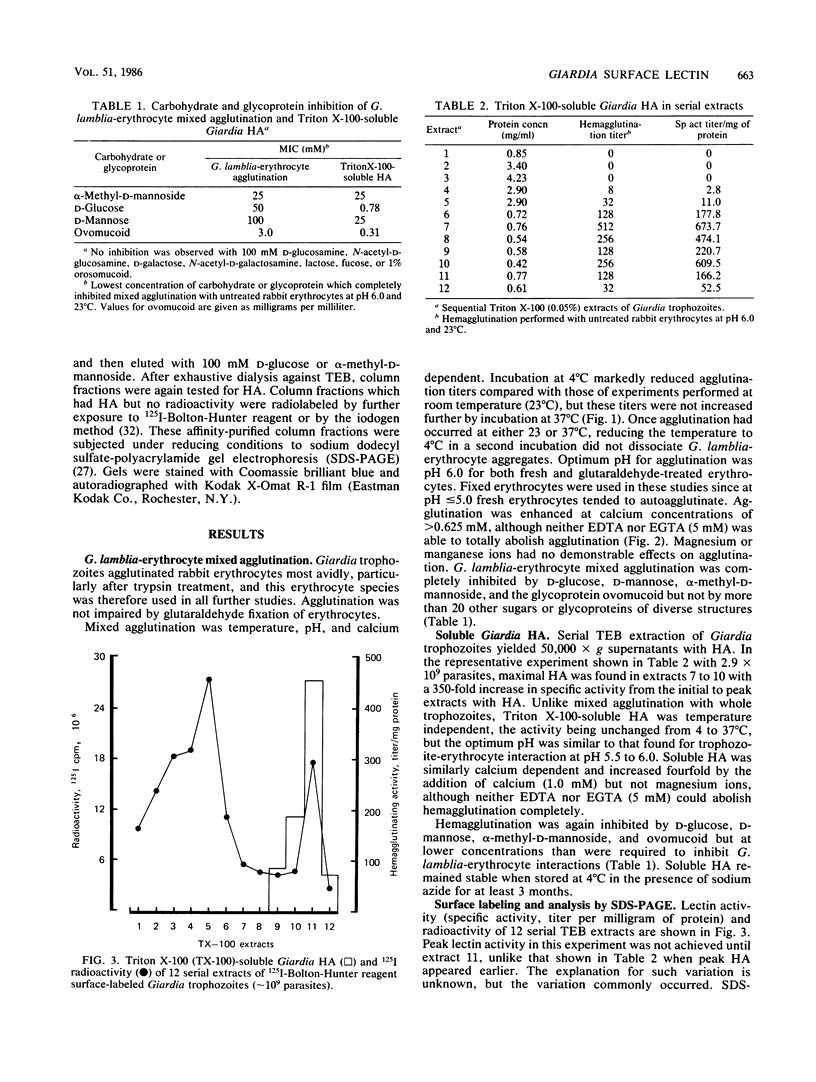
The mechanisms by which the human enteric pathogen Giardia lamblia colonizes the proximal small intestine are poorly understood. Although the parasite possesses an attachment organelle on its ventral surface, the "sucking" disk, we considered that like many bacteria and some protozoa, G. lamblia might also have a surface membrane-associated modality for adherence to its host. Using an erythrocyte mixed-agglutination model, we demonstrated a parasite surface lectin with specificities for D-glucosyl and D-mannosyl residues. This lectin is soluble in Triton X-100, is calcium dependent, and is maximally active at pH 5.5 to 6.0. Partial purification was achieved by serial extraction of parasites in Triton X-100 followed by Sephadex G-150 affinity chromatography. The lectin could not be surface radiolabeled with 125I-Bolton-Hunter reagent, but radiolabeling of the hapten eluate from an affinity column produced four bands of 57,000 to 78,000 Mr on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels under reducing conditions. The biological function of this lectin is unknown. The presence of mannosyl residues on the luminal surface of human small intestinal epithelial cells suggests that there are receptors for Giardia lectin at the site of colonization.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal B. B., Goldstein I. J. Protein-carbohydrate interaction. VI. Isolation of concanavalin A by specific adsorption on cross-linked dextran gels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 23;147(2):262–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barondes S. H. Lectins: their multiple endogenous cellular functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:207–231. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beachey E. H. Bacterial adherence: adhesin-receptor interactions mediating the attachment of bacteria to mucosal surface. J Infect Dis. 1981 Mar;143(3):325–345. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.3.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L. S., Harlow D. R., Cunnick C. C. A new medium for the axenic cultivation of Entamoeba histolytica and other Entamoeba. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1978;72(4):431–432. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(78)90144-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandsen S. L., Chase D. G. Morphological alterations in the microvillous border of villous epithelial cells produced by intestinal microorganisms. Am J Clin Nutr. 1974 Nov;27(11):1277–1286. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/27.11.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshdat Y., Ofek I., Yashouv-Gan Y., Sharon N., Mirelman D. Isolation of a mannose-specific lectin from Escherichia coli and its role in the adherence of the bacteria to epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1551–1559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing M. J., Pereira M. E., Keusch G. T. Giardia lamblia: evaluation of roller bottle cultivation. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Dec;54(3):410–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farthing M. J., Varon S. R., Keusch G. T. Mammalian bile promotes growth of Giardia lamblia in axenic culture. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1983;77(4):467–469. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(83)90115-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feely D. E., Erlandsen S. L. Effect of cytochalasin-B, low Ca++ concentration, iodoacetic acid, and quinacrine-HCl on the attachment of Giardia trophozoites in vitro. J Parasitol. 1982 Oct;68(5):869–873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feely D. E., Schollmeyer J. V., Erlandsen S. L. Giardia spp.: distribution of contractile proteins in the attachment organelle. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Feb;53(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Locklear T. W. Ionic constituents and osmolality of gastric and small-intestinal fluids after eating. Am J Dig Dis. 1966 Jul;11(7):503–521. doi: 10.1007/BF02233563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S. The fine structure of Giardia muris. J Cell Biol. 1966 May;29(2):317–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.29.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galbraith W., Goldstein I. J. Phytohemagglutinin of the lima bean (Phaseolus lunatus). Isolation, characterization, and interaction with type A blood-group substance. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 10;11(21):3976–3984. doi: 10.1021/bi00771a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H. J., Hellman B., Lernmark A., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. B. The pancreatic beta-cell recognition of insulin secretogogues. Influence of neuraminidase treatment on the release of insulin and the islet content of insulin, sialic acid, and cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5275–5284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holberton D. V. Attachment of Giardia-a hydrodynamic model based on flagellar activity. J Exp Biol. 1974 Feb;60(1):207–221. doi: 10.1242/jeb.60.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holberton D. V. Fine structure of the ventral disk apparatus and the mechanism of attachment in the flagellate Giardia muris. J Cell Sci. 1973 Jul;13(1):11–41. doi: 10.1242/jcs.13.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holberton D. V., Ward A. P. Isolation of the cytoskeleton from Giardia. Tubulin and a low-molecular-weight protein associated with microribbon structures. J Cell Sci. 1981 Feb;47:139–166. doi: 10.1242/jcs.47.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Levitzki A. Metal-binding sites of concanavalin A and their role in the binding of alpha-methyl d-glucopyranoside. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):669–672. doi: 10.1042/bj1090669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalb A. J., Lustig A. The molecular weight of concanavalin A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Oct 21;168(2):366–367. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(68)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki T., Ashwell G. Chemical and physical properties of an hepatic membrane protein that specifically binds asialoglycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1296–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobiler D., Mirelman D. Lectin activity in Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):221–225. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.221-225.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzsonn V., Olsen W. A. In vivo responses of rat intestinal epithelium to intraluminal dietary lectins. Gastroenterology. 1982 May;82(5 Pt 1):838–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M. L., Blair J. A., Cooper B., Matty A. J. Further investigations with pH microelectrodes into the jejunal microclimate in rat and man. Gut. 1975 Oct;16(10):844–844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas M. L., Lei F. H., Blair J. A. The influence of buffer pH, glucose and sodium ion concentration on the acid microclimate in rat proximal jejunum in vitro. Pflugers Arch. 1980 May;385(2):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00588693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald T. T., Ferguson A. Small intestinal epithelial cell kinetics and protozoal infection in mice. Gastroenterology. 1978 Mar;74(3):496–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Surface-specific iodination of membrane proteins of viruses and eucaryotic cells using 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro-3alpha,6alpha-diphenylglycoluril. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4807–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy B., Moon H. W., Isaacson R. E. Colonization of porcine small intestine by Escherichia coli: ileal colonization and adhesion by pig enteropathogens that lack K88 antigen and by some acapsular mutants. Infect Immun. 1976 Apr;13(4):1214–1220. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.4.1214-1220.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. The interactions of lectins with animal cell surfaces. Int Rev Cytol. 1974;39:89–190. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60939-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofek I., Mirelman D., Sharon N. Adherence of Escherichia coli to human mucosal cells mediated by mannose receptors. Nature. 1977 Feb 17;265(5595):623–625. doi: 10.1038/265623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. L. The ultrastructural basis of Giardia function. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(4):429–433. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Gruezo F., Kabat E. A. Purification and characterization of lectin II from Ulex europaeus seeds and an immunochemical study of its combining site. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 May;194(2):511–525. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90646-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Kabat E. A. Immunochemical studies on lectins and their application to the fractionation of blood group substances and cells. CRC Crit Rev Immunol. 1979 Nov;1(1):33–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira M. E., Loures M. A., Villalta F., Andrade A. F. Lectin receptors as markers for Trypanosoma cruzi. Developmental stages and a study of the interaction of wheat germ agglutinin with sialic acid residues on epimastigote cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Nov 1;152(5):1375–1392. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.5.1375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poley J. R., Rosenfield S. Malabsorption in giardiasis: presence of a luminal barrier (mucoid pseudomembrane). A scanning and transmission electron microscopic study. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1982;1(1):63–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravdin J. I., Guerrant R. L. Role of adherence in cytopathogenic mechanisms of Entamoeba histolytica. Study with mammalian tissue culture cells and human erythrocytes. J Clin Invest. 1981 Nov;68(5):1305–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI110377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S. Axenic growth of Giardia lamblia in Diamond's TPS-1 medium. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1980;74(2):213–215. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(80)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Inbar M., Sachs L. Temperature-sensitive agglutinability of human erythrocytes by lectins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):364–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90184-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Concanavalin A agglutination of intestinal cells from the human fetus. Science. 1972 Aug 11;177(4048):525–526. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4048.525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiser M. M. Intestinal epithelial cell surface membrane glycoprotein synthesis. I. An indicator of cellular differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2536–2541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]