Abstract
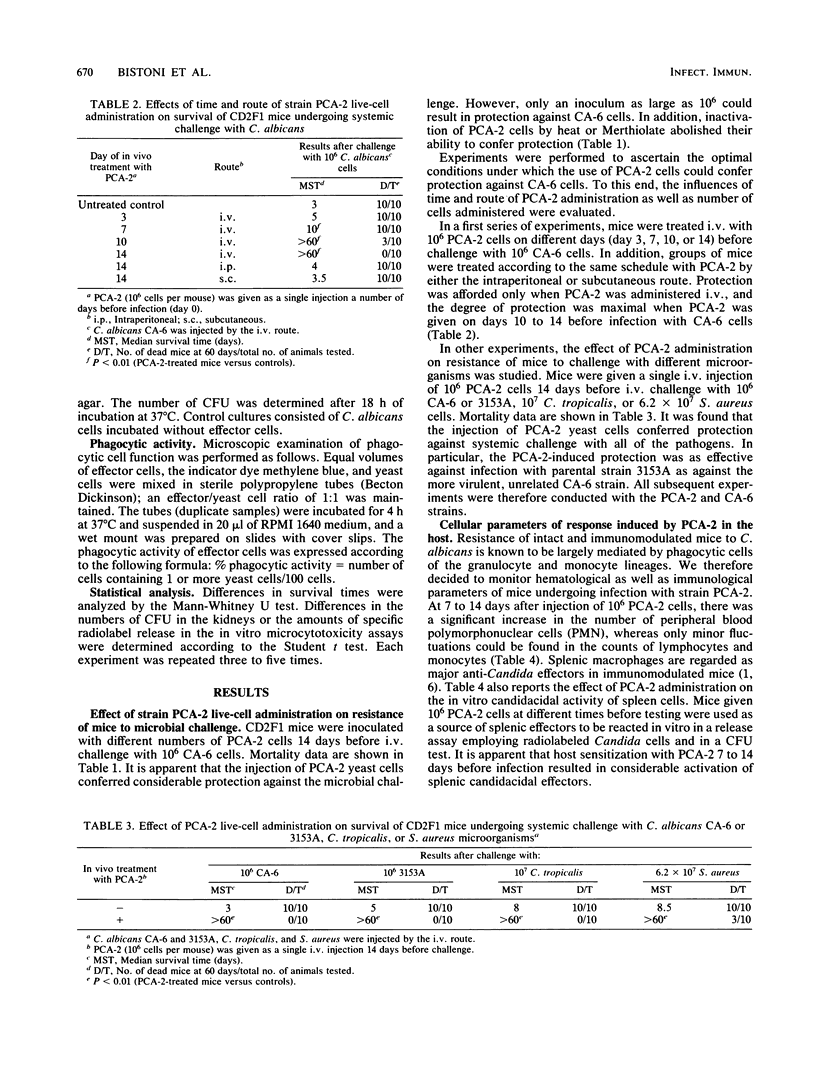
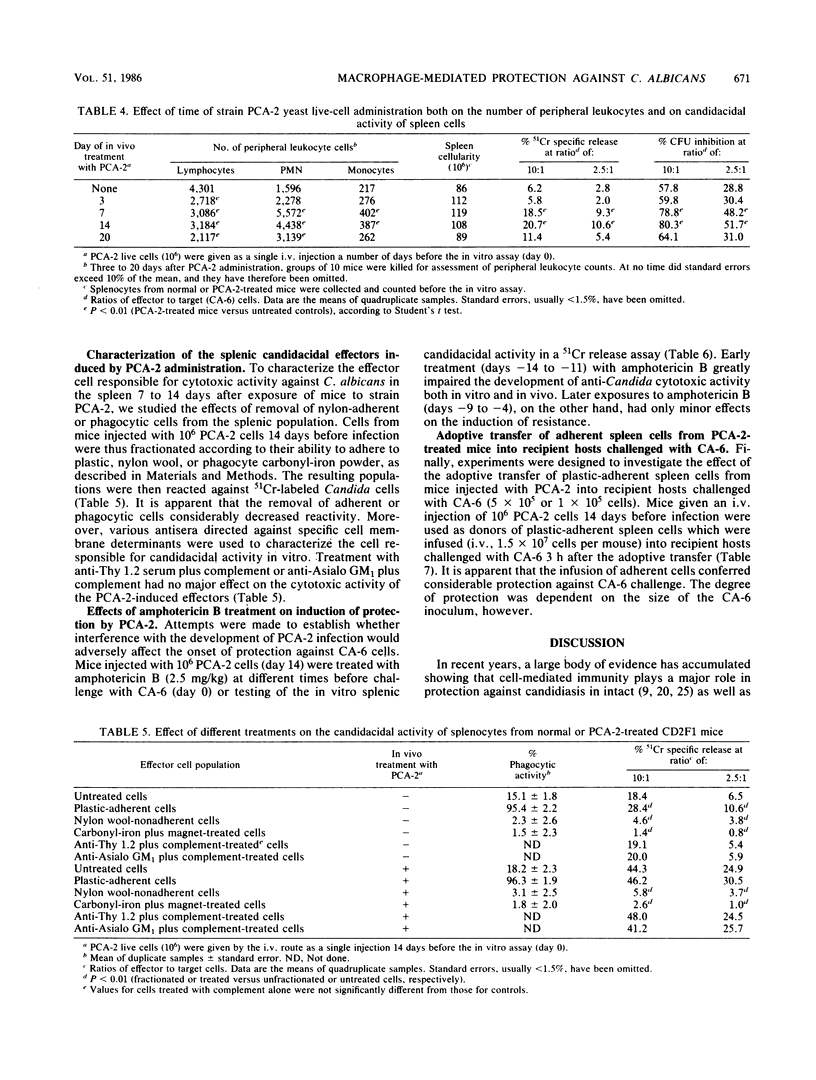
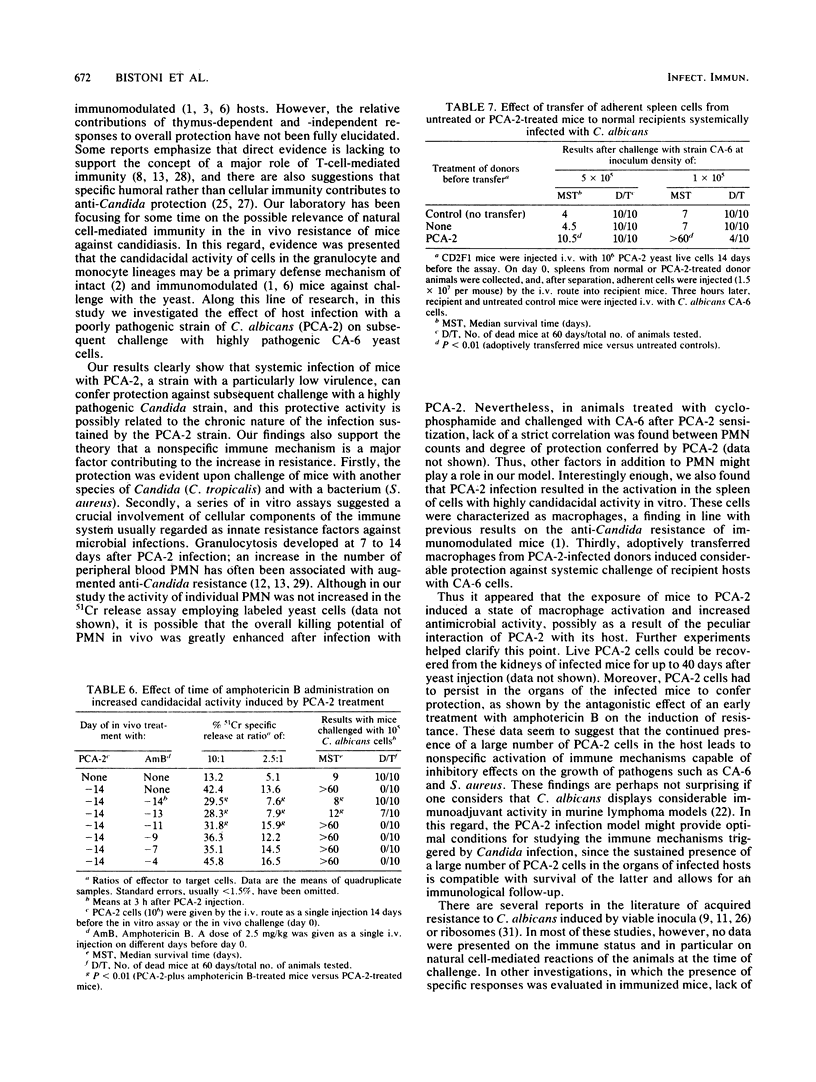
Systemic infection of mice with a Candida albicans strain (PCA-2) incapable of yeast-mycelial conversion conferred protection against a subsequent intravenous challenge with the pathogenic strain of the parent organism, strain CA-6. Protection was nonspecific since it was also detected upon challenge of mice with Staphylococcus aureus. Moreover, the PCA-2 organisms had to be viable, their effects being most evident when they were given intravenously at a dose of 10(6) cells 7 to 14 days prior to microbial challenge. Thus, all mice pretreated with PCA-2 and challenged 14 days later with viable CA-6 cells lived through a 60-day observation period, whereas all control mice not treated with PCA-2 died within 3 days. In an attempt to correlate the immunostimulatory effects observed in vivo with possible modifications in in vitro functions, it was found that administration of PCA-2 was accompanied by an increase in the number of peripheral blood polymorphonuclear cells and by the activation in the spleen of cells with highly candidacidal activity in vitro. Moreover, the adoptive transfer of plastic-adherent cells from PCA-2-infected mice into histocompatible recipients conferred considerable protection against subsequent CA-6 challenge.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baccarini M., Bistoni F., Puccetti P., Garaci E. Natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity against Candida albicans induced by cyclophosphamide: nature of the in vitro cytotoxic effector. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):1–9. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.1-9.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baccarini M., Blasi E., Puccetti P., Bistoni F. Phagocytic killing of Candida albicans by different murine effector cells. Sabouraudia. 1983 Dec;21(4):271–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistoni F., Baccarini M., Blasi E., Marconi P., Puccetti P., Garaci E. Correlation between in vivo and in vitro studies of modulation of resistance to experimental Candida albicans infection by cyclophosphamide in mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):46–55. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.46-55.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistoni F., Baccarini M., Blasi E., Puccetti P., Marconi P. A radiolabel release microassay for phagocytic killing of Candida albicans. J Immunol Methods. 1982 Aug 13;52(3):369–377. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(82)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistoni F., Vecchiarelli A., Cenci E., Sbaraglia G., Perito S., Cassone A. A comparison of experimental pathogenicity of Candida species in cyclophosphamide-immunodepressed mice. Sabouraudia. 1984;22(5):409–418. doi: 10.1080/00362178485380661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistoni F., Vecchiarelli A., Mazzolla R., Puccetti P., Marconi P., Garaci E. Immunoadjuvant activity of amphotericin B as displayed in mice infected with Candida albicans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):625–631. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chilgren R. A., Quie P. G., Meuwissen H. J., Hong R. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis, deficiency of delayed hypersensitivity, and selective local antibody defect. Lancet. 1967 Sep 30;2(7518):688–693. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90974-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Acute systemic candidiasis in normal and congenitally thymic-deficient (nude) mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Feb;19(2):121–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger D. K., Domer J. E., McQuitty J. T., Jr Experimental murine candidiasis: pathological and immune responses to cutaneous inoculation with Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1978 Feb;19(2):499–509. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.2.499-509.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giger D. K., Domer J. E., Moser S. A., McQuitty J. T., Jr Experimental murine candidiasis: pathological and immune responses in T-lymphocyte-depleted mice. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):729–737. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.729-737.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASENCLEVER H. F., MITCHELL W. O. ACQUIRED IMMUNITY TO CANDIDIASIS IN MICE. J Bacteriol. 1963 Sep;86:401–406. doi: 10.1128/jb.86.3.401-406.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtrel B., Lagrange P. H., Michel J. C. Systemic candidiasis in mice. II.--Main role of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in resistance to infection. Ann Immunol (Paris) 1980 Jan-Feb;131C(1):105–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtrel B., Langrange P. H., Michel J. C. Absence of correlation between delayed-type hypersensitivity and protection in experimental systemic candidiasis in immunized mice. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):95–101. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.95-101.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius M. H., Simpson E., Herzenberg L. A. A rapid method for the isolation of functional thymus-derived murine lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1973 Oct;3(10):645–649. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830031011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tada T. A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. H., Chandler J. W., Schimke R. N. Chronic mucocutaneous moniliasis with impaired delayed hypersensitivity. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 Mar;6(3):375–385. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. H., Rich R. R., Bennett J. E. Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis: model-building in cellular immunity. Ann Intern Med. 1971 Jun;74(6):955–978. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-74-6-955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfo S., Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Macrophage-lymphocyte interaction in migration inhibition factor (MIF) production against soluble or cellular tumor-associated antigens. I. Characteristics and genetic control of two different mechanisms of stimulating MIF production. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):695–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijh P. C., van den Barselaar M. T., van Furth R. Kinetics of phagocytosis and intracellular killing of Candida albicans by human granulocytes and monocytes. Infect Immun. 1977 Aug;17(2):313–318. doi: 10.1128/iai.17.2.313-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOURAD S., FRIEDMAN L. Pathogenicity of Candida. J Bacteriol. 1961 Apr;81:550–556. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.4.550-556.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi P., Bistoni F., Boncio L., Bersiani A., Bravi P., Pitzurra M. Utilizzazione di soluzione salina ipertonica di cloruro di potassio (3M KC1) per l'estrazione di antigeni solubili da Candia albicans. Ann Sclavo. 1976 Jan-Feb;18(1):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marconi P., Cassone A., Tissi L., Baccarini M., Puccetti P., Garaci E., Bonmassar E., Bistoni F. Cellular mechanisms underlying the adjuvant activity of Candida albicans in a mouse lymphoma model. Int J Cancer. 1982 Apr 15;29(4):483–488. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattia E., Carruba G., Angiolella L., Cassone A. Induction of germ tube formation by N-acetyl-D-glucosamine in Candida albicans: uptake of inducer and germinative response. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):555–562. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.555-562.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser S. A., Domer J. E. Effects of cyclophosphamide on murine candidiasis. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):376–386. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.376-386.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser S. A., Domer J. E., Mather F. J. Experimental murine candidiasis: cell-mediated immunity after cutaneous challenge. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):140–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.140-149.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearsall N. N., Adams B. L., Bunni R. Immunologic responses to Candida albicans. III. Effects of passive transfer of lymphoid cells or serum on murine candidiasis. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1176–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers T. J., Balish E., Manning D. D. The role of thymus-dependent cell-mediated immunity in resistance to experimental disseminated candidiasis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1976 Oct;20(4):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruthe R. C., Andersen B. R., Cunningham B. L., Epstein R. B. Efficacy of granulocyte transfusions in the control of systemic candidiasis in the leukopenic host. Blood. 1978 Sep;52(3):493–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltarelli C. G., Gentile K. A., Mancuso S. C. Lethality of Candida strains as influenced by the host. Can J Microbiol. 1975 May;21(5):648–654. doi: 10.1139/m75-093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal E., Sandovsky-Losica H. Experimental vaccination with Candida albicans ribosomes in cyclophosphamide-treated animals. Sabouraudia. 1981 Dec;19(4):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdimarsson H., Holt L., Riches H. R., Hobbs J. R. Lymphocyte abnormality in chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis. Lancet. 1970 Jun 13;1(7659):1259–1261. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91742-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



