Abstract
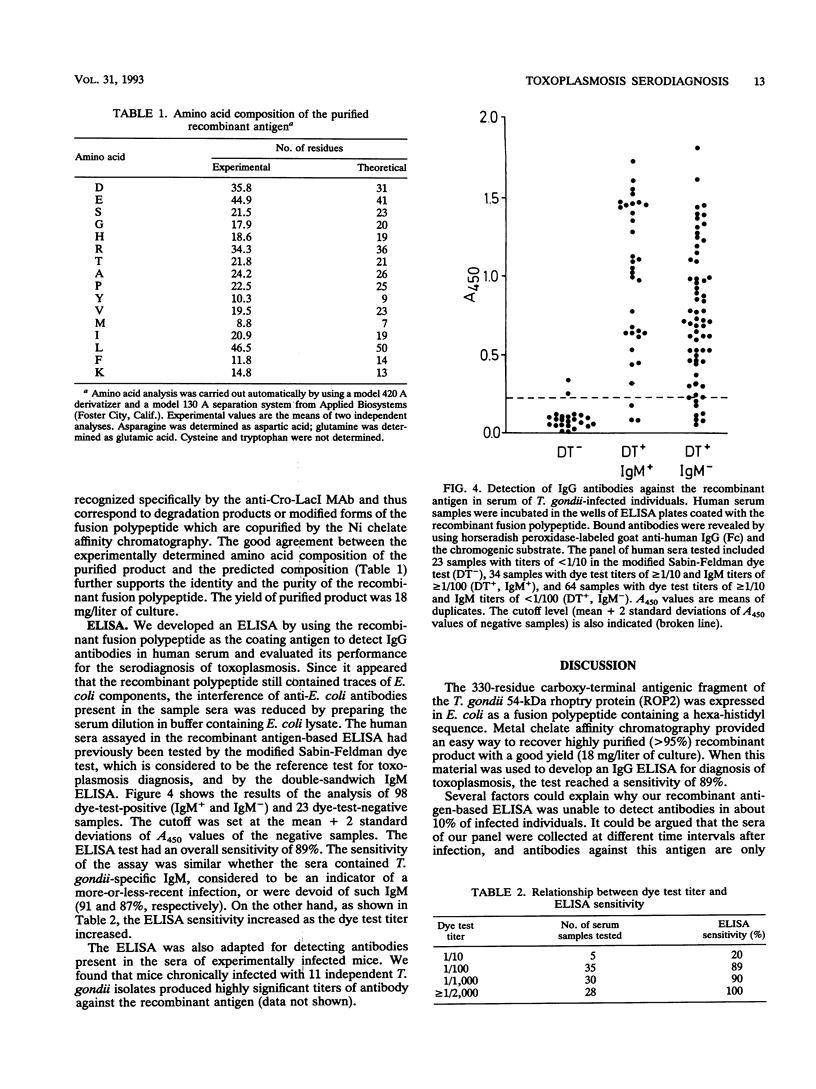
A 330-residue carboxy-terminal antigenic fragment of the Toxoplasma gondii 54-kDa rhoptry protein (ROP2) was expressed in Escherichia coli as a fusion polypeptide containing a 48-amino-acid sequence derived from phage lambda protein Cro and E. coli protein LacI followed by six consecutive histidyl residues. Metal chelate affinity chromatography provided an easy way to isolate the recombinant product in a highly purified form (> 95%). When this material was used to develop an immunoglobulin G (IgG) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis, the test reached a sensitivity of 89%. The sensitivity of the assay was similar whether the sera contained T. gondii-specific IgM or were devoid of such IgM. It was also found that ROP2 is a conserved antigen since antibodies against the recombinant antigen could be detected in mice experimentally infected with 11 independent T. gondii isolates originating from infected human tissues tested. Thus, the 54-kDa rhoptry antigen could advantageously complement other previously described T. gondii antigens for the development of more-sensitive and more-informative recombinant antigen-based tests for toxoplasmosis diagnosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg J. L., Perelman D., Kasper L. H., Ware P. L., Boothroyd J. C. Molecular analysis of the gene encoding the major surface antigen of Toxoplasma gondii. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 15;141(10):3584–3591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesbron-Delauw M. F., Guy B., Torpier G., Pierce R. J., Lenzen G., Cesbron J. Y., Charif H., Lepage P., Darcy F., Lecocq J. P. Molecular characterization of a 23-kilodalton major antigen secreted by Toxoplasma gondii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7537–7541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross U., Müller W. A., Knapp S., Heesemann J. Identification of a virulence-associated antigen of Toxoplasma gondii by use of a mouse monoclonal antibody. Infect Immun. 1991 Dec;59(12):4511–4516. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.12.4511-4516.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes H. P. Toxoplasmosis: the need for improved diagnostic techniques and accurate risk assessment. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;120:105–139. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-09197-5_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. M., Illana S., McDonald P. J., Asai T. Cloning, expression and nucleotide sequence of the gene fragment encoding an antigenic portion of the nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase of Toxoplasma gondii. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):215–220. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LELONG M., DESMONTS G. L'emploi du microscope à contraste de phase dans la réaction de Sabin-Feldman. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1951 Nov;145(21-22):1660–1661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leriche M. A., Dubremetz J. F. Characterization of the protein contents of rhoptries and dense granules of Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites by subcellular fractionation and monoclonal antibodies. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Apr;45(2):249–259. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90092-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossorio P. N., Schwartzman J. D., Boothroyd J. C. A Toxoplasma gondii rhoptry protein associated with host cell penetration has unusual charge asymmetry. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1992 Jan;50(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(92)90239-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmley S. F., Sgarlato G. D., Mark J., Prince J. B., Remington J. S. Expression, characterization, and serologic reactivity of recombinant surface antigen P22 of Toxoplasma gondii. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1127–1133. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1127-1133.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potasman I., Araujo F. G., Desmonts G., Remington J. S. Analysis of Toxoplasma gondii antigens recognized by human sera obtained before and after acute infection. J Infect Dis. 1986 Oct;154(4):650–657. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.4.650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince J. B., Araujo F. G., Remington J. S., Burg J. L., Boothroyd J. C., Sharma S. D. Cloning of cDNAs encoding a 28 kilodalton antigen of Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1989 Apr;34(1):3–13. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(89)90014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read S. M., Northcote D. H. Minimization of variation in the response to different proteins of the Coomassie blue G dye-binding assay for protein. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaut E., Tsao H., Fiers W. Improved plasmid vectors with a thermoinducible expression and temperature-regulated runaway replication. Gene. 1983 Apr;22(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90069-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saavedra R., de Meuter F., Decourt J. L., Hérion P. Human T cell clone identifies a potentially protective 54-kDa protein antigen of Toxoplasma gondii cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 15;147(6):1975–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadak A., Taghy Z., Fortier B., Dubremetz J. F. Characterization of a family of rhoptry proteins of Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jun;29(2-3):203–211. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saman E., Breugelmans K., Heyndrickx L., Merregaert J. The open reading frame ORF S3 of equine infectious anemia virus is expressed during the viral life cycle. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6319–6324. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6319-6324.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenter A. M., Johnson A. M. Recognition of recombinant Toxoplasma gondii antigens by human sera in an ELISA. Parasitol Res. 1991;77(3):197–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00930858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verhofstede C., Van Gelder P., Rabaey M. The infection-stage-related IgG response to Toxoplasma gondii studied by immunoblotting. Parasitol Res. 1988;74(6):516–520. doi: 10.1007/BF00531628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware P. L., Kasper L. H. Strain-specific antigens of Toxoplasma gondii. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):778–783. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.778-783.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Udem S. A., Tanowitz H., Wittner M. Western blot analysis of the antibody response of patients with AIDS and toxoplasma encephalitis: antigenic diversity among Toxoplasma strains. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):7–13. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]