Abstract
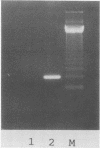
We developed a polymerase chain reaction-based assay for Francisella tularensis which we evaluated by using spiked blood samples and experimentally infected mice. The assay detected both type A and type B F. tularensis at levels equivalent to one CFU/microliter of spiked blood. Results from polymerase chain reaction-based assay of limiting dilutions of blood from mice infected with the live vaccine strain agreed closely with results from blood culture.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anthony L. D., Burke R. D., Nano F. E. Growth of Francisella spp. in rodent macrophages. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3291–3296. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3291-3296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. N., Hollis D. G., Thornsberry C. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing of Francisella tularensis with a modified Mueller-Hinton broth. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Aug;22(2):212–215. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.2.212-215.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier A. H., Polsinelli T., Green S. J., Nacy C. A. Activation of macrophages for destruction of Francisella tularensis: identification of cytokines, effector cells, and effector molecules. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):817–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.817-825.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier A. H., Slayter M. V., Ziemba R., Meltzer M. S., Nacy C. A. Live vaccine strain of Francisella tularensis: infection and immunity in mice. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):2922–2928. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.2922-2928.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Nishiyama K., Hyodo S., Shigeta S., Ito T. Weight reduction of thymus and depletion of lymphocytes of T-dependent areas in peripheral lymphoid tissues of mice infected with Francisella tularensis. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):812–818. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.812-818.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowitz L. E., Hynes N. A., de la Cruz P., Campos E., Barbaree J. M., Plikaytis B. D., Mosier D., Kaufmann A. F. Tick-borne tularemia. An outbreak of lymphadenopathy in children. JAMA. 1985 Nov 22;254(20):2922–2925. doi: 10.1001/jama.254.20.2922. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara Y., Sato T., Fujita H., Ueno T., Homma M. Clinical manifestations of tularemia in Japan--analysis of 1,355 cases observed between 1924 and 1987. Infection. 1991 Jan-Feb;19(1):14–17. doi: 10.1007/BF01643750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Provenza J. M., Klotz S. A., Penn R. L. Isolation of Francisella tularensis from blood. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Sep;24(3):453–455. doi: 10.1128/jcm.24.3.453-455.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Fujita H., Ohara Y., Homma M. Microagglutination test for early and specific serodiagnosis of tularemia. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Oct;28(10):2372–2374. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.10.2372-2374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöstedt A., Sandström G., Tärnvik A., Jaurin B. Nucleotide sequence and T cell epitopes of a membrane protein of Francisella tularensis. J Immunol. 1990 Jul 1;145(1):311–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syrjälä H., Koskela P., Ripatti T., Salminen A., Herva E. Agglutination and ELISA methods in the diagnosis of tularemia in different clinical forms and severities of the disease. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):142–145. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. P., Istre G. R., McChesney T. C., Satalowich F. T., Parker R. L., McFarland L. M. Epidemiologic characteristics of human tularemia in the southwest-central states, 1981-1987. Am J Epidemiol. 1991 May 15;133(10):1032–1038. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tärnvik A. Nature of protective immunity to Francisella tularensis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 May-Jun;11(3):440–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhari M., Syrjälä H., Salminen A. Tularemia in children caused by Francisella tularensis biovar palaearctica. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Feb;9(2):80–83. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199002000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]