Abstract
We show that solid and liquid media, supplemented only with cyclodextrins and free of blood and its derivatives, support the growth of Helicobacter pylori. These media can be used for primary isolation of the bacteria from biopsy samples, routine laboratory growth, and large-scale industrial fermentation.
Full text
PDF
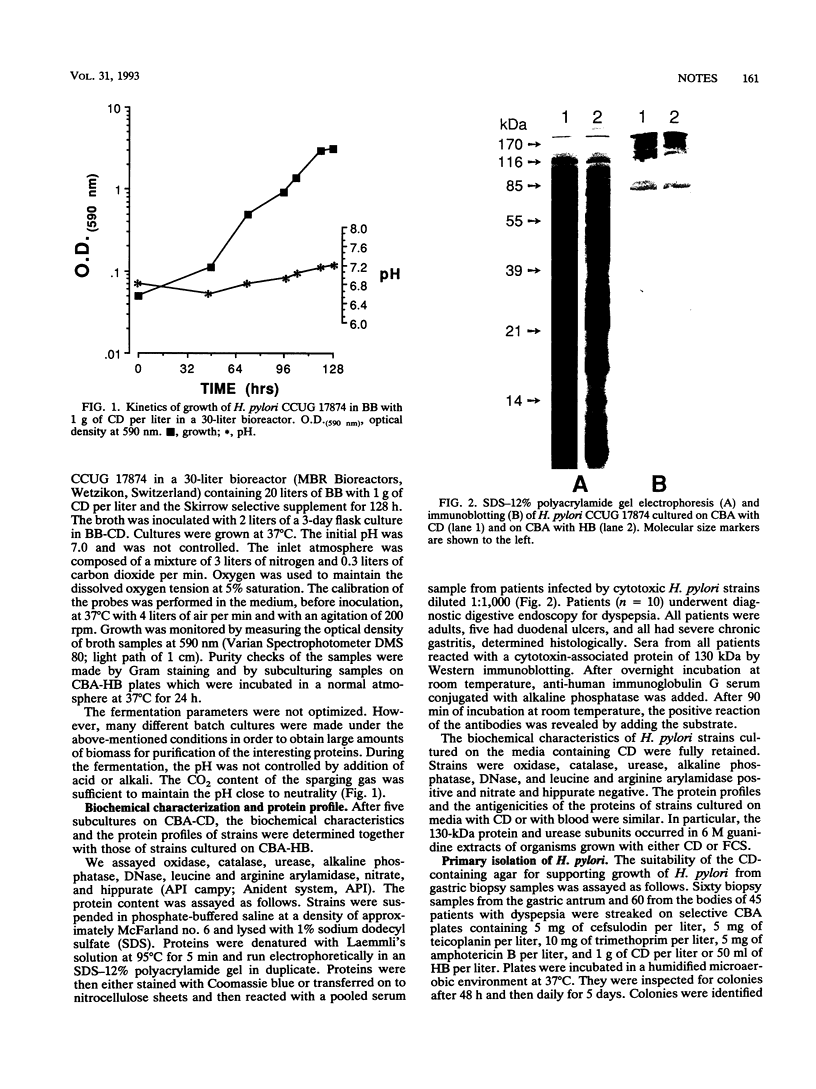

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaser M. J. Helicobacter pylori and the pathogenesis of gastroduodenal inflammation. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):626–633. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazell S. L., Graham D. Y. Unsaturated fatty acids and viability of Helicobacter (Campylobacter) pylori. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 May;28(5):1060–1061. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.5.1060-1061.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. R., Freedman R., Depew C. E., Kraft W. G. Growth of Campylobacter pylori in liquid media. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2123–2125. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2123-2125.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]