Abstract
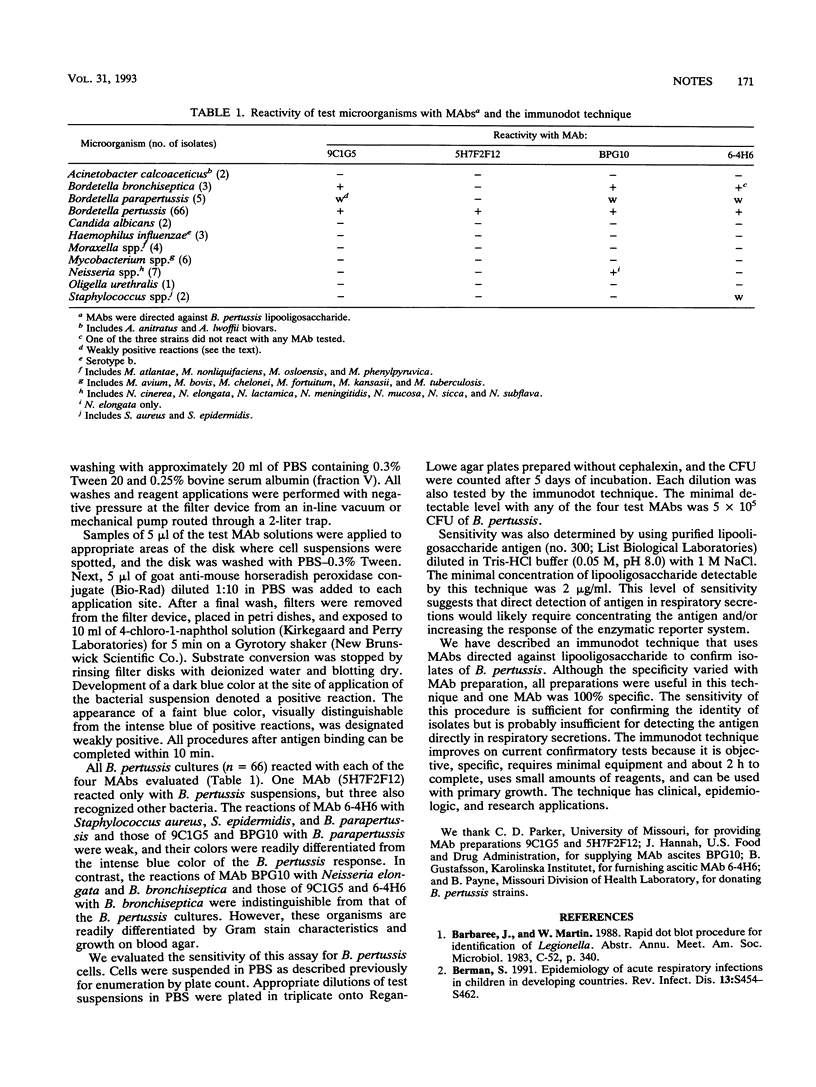
We developed and evaluated a rapid test with monoclonal antibodies to identify cultures of Bordetella pertussis. Samples of 5 microliters of cells suspended in formalin-saline were dried onto a nitrocellulose disk. The disk was placed in a filtration device, and 5-microliters volumes of murine monoclonal antibody directed against B. pertussis lipooligosaccharide and peroxidase conjugate were added consecutively, with washing after each addition. The disk was removed and immersed in peroxidase substrate solution. All of 66 B. pertussis isolates confirmed by direct fluorescent-antibody assay were correctly identified by using four different monoclonal antibodies. One of the monoclonal antibodies did not react with over 20 bacterial species tested, including other Bordetella, Acinetobacter, Haemophilus, Moraxella, Mycobacterium, Neisseria, and Staphylococcus spp. This technique detected > or = 2 micrograms of lipooligosaccharide per ml or > or = 5 x 10(8) B. pertussis cells per ml. This rapid procedure used small amounts of reagents, needed less equipment, and was less subjective and more specific than the direct fluorescent-antibody assay.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman S. Epidemiology of acute respiratory infections in children of developing countries. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 May-Jun;13 (Suppl 6):S454–S462. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.supplement_6.s454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farizo K. M., Cochi S. L., Zell E. R., Brink E. W., Wassilak S. G., Patriarca P. A. Epidemiological features of pertussis in the United States, 1980-1989. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14(3):708–719. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.3.708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank D. W., Parker C. D. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies to Bordetella pertussis. J Biol Stand. 1984 Oct;12(4):353–365. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(84)80060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. L. Pertussis: the disease and new diagnostic methods. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1988 Oct;1(4):365–376. doi: 10.1128/cmr.1.4.365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Askelöf P. Rapid detection of Bordetella pertussis by a monoclonal antibody-based colony blot assay. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):628–631. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.628-631.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Lindquist U., Andersson M. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed against Bordetella pertussis lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Feb;26(2):188–193. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.2.188-193.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. M., Cowell J. L., Brennan M. J., Burns D. L., Manclark C. R. Agglutinating monoclonal antibodies that specifically recognize lipooligosaccharide A of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1988 Mar;56(3):699–702. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.3.699-702.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onorato I. M., Wassilak S. G. Laboratory diagnosis of pertussis: the state of the art. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1987 Feb;6(2):145–151. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198702000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroffolini T., Giammanco A., Chiarini A., Taormina S., Sarzana A., Mazza G., Maggio M., Chiaramonte M., Ngatchu T., Lantum D. Seroepidemiology of pertussis infection in an urban childhood population in Cameroon. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 Jan;7(1):64–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00221343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroffolini T., Giammanco A., De Crescenzo L., Lupo F., Nicosia V., Torres G., Valenza A. R., Cascio A., Taormina S., Nisticò L. Prevalence of pertussis IgG antibodies in children in Palermo, Italy. Infection. 1989 Sep-Oct;17(5):280–283. doi: 10.1007/BF01650708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama N., Watanabe H., Fujita I., Minamitani M. Seroepidemiology of pertussis in the Japanese population. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1989;178(1):1–8. doi: 10.1007/BF00202286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M. G. Epidemiology of pertussis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Mar-Apr;11(2):255–262. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.2.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


