Abstract
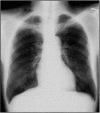
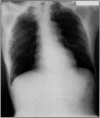
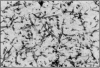
We present an autopsy case of concomitant pulmonary aspergillosis and nocardiosis undiagnosed during life in a long-term surviving renal transplant recipient. The patient had fever and a newly developed cavitary lesion on a chest x-ray. The working diagnosis was pulmonary tuberculosis with possible colonization by Aspergillus species. Cultures of bronchial washings became positive for Aspergillus fumigatus 1 day after death. The study of tissue from the lung cavity at autopsy revealed Aspergillus fumigatus (confirmed by postmortem culture) and the filaments of Nocardia species. Increased numbers of surviving immunosuppressed patients will require aggressive, comprehensive diagnostic techniques for the detection of polymicrobial infections.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Peterson P. K., Balfour H. H., Jr, Fryd D. S., Ferguson R. M., Simmons R. L. Fever in renal transplant recipients: causes, prognostic significance and changing patterns at the University of Minnesota Hospital. Am J Med. 1981 Sep;71(3):345–351. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(81)90149-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenow E. C., 3rd, Wilson W. R., Cockerill F. R., 3rd Pulmonary disease in the immunocompromised host. 1. Mayo Clin Proc. 1985 Jul;60(7):473–487. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60872-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washer G. F., Schröter G. P., Starzl T. E., Weil R., 3rd Causes of death after kidney transplantation. JAMA. 1983 Jul 1;250(1):49–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson W. R., Cockerill F. R., 3rd, Rosenow E. C., 3rd Pulmonary disease in the immunocompromised host (2). Mayo Clin Proc. 1985 Sep;60(9):610–631. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60985-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]