Abstract
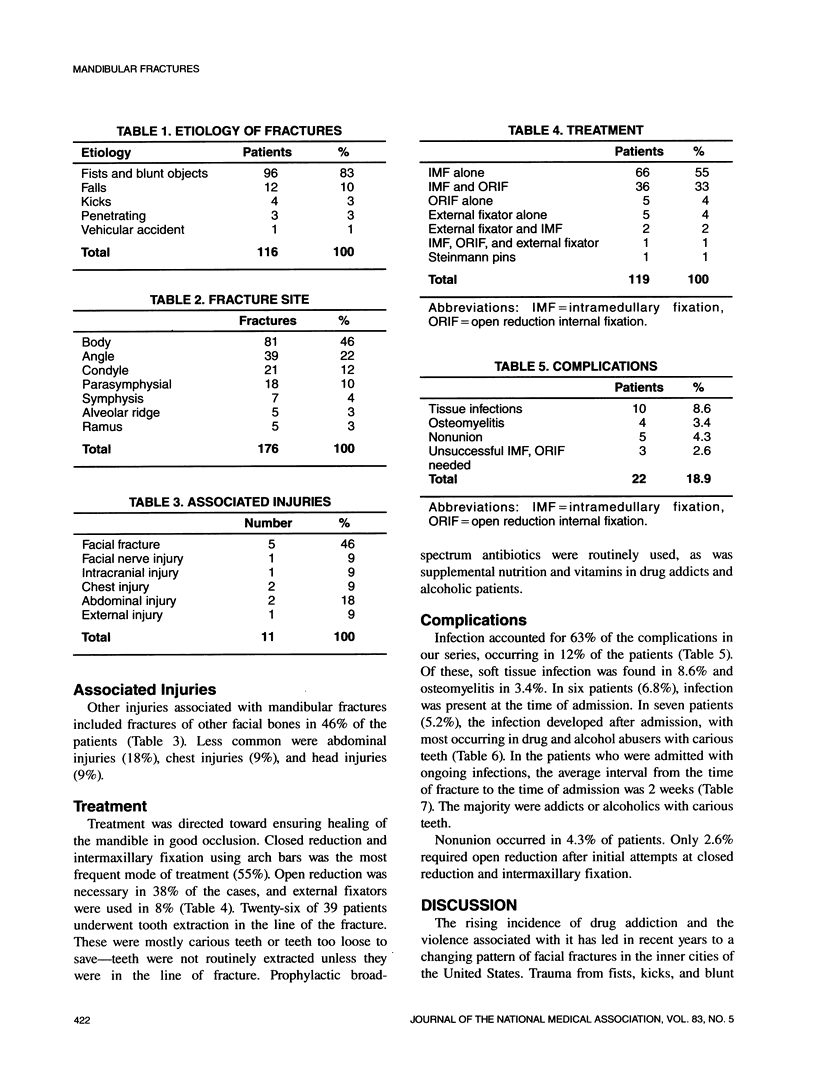
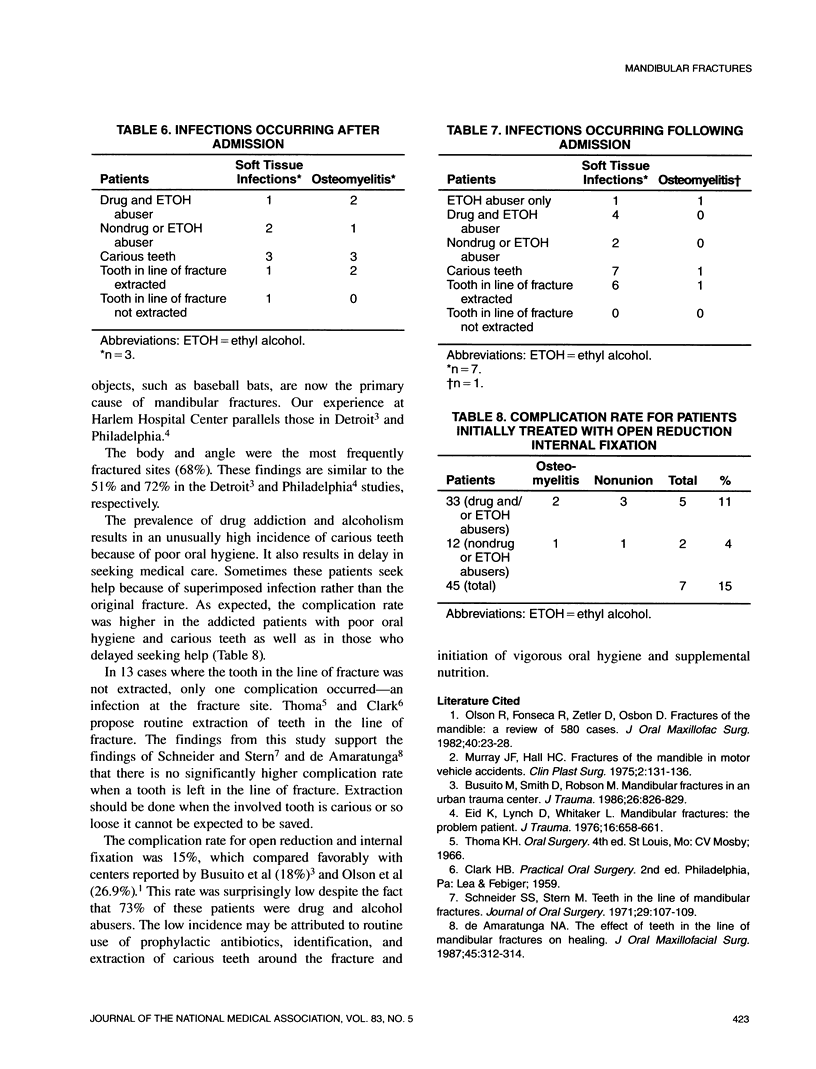
A retrospective study of 116 patients treated at Harlem Hospital for mandibular fractures between 1984 and 1987 was performed. Men comprised 84% of the population studied. The mechanisms of injury were assault with fists and blunt objects (33%), falls (10%), kicking (3%), penetrating injuries (3%), and vehicular accidents (1%). The body of the mandible (46%) and the angle (22%) were the most common fracture sites. Intermaxillary fixation with arch bars was the most frequent method of treatment (55%), followed by open reduction and internal fixation (33%). The complication rate with open reduction was relatively low (15%) despite the fact that 73% of these patients were heavy drug or alcohol abusers with documented poor oral hygiene. This study further substantiates the findings that in the poor inner cities, blunt trauma from drug-related violence has become the major cause of mandibular fracture. Treatment of these patients should include prophylactic broad-spectrum antibiotics, improved oral hygiene, and supplemental nutrition.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Busuito M. J., Smith D. J., Jr, Robson M. C. Mandibular fractures in an urban trauma center. J Trauma. 1986 Sep;26(9):826–829. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198609000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eid K., Lynch D. J., Whitaker L. A. Mandibular fractures: the problem patient. J Trauma. 1976 Aug;16(08):658–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider S. S., Stern M. Teeth in the line of mandibular fractures. J Oral Surg. 1971 Feb;29(2):107–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. C. Maxillofacial injuries from vehicular accidents. Foreword. Clin Plast Surg. 1975 Jan;2(1):1–2. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


