Abstract
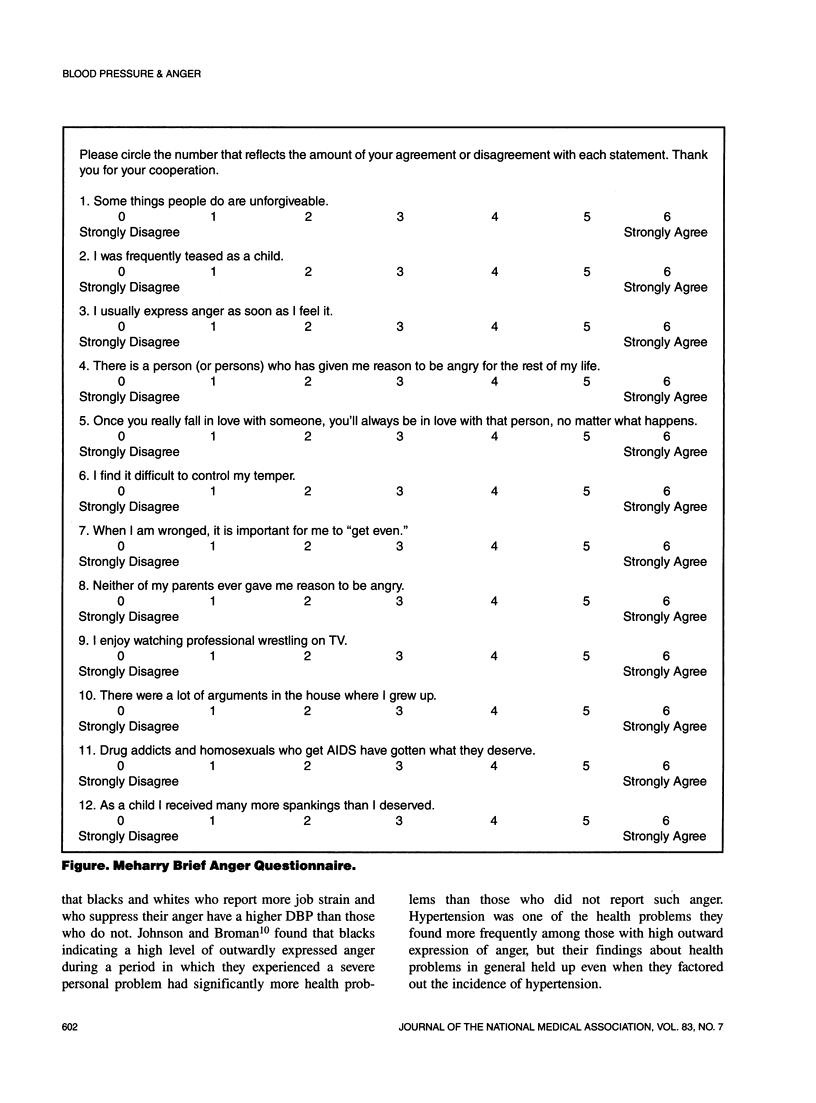
A brief questionnaire (12 items) was developed to assess aspects of anger that could be expeditiously obtained during health screenings where medical students and residents can acquire valuable research and clinical experience simultaneously. Blood pressures were measured immediately upon sitting and after 3 minutes in 179 subjects who attended a health fair in Nashville. The questionnaire was administered after both blood pressure measurements were acquired. Scores on the measure of anger correlated significantly (P = .0009) with resting systolic blood pressure (SBP) in both blacks and whites while a measure of "John Henryism" showed no correlation with blood pressure in either group (P = .81). The findings are consistent with the literature in supporting a connection between anger and blood pressure but do not support the relationship between John Henryism and blood pressure.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cottington E. M., Matthews K. A., Talbott E., Kuller L. H. Occupational stress, suppressed anger, and hypertension. Psychosom Med. 1986 Mar-Apr;48(3-4):249–260. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198603000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimsdale J. E., Pierce C., Schoenfeld D., Brown A., Zusman R., Graham R. Suppressed anger and blood pressure: the effects of race, sex, social class, obesity, and age. Psychosom Med. 1986 Jul-Aug;48(6):430–436. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198607000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst F. A., Enwonwu C. O., Francis R. A. Calcium attenuates cardiovascular reactivity to sodium and stress in blacks. Am J Hypertens. 1990 Jun;3(6 Pt 1):451–457. doi: 10.1093/ajh/3.6.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst F. A., Francis R. A., Enwonwu C. O. Manifest hostility may affect habituation of cardiovascular reactivity in blacks. Behav Med. 1990 Fall;16(3):119–124. doi: 10.1080/08964289.1990.9934599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. A., Hartnett S. A., Kalsbeek W. D. John Henryism and blood pressure differences among black men. J Behav Med. 1983 Sep;6(3):259–278. doi: 10.1007/BF01315113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. H., Broman C. L. The relationship of anger expression to health problems among black Americans in a national survey. J Behav Med. 1987 Apr;10(2):103–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00846419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koskenvuo M., Kaprio J., Rose R. J., Kesäniemi A., Sarna S., Heikkilä K., Langinvainio H. Hostility as a risk factor for mortality and ischemic heart disease in men. Psychosom Med. 1988 Jul-Aug;50(4):330–340. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198807000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews K. A. Coronary heart disease and type A behaviors: update on and alternative to the Booth-Kewley and Friedman (1987) quantitative review. Psychol Bull. 1988 Nov;104(3):373–380. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.104.3.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarron D. A., Morris C. D., Henry H. J., Stanton J. L. Blood pressure and nutrient intake in the United States. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1392–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.6729459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shekelle R. B., Hulley S. B., Neaton J. D., Billings J. H., Borhani N. O., Gerace T. A., Jacobs D. R., Lasser N. L., Mittlemark M. B., Stamler J. The MRFIT behavior pattern study. II. Type A behavior and incidence of coronary heart disease. Am J Epidemiol. 1985 Oct;122(4):559–570. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a114135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez E. C., Williams R. B., Jr The relationships between dimensions of hostility and cardiovascular reactivity as a function of task characteristics. Psychosom Med. 1990 Sep-Oct;52(5):558–570. doi: 10.1097/00006842-199009000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. B., Jr, Haney T. L., Lee K. L., Kong Y. H., Blumenthal J. A., Whalen R. E. Type A behavior, hostility, and coronary atherosclerosis. Psychosom Med. 1980 Nov;42(6):539–549. doi: 10.1097/00006842-198011000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


