Abstract
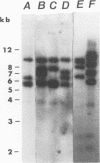
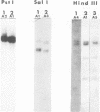
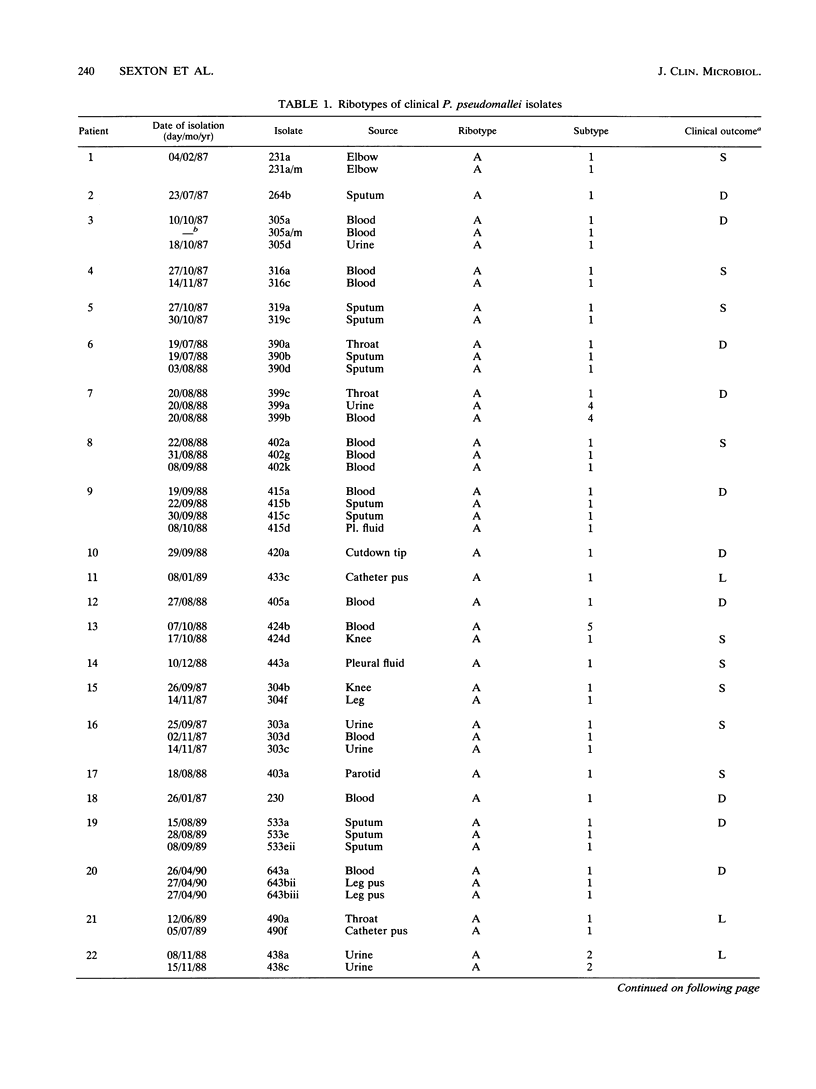
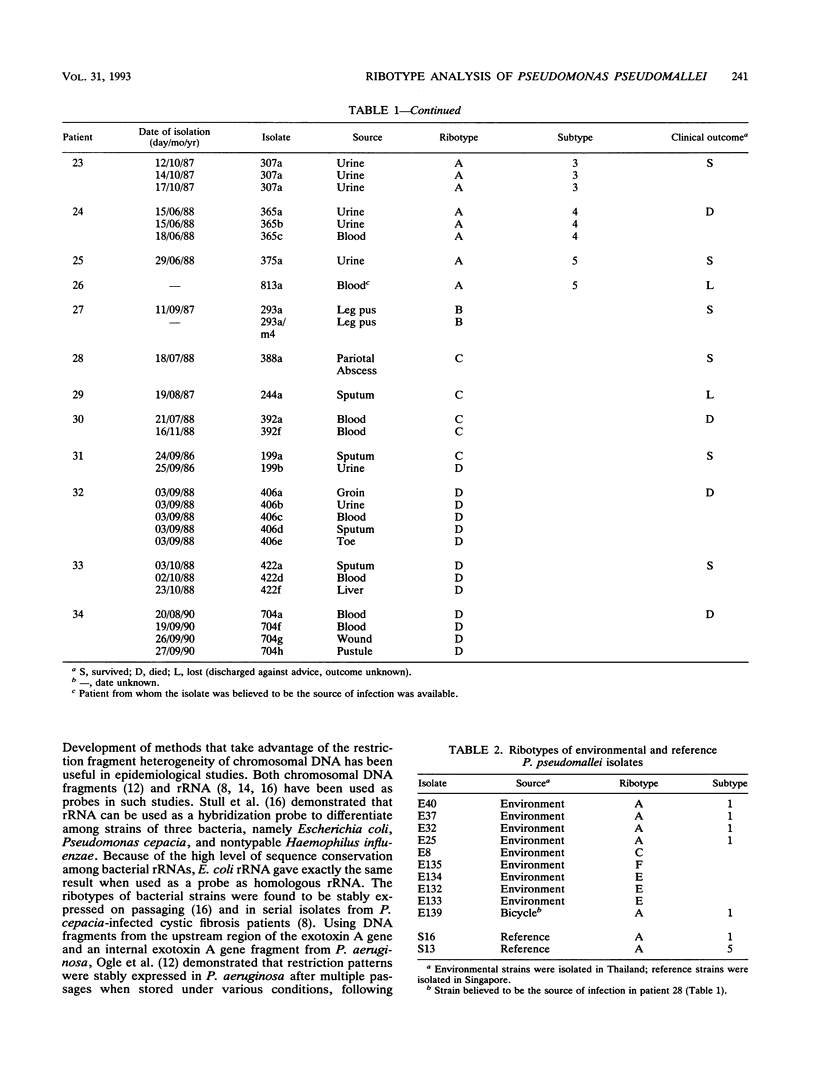
No epidemiological typing system to differentiate among Pseudomonas pseudomallei isolates has been available. Ribotype analysis was developed and used to examine 74 clinical and 10 environmental isolates of P. pseudomallei from Thailand. Six P. pseudomallei ribotypes were identified from restriction fragment polymorphisms of EcoRI chromosomal digests. The predominant ribotype, A, was found in 59 of the isolates examined. By using patterns from hybridizations with SalI, HindIII, and PstI restriction digests, isolates of ribotype A were subdivided into a further five subtypes, giving a total of 10 differentiable P. pseudomallei types. In 23 of 34 melioidosis patients studied, multiple P. pseudomallei isolates were present. In all but one of these patients, a single ribotype of the organism was present. Isolation of two different ribotypes of P. pseudomallei from one patient, one each in sputum and urine, suggests that superinfection may have occurred. The ribotype was shown to be conserved during the course of antibiotic treatments in seven patients studied, although the antibiotic sensitivity patterns in the isolates from these patients varied. The prevalence of subtype A1 in clinical and environmental specimens suggests that this strain may be predominant in this geographical location. These results demonstrate the usefulness of the ribotyping method for epidemiological studies of P. pseudomallei.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chaowagul W., White N. J., Dance D. A., Wattanagoon Y., Naigowit P., Davis T. M., Looareesuwan S., Pitakwatchara N. Melioidosis: a major cause of community-acquired septicemia in northeastern Thailand. J Infect Dis. 1989 May;159(5):890–899. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.5.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dance D. A., Wuthiekanun V., White N. J., Chaowagul W. Antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas pseudomallei. Lancet. 1988 Apr 30;1(8592):994–995. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)91810-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. B., Ohman D. E. Cloning and expression in Pseudomonas aeruginosa of a gene involved in the production of alginate. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1115–1121. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1115-1121.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govan J. R., Harris G. Typing of Pseudomonas cepacia by bacteriocin susceptibility and production. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Oct;22(4):490–494. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.4.490-494.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Dasen S. E., Nielson D. W., Stern R. C., Stull T. L. Person-to-person transmission of Pseudomonas cepacia between patients with cystic fibrosis. Lancet. 1990 Nov 3;336(8723):1094–1096. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92571-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Fisher M. C., Dasen S. E., Mortensen J. E., Stull T. L. Ribotype stability of serial pulmonary isolates of Pseudomonas cepacia. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jul;164(1):133–136. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiPuma J. J., Mortensen J. E., Dasen S. E., Edlind T. D., Schidlow D. V., Burns J. L., Stull T. L. Ribotype analysis of Pseudomonas cepacia from cystic fibrosis treatment centers. J Pediatr. 1988 Nov;113(5):859–862. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays E. E., Ricketts E. A. Melioidosis: recrudescence associated with bronchogenic carcinoma twenty-six years following initial geographic exposure. Chest. 1975 Aug;68(2):261–263. doi: 10.1378/chest.68.2.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogle J. W., Janda J. M., Woods D. E., Vasil M. L. Characterization and use of a DNA probe as an epidemiological marker for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jan;155(1):119–126. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parisi J. T. Coagulase-negative staphylococci and the epidemiological typing of Staphylococcus epidermidis. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Jun;49(2):126–139. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.2.126-139.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabkin C. S., Jarvis W. R., Anderson R. L., Govan J., Klinger J., LiPuma J., Martone W. J., Monteil H., Richard C., Shigeta S. Pseudomonas cepacia typing systems: collaborative study to assess their potential in epidemiologic investigations. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Jul-Aug;11(4):600–607. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.4.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stull T. L., LiPuma J. J., Edlind T. D. A broad-spectrum probe for molecular epidemiology of bacteria: ribosomal RNA. J Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;157(2):280–286. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.2.280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanphaichitra D. Tropical disease in the immunocompromised host: melioidosis and pythiosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Nov-Dec;11 (Suppl 7):S1629–S1643. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_7.s1629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White N. J., Dance D. A., Chaowagul W., Wattanagoon Y., Wuthiekanun V., Pitakwatchara N. Halving of mortality of severe melioidosis by ceftazidime. Lancet. 1989 Sep 23;2(8665):697–701. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Sokol P. A., Bryan L. E., Storey D. G., Mattingly S. J., Vogel H. J., Ceri H. In vivo regulation of virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa associated with genetic rearrangement. J Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;163(1):143–149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.1.143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierdt C. H., Robertson E. A., Williams R. L., MacLowry J. D. Computer analysis of Staphylococcus aureus phage typing data from 1957 to 1975, citing epidemiological trends and natural evolution within the phage typing system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Mar;39(3):623–629. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.3.623-629.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]