Abstract
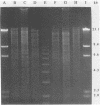
Severe nosocomial infections due to Enterobacter taylorae (formerly known as CDC Enteric Group 19) are described in four patients. Unlike most members of the Enterobacter genus, the isolates were not susceptible to penicillins or cephalosporins. Restriction endonuclease analysis of E. taylorae DNA obtained from three patients identified two distinct strains. One strain was found in two patients, suggesting a common source which we were not able to identify. We postulate that in patients harboring E. taylorae, the combination of cephalosporin therapy and instrumentation enables this organism to become an opportunistic pathogen.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarado C. J., Stolz S. M., Maki D. G. Nosocomial infections from contaminated endoscopes: a flawed automated endoscope washer. An investigation using molecular epidemiology. Am J Med. 1991 Sep 16;91(3B):272S–280S. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(91)90381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audisio R. A., Bozzetti F., Severini A., Bellegotti L., Bellomi M., Cozzi G., Pisani P., Callegari L., Doci R., Gennari L. The occurrence of cholangitis after percutaneous biliary drainage: evaluation of some risk factors. Surgery. 1988 May;103(5):507–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauernfeind A. Classification of beta-lactamases. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8 (Suppl 5):S470–S481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow J. W., Fine M. J., Shlaes D. M., Quinn J. P., Hooper D. C., Johnson M. P., Ramphal R., Wagener M. M., Miyashiro D. K., Yu V. L. Enterobacter bacteremia: clinical features and emergence of antibiotic resistance during therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Oct 15;115(8):585–590. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-8-585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Classen D. C., Jacobson J. A., Burke J. P., Jacobson J. T., Evans R. S. Serious Pseudomonas infections associated with endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Am J Med. 1988 Mar;84(3 Pt 2):590–596. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90141-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouse M. E., Evans D., Costello P., Alday M., Edwards S. A., McDermott W. V., Jr Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage. Complications due to multiple duct obstructions. Ann Surg. 1983 Jul;198(1):25–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Davis B. R., Hickman-Brenner F. W., McWhorter A., Huntley-Carter G. P., Asbury M. A., Riddle C., Wathen-Grady H. G., Elias C., Fanning G. R. Biochemical identification of new species and biogroups of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):46–76. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.46-76.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer J. J., 3rd, Fanning G. R., Davis B. R., O'Hara C. M., Riddle C., Hickman-Brenner F. W., Asbury M. A., Lowery V. A., 3rd, Brenner D. J. Escherichia fergusonii and Enterobacter taylorae, two new species of Enterobacteriaceae isolated from clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Jan;21(1):77–81. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.1.77-81.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn D. M., Weinstein R. A., Nathan C., Gaston M. A., Kabins S. A. Patients' endogenous flora as the source of "nosocomial" Enterobacter in cardiac surgery. J Infect Dis. 1987 Aug;156(2):363–368. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.2.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Archer G. L. New mechanisms of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial agents. N Engl J Med. 1991 Feb 28;324(9):601–612. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199102283240906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki D. G., Rhame F. S., Mackel D. C., Bennett J. V. Nationwide epidemic of septicemia caused by contaminated intravenous products. I. Epidemiologic and clinical features. Am J Med. 1976 Apr;60(4):471–485. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(76)90713-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray B. E., Singh K. V., Heath J. D., Sharma B. R., Weinstock G. M. Comparison of genomic DNAs of different enterococcal isolates using restriction endonucleases with infrequent recognition sites. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):2059–2063. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.2059-2063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muytjens H. L., van der Ros-van de Repe J. Comparative in vitro susceptibilities of eight Enterobacter species, with special reference to Enterobacter sakazakii. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Feb;29(2):367–370. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.2.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippon A., Labia R., Jacoby G. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1131–1136. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reina J., Salva F., Gil J., Alomar P. Urinary tract infection caused by Enterobacter taylorae. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Dec;27(12):2877–2877. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.12.2877-.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr Type I beta-lactamases of gram-negative bacteria: interactions with beta-lactam antibiotics. J Infect Dis. 1986 Nov;154(5):792–800. doi: 10.1093/infdis/154.5.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurnherr N., Brühlmann W. F., Krejs G. I., Bianchi L., Faust H., Blum A. L. Fulminant cholangitis and septicemia after endoscopic retrograde cholangiography (ERC) in two patients with obstructive jaundice. Am J Dig Dis. 1976 Jun;21(6):477–481. doi: 10.1007/BF01072133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westblom T. U., Coggins M. E. Osteomyelitis caused by Enterobacter taylorae, formerly enteric group 19. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Dec;25(12):2432–2433. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.12.2432-2433.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]