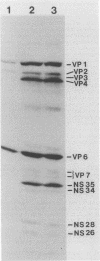
Abstract
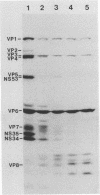
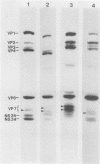
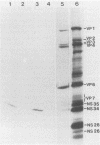
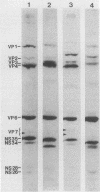
Three sequential serum samples collected from each of 20 young children with a naturally acquired primary rotavirus infection were assayed by the radioimmunoprecipitation technique for immunoglobulin G antibodies to rotavirus structural and nonstructural proteins of the four major human rotavirus serotypes G1, P1A; G2, P1B; G3, P2; and G4, P2. Fourteen children were infected with a serotype G1 rotavirus strain and six children were infected with a serotype G4 rotavirus strain. Sera were collected from each child in the acute and convalescent periods postinfection and also approximately 4 months later. Serum immune responses to rotavirus core antigens VP2 and VP3, to the major inner capsid antigen VP6, to nonstructural proteins NS35, NS28, and NS26, and to the outer capsid neutralization antigen VP4 of all test strains were detected in the majority of patients. These responses do not appear to be influenced by the G type or P type of the rotavirus strain used in the reactions. Homologous responses to the main neutralization antigen VP7 were detected in 93% of patients with serotype G1 infections and 50% of patients with serotype G4 infections. Heterologous VP7 responses were less frequently detected and were restricted to G1, G3, and G4 serotype rotavirus strains. No responses to VP7 of the serotype G2 rotavirus strain were detected in any patients. Heterotypic immune responses to the neutralization antigens, at least following serotype G1 and G4 infections, therefore appear to consist primarily of responses to VP4 rather than to VP7.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert M. J., Bishop R. F. Cultivation of human rotaviruses in cell culture. J Med Virol. 1984;13(4):377–383. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890130409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bass D. M., Mackow E. R., Greenberg H. B. NS35 and not vp7 is the soluble rotavirus protein which binds to target cells. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):322–330. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.322-330.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R. F., Barnes G. L., Cipriani E., Lund J. S. Clinical immunity after neonatal rotavirus infection. A prospective longitudinal study in young children. N Engl J Med. 1983 Jul 14;309(2):72–76. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198307143090203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Both G. W., Jennings P. A. Gene cloning to study viral antigens: prospects for novel influenza and rotavirus vaccines. Prog Vet Microbiol Immunol. 1987;3:179–213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba S., Yokoyama T., Nakata S., Morita Y., Urasawa T., Taniguchi K., Urasawa S., Nakao T. Protective effect of naturally acquired homotypic and heterotypic rotavirus antibodies. Lancet. 1986 Aug 23;2(8504):417–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. F., Borian F. E., Bell L. M., Modesto K., Gouvea V., Plotkin S. A. Protective effect of WC3 vaccine against rotavirus diarrhea in infants during a predominantly serotype 1 rotavirus season. J Infect Dis. 1988 Sep;158(3):570–587. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.3.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulson B. S., Unicomb L. E., Pitson G. A., Bishop R. F. Simple and specific enzyme immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies for serotyping human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Mar;25(3):509–515. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.3.509-515.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes M. K., Graham D. Y. Rotavirus antigens. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;185:201–214. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7974-4_13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores J., Perez-Schael I., Blanco M., Vilar M., Garcia D., Perez M., Daoud N., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z. Reactions to and antigenicity of two human-rhesus rotavirus reassortant vaccine candidates of serotypes 1 and 2 in Venezuelan infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Mar;27(3):512–518. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.3.512-518.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Midthun K., Gorziglia M., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Flores J. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of the major neutralization protein of four human rotavirus serotypes. Virology. 1987 Nov;161(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green K. Y., Taniguchi K., Mackow E. R., Kapikian A. Z. Homotypic and heterotypic epitope-specific antibody responses in adult and infant rotavirus vaccinees: implications for vaccine development. J Infect Dis. 1990 Apr;161(4):667–679. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.4.667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimwood K., Lund J. C., Coulson B. S., Hudson I. L., Bishop R. F., Barnes G. L. Comparison of serum and mucosal antibody responses following severe acute rotavirus gastroenteritis in young children. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):732–738. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.732-738.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halsey N. A., Anderson E. L., Sears S. D., Steinhoff M., Wilson M., Belshe R. B., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Samorodin R. Human-rhesus reassortant rotavirus vaccines: safety and immunogenicity in adults, infants, and children. J Infect Dis. 1988 Dec;158(6):1261–1267. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.6.1261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Cline W. L., Greenberg H. B., Wyatt R. G., Kalica A. R., Banks C. E., James H. D., Jr, Flores J., Chanock R. M. Antigenic characterization of human and animal rotaviruses by immune adherence hemagglutination assay (IAHA): evidence for distinctness of IAHA and neutralization antigens. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):415–425. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.415-425.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M., Offit P. A., Estes M. K. Identification of the simian rotavirus SA11 genome segment 3 product. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90230-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackow E. R., Shaw R. D., Matsui S. M., Vo P. T., Dang M. N., Greenberg H. B. The rhesus rotavirus gene encoding protein VP3: location of amino acids involved in homologous and heterologous rotavirus neutralization and identification of a putative fusion region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):645–649. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S. M., Mackow E. R., Greenberg H. B. Molecular determinant of rotavirus neutralization and protection. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:181–214. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60585-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui S. M., Offit P. A., Vo P. T., Mackow E. R., Benfield D. A., Shaw R. D., Padilla-Noriega L., Greenberg H. B. Passive protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea by monoclonal antibodies to the heterotypic neutralization domain of VP7 and the VP8 fragment of VP4. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):780–782. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.780-782.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midthun K., Greenberg H. B., Hoshino Y., Kapikian A. Z., Wyatt R. G., Chanock R. M. Reassortant rotaviruses as potential live rotavirus vaccine candidates. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):949–954. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.949-954.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F., Blavat G., Greenberg H. B. Reassortant rotaviruses containing structural proteins vp3 and vp7 from different parents induce antibodies protective against each parental serotype. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):491–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.491-496.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Clark H. F. Protection against rotavirus-induced gastroenteritis in a murine model by passively acquired gastrointestinal but not circulating antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):58–64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.58-64.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offit P. A., Shaw R. D., Greenberg H. B. Passive protection against rotavirus-induced diarrhea by monoclonal antibodies to surface proteins vp3 and vp7. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):700–703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.700-703.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reves R. R., Hossain M. M., Midthun K., Kapikian A. Z., Naguib T., Zaki A. M., DuPont H. L. An observational study of naturally acquired immunity to rotaviral diarrhea in a cohort of 363 Egyptian children. Calculation of risk for second episodes using age-specific person-years of observation. Am J Epidemiol. 1989 Nov;130(5):981–988. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a115431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
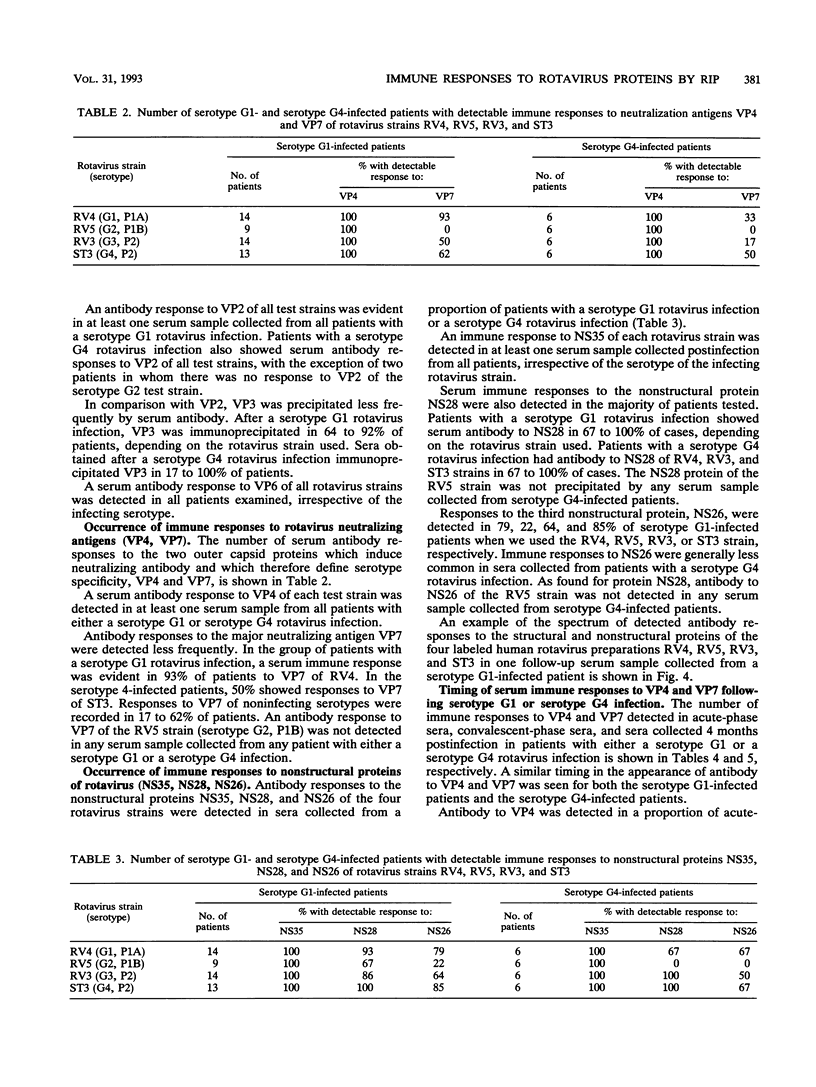
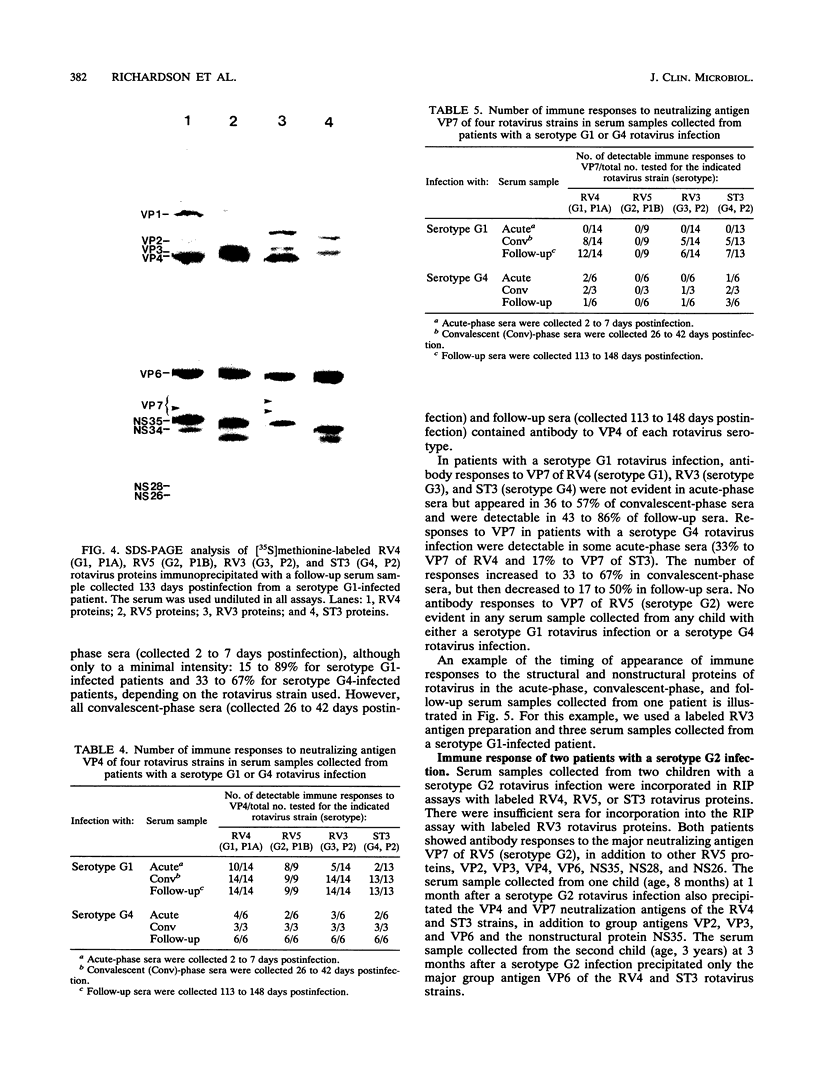
- Richardson S. C., Bishop R. F. Homotypic serum antibody responses to rotavirus proteins following primary infection of young children with serotype 1 rotavirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Sep;28(9):1891–1897. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.9.1891-1897.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw R. D., Fong K. J., Losonsky G. A., Levine M. M., Maldonado Y., Yolken R., Flores J., Kapikian A. Z., Vo P. T., Greenberg H. B. Epitope-specific immune responses to rotavirus vaccination. Gastroenterology. 1987 Nov;93(5):941–950. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90555-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass D. R., Wells P. W. Passive immunity in rotaviral infections. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1978 Sep 1;173(5 Pt 2):565–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson L., Sheshberadaran H., Vene S., Norrby E., Grandien M., Wadell G. Serum antibody responses to individual viral polypeptides in human rotavirus infections. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):643–651. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Maloy W. L., Nishikawa K., Green K. Y., Hoshino Y., Urasawa S., Kapikian A. Z., Chanock R. M., Gorziglia M. Identification of cross-reactive and serotype 2-specific neutralization epitopes on VP3 of human rotavirus. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2421–2426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2421-2426.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Urasawa T., Urasawa S. Reactivity patterns to human rotavirus strains of a monoclonal antibody against VP2, a component of the inner capsid of rotavirus. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1986;87(1-2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01310550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesikari T., Isolauri E., D'Hondt E., Delem A., André F. E., Zissis G. Protection of infants against rotavirus diarrhoea by RIT 4237 attenuated bovine rotavirus strain vaccine. Lancet. 1984 May 5;1(8384):977–981. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92323-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., Knowlton D. R., Schiff G. M., Hoshino Y., Greenberg H. B. Relative concentrations of serum neutralizing antibody to VP3 and VP7 proteins in adults infected with a human rotavirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1543–1549. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1543-1549.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward R. L., McNeal M. M., Sheridan J. F. Evidence that active protection following oral immunization of mice with live rotavirus is not dependent on neutralizing antibody. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90734-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]