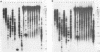Abstract
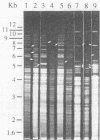
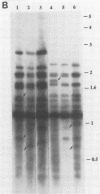
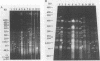
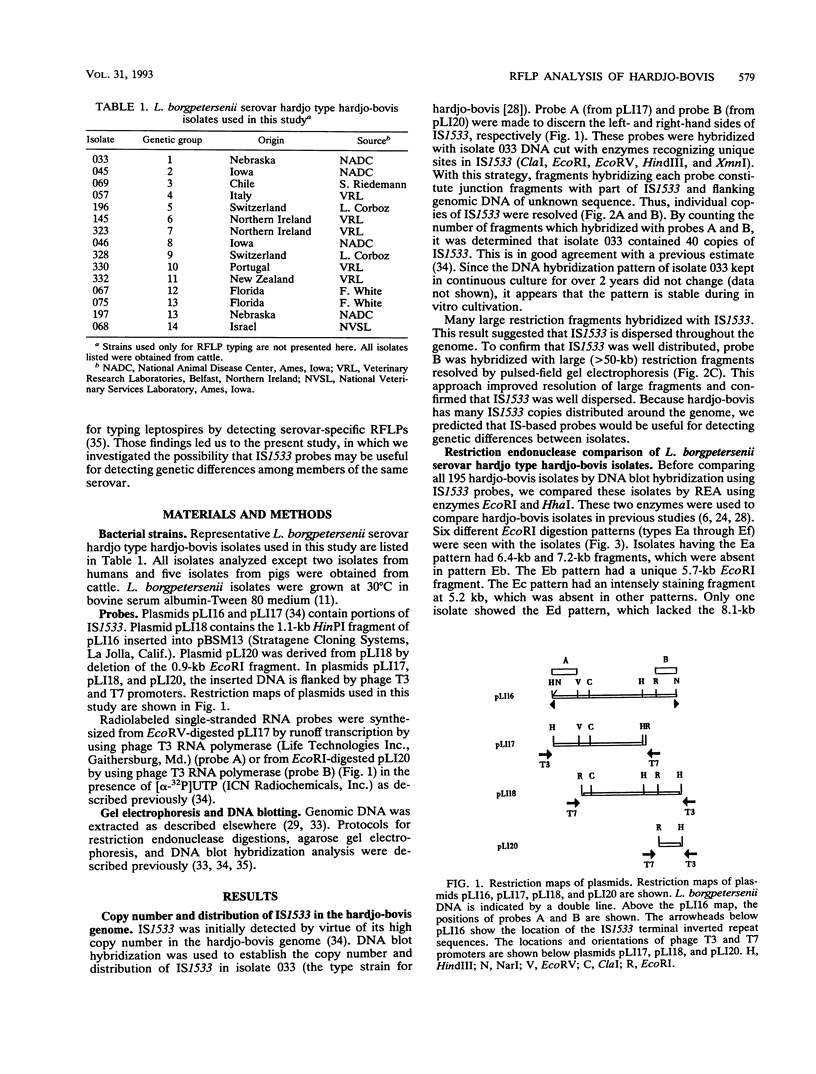
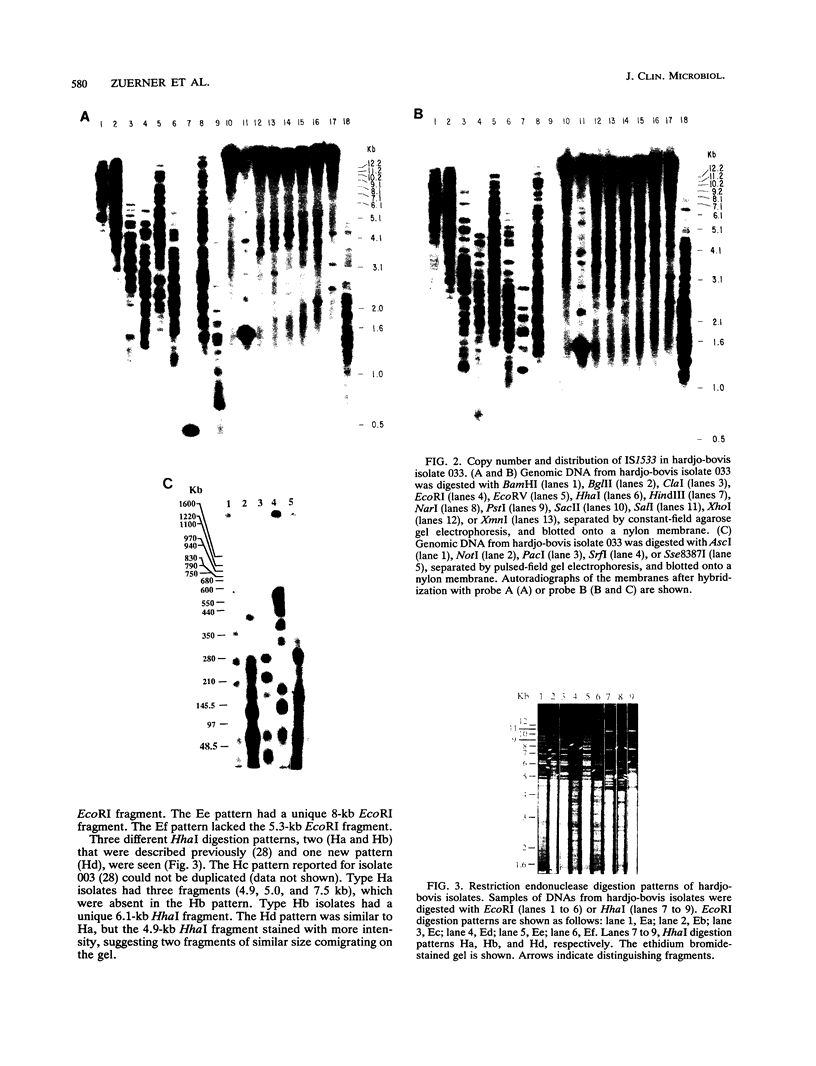
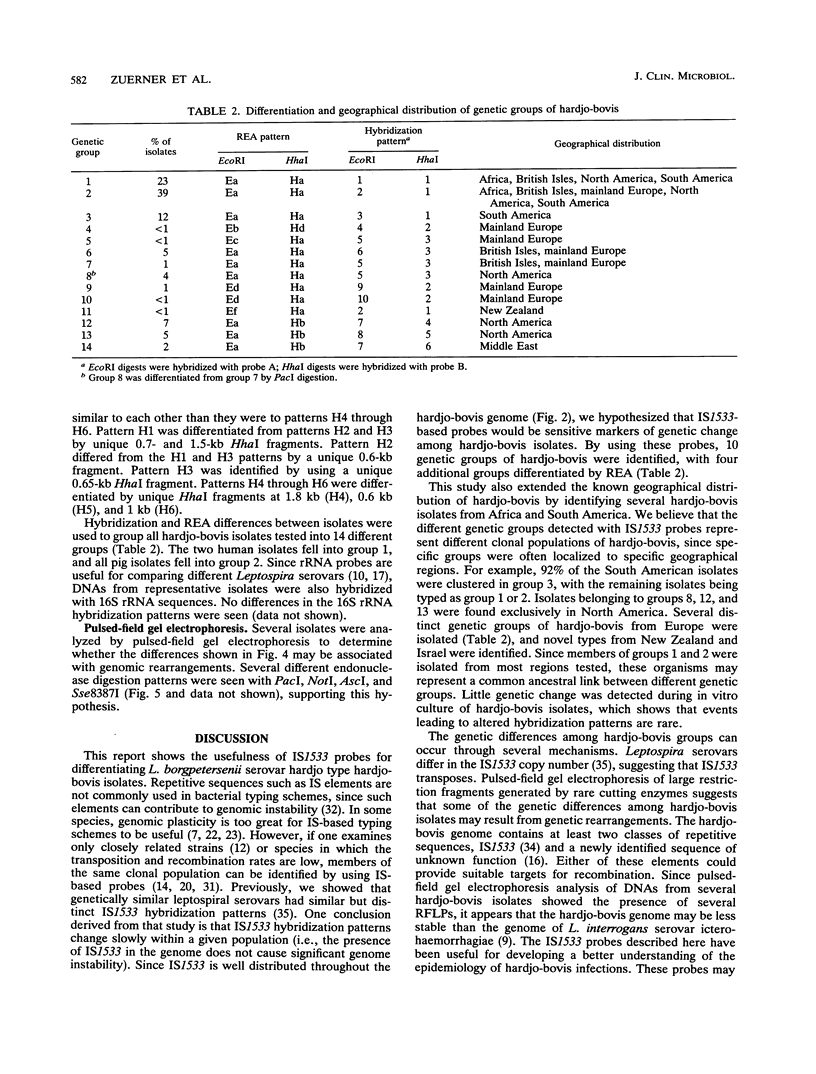
Genetic variability among Leptospira borgpetersenii serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis isolates representing several geographical regions was determined by restriction endonuclease analysis. Five previously unidentified EcoRI digestion patterns and one previously unidentified HhaI digestion pattern were seen with the various isolates. The copy number and genomic distribution of an L. borgpetersenii insertion sequence (IS1533) was determined. Hardjo-bovis isolate 033 (the type strain for hardjo-bovis) contained 40 well dispersed copies of IS1533. IS1533 probes were used to compare hardjo-bovis isolates by DNA blot hybridization analysis. Use of these probes showed the presence of additional genetic heterogeneity among hardjo-bovis isolates, which restriction endonuclease analysis did not show. Pulsed-field gel electrophoretic analysis of DNAs from several isolates suggested that some polymorphisms arose by genomic rearrangements. All hardjo-bovis isolates were categorized into 14 distinct groups on the basis of common hybridization and endonuclease digestion patterns. Most of these groups were isolated from distinct geographical regions, suggesting that several different clonal populations of hardjo-bovis exist.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aycardi E. R., Torres B., Guzmán V. H., Cortés M. Leptospirosis in Colombia. Isolation of Leptospira hardjo from beef cattle grazing tropical savannas. Rev Latinoam Microbiol. 1980 Apr-Jun;22(2):73–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chappel R. J., Millar B. D., Adler B., Hill J., Jeffers M. J., Jones R. T., McCaughan C. J., Mead L. J., Skilbeck N. W. Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo is not a major cause of bovine abortion in Victoria. Aust Vet J. 1989 Oct;66(10):330–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1989.tb09719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa M. O. Human leptospirosis in Brazil. Int J Zoonoses. 1975 Jun;2(1):1–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., O'Brien J. J., Bryson D. G., Mackie D. P. Bovine leptospirosis: some clinical features of serovar hardjo infection. Vet Rec. 1985 Aug 3;117(5):101–104. doi: 10.1136/vr.117.5.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., O'Brien J. J., Neill S. D., Hanna J. Bovine leptospirosis: serological findings in aborting cows. Vet Rec. 1982 Feb 20;110(8):178–180. doi: 10.1136/vr.110.8.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. A., Thiermann A. B., Montgomery J., Handsaker A., Winter P. J., Marshall R. B. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo isolates from cattle. Res Vet Sci. 1988 May;44(3):375–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores M., González V., Pardo M. A., Leija A., Martínez E., Romero D., Piñero D., Dávila G., Palacios R. Genomic instability in Rhizobium phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1191–1196. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1191-1196.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gsell O. The changing epidemiology of leptospirosis in Europe. A report on the 6th meeting of European Leptospira workers, Brnò, Czechoslovakia, September 1988. Zentralbl Bakteriol. 1990 Aug;273(3):412–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann J. L., Baril C., Bellenger E., Perolat P., Baranton G., Saint Girons I. Genome conservation in isolates of Leptospira interrogans. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7582–7588. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7582-7588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hookey J. V. The detection of genetic variation in Leptospira interrogans serogroup ICTEROHAEMORRHAGIAE by ribosomal RNA gene restriction fragment patterns. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Nov;60(3):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90326-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Harris V. G. Differentiation of pathogenic and saprophytic letospires. I. Growth at low temperatures. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):27–31. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.27-31.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. G., Dykhuizen D. E., DuBose R. F., Hartl D. L. Phylogenetic analysis using insertion sequence fingerprinting in Escherichia coli. Mol Biol Evol. 1989 Jan;6(1):1–14. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackintosh C. G., Schollum L. M., Harris R. E., Blackmore D. K., Willis A. F., Cook N. R., Stoke J. C. Epidemiology of leptospirosis in dairy farm workers in the Manawatu. Part I: A cross-sectional serological survey and associated occupational factors. N Z Vet J. 1980 Dec;28(12):245–250. doi: 10.1080/00480169.1980.34769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurek G. H., Cave M. D., Eisenach K. D., Wallace R. J., Jr, Bates J. H., Crawford J. T. Chromosomal DNA fingerprint patterns produced with IS6110 as strain-specific markers for epidemiologic study of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(9):2030–2033. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.9.2030-2033.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. A., Wilson M. A., Beran G. W. Survey to estimate prevalence of Leptospira interrogans infection in mature cattle in the United States. Am J Vet Res. 1991 Nov;52(11):1761–1765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacciarini M. L., Savio M. L., Tagliabue S., Rossi C. Repetitive sequences cloned from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo genotype hardjoprajitno and their application to serovar identification. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 May;30(5):1243–1249. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.5.1243-1249.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott J. F., Miller R. B., Nicholson V. M., Martin S. W., Lesnick T. Seroprevalence and association with abortion of leptospirosis in cattle in Ontario. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Apr;52(2):210–215. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérolat P., Grimont F., Regnault B., Grimont P. A., Fournié E., Thevenet H., Baranton G. rRNA gene restriction patterns of Leptospira: a molecular typing system. Res Microbiol. 1990 Feb;141(2):159–171. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90025-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadass P., Jarvis B. D., Corner R. J., Penny D., Marshall R. B. Genetic characterization of pathogenic Leptospira species by DNA hybridization. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;42(2):215–219. doi: 10.1099/00207713-42-2-215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappuoli R., Perugini M., Ratti G. DNA element of Corynebacterium diphtheriae with properties of an insertion sequence and usefulness for epidemiological studies. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):308–312. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.308-312.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Doolittle W. F. Unusual physical organization of the Halobacterium genome. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):384–389. doi: 10.1038/295384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza C., Rose M. R., Doolittle W. F. High-frequency genomic rearrangements involving archaebacterial repeat sequence elements. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):182–185. doi: 10.1038/299182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silbreck N. W., Davies W. D. Restriction endonuclease analysis of Australian isolates of Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo. Aust Vet J. 1989 Jun;66(6):183–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1989.tb09798.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swart K. S., Wilks C. R., Jackson K. B., Hayman J. A. Human leptospirosis in Victoria. Med J Aust. 1983 May 14;1(10):460–463. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1983.tb136166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Te Brugge L. A., Dreyer T. Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo associated with bovine abortion in South Africa. Onderstepoort J Vet Res. 1985 Mar;52(1):51–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B. Experimental leptospiral infections in pregnant cattle with organisms of the Hebdomadis serogroup. Am J Vet Res. 1982 May;43(5):780–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Foley J. W., White F. H., Kingscote B. F. Reclassification of North American leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroups Mini and Sejroe by restriction endonuclease analysis. Am J Vet Res. 1986 Jan;47(1):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiermann A. B., Handsaker A. L., Moseley S. L., Kingscote B. New method for classification of leptospiral isolates belonging to serogroup pomona by restriction endonuclease analysis: serovar kennewicki. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Apr;21(4):585–587. doi: 10.1128/jcm.21.4.585-587.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eys G. J., Gerritsen M. J., Korver H., Schoone G. J., Kroon C. C., Terpstra W. J. Characterization of serovars of the genus Leptospira by DNA hybridization with hardjobovis and icterohaemorrhagiae recombinant probes with special attention to serogroup sejroe. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):1042–1048. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.1042-1048.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkins B. M. Organization and plasticity of enterobacterial genomes. Soc Appl Bacteriol Symp Ser. 1988;17:51S–69S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Bolin C. A. Nucleic acid probe characterizes Leptospira interrogans serovars by restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Vet Microbiol. 1990 Sep;24(3-4):355–366. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90183-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L., Bolin C. A. Repetitive sequence element cloned from Leptospira interrogans serovar hardjo type hardjo-bovis provides a sensitive diagnostic probe for bovine leptospirosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Dec;26(12):2495–2500. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.12.2495-2500.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuerner R. L. Physical map of chromosomal and plasmid DNA comprising the genome of Leptospira interrogans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4857–4860. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Soolingen D., Hermans P. W., de Haas P. E., Soll D. R., van Embden J. D. Occurrence and stability of insertion sequences in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex strains: evaluation of an insertion sequence-dependent DNA polymorphism as a tool in the epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2578–2586. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2578-2586.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]